|
Penman Equation
The Penman equation describes evaporation (''E'') from an open water surface, and was developed by Howard Penman in 1948. Penman's equation requires daily mean temperature, wind speed, air pressure, and solar radiation to predict E. Simpler Hydrometeorological equations continue to be used where obtaining such data is impractical, to give comparable results within specific contexts, e.g. humid vs arid climates. Details Numerous variations of the Penman equation are used to estimate evaporation from water, and land. Specifically the Penman–Monteith equation refines weather based potential evapotranspiration (PET) estimates of vegetated land areas. It is widely regarded as one of the most accurate models, in terms of estimates. The original equation was developed by Howard Penman at the Rothamsted Experimental Station, Harpenden, UK. The equation for evaporation given by Penman is: :E_=\frac where: :''m'' = Slope of the saturation vapor pressure curve (Pa K−1) :''R''n = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate until the surrounding a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
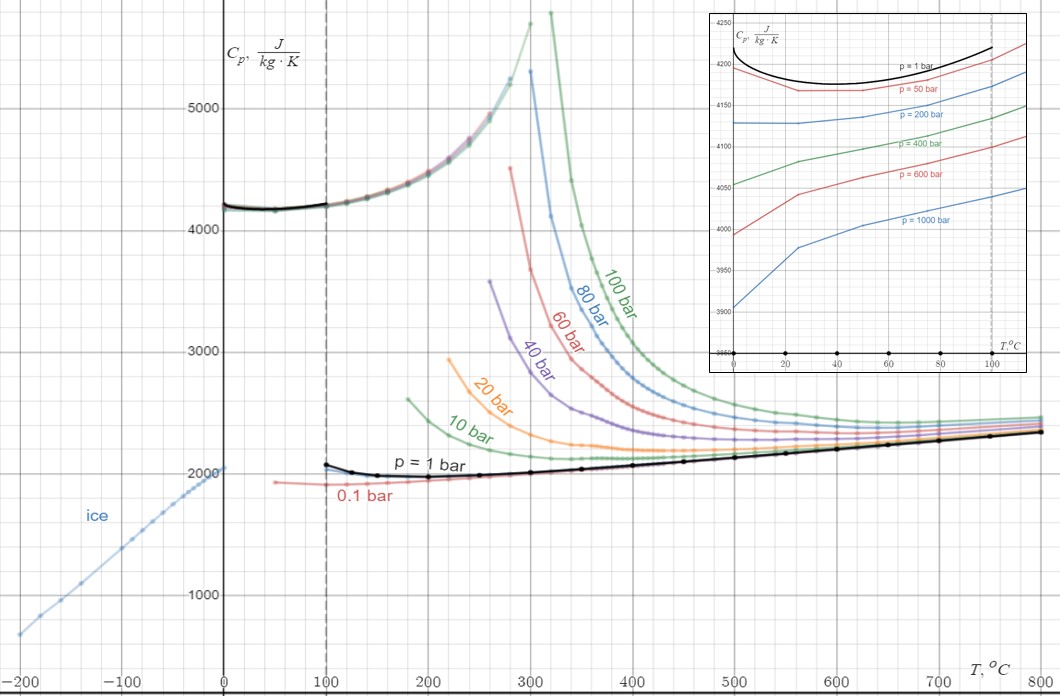
Heat Capacity
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a physical property of matter, defined as the amount of heat to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature. The SI unit of heat capacity is joule per kelvin (J/K). Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume. In architecture and civil engineering, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its thermal mass. Definition Basic definition The heat capacity of an object, denoted by C, is the limit : C = \lim_\frac, where \Delta Q is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by \Delta T. The value of this parameter usually varies considerably dependin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agronomy
Agronomy is the science and technology of producing and using plants by agriculture for food, fuel, fiber, chemicals, recreation, or land conservation. Agronomy has come to include research of plant genetics, plant physiology, meteorology, and soil science. It is the application of a combination of sciences such as biology, chemistry, economics, ecology, earth science, and genetics. Professionals of agronomy are termed agronomists. Plant breeding This topic of agronomy involves selective breeding of plants to produce the best crops for various conditions. Plant breeding has increased crop yields and has improved the nutritional value of numerous crops, including corn, soybeans, and wheat. It has also resulted in the development of new types of plants. For example, a hybrid grain named triticale was produced by crossbreeding rye and wheat. Triticale contains more usable protein than does either rye or wheat. Agronomy has also been instrumental for fruit and vegetable produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaney–Criddle Equation
The Blaney–Criddle equation (named after H. F. Blaney and W. D. Criddle) is a method for estimating reference crop evapotranspiration. Usage The Blaney–Criddle equation is a relatively simplistic method for calculating evapotranspiration. When sufficient meteorological data is available the Penman–Monteith equation is usually preferred. However, the Blaney–Criddle equation is ideal when only air-temperature datasets are available for a site. Given the coarse accuracy of the Blaney–Criddle equation, it is recommended that it be used to calculate evapotranspiration for periods of one month or greater. The equation calculates evapotranspiration for a 'reference crop', which is taken as actively growing green grass of 8–15 cm height. Equation ''ETo'' = ''p'' ·(0.457·''Tmean'' + 8.128) Where: ''ETo'' is the reference evapotranspiration m day−1(monthly) ''Tmean'' is the mean daily temperature �Cgiven as ''Tmean = (Tmax + Tmin )/ 2'' ''p'' is the mean d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thornthwaite Model
Thornthwaite is a village in Cumbria, England. Historically in Cumberland, it is just off the A66 road, south of Bassenthwaite Lake and within the Lake District National Park. It is by road from Keswick. In 1861 the township had a population of 153. For administrative purposes, Thornthwaite lies within the civil parish of Above Derwent, the district of Allerdale, and the county of Cumbria. It is within the Copeland constituency of the United Kingdom Parliament. Prior to Brexit in 2020 it was part of the North West England constituency of the European Parliament The European Parliament (EP) is one of the legislative bodies of the European Union and one of its seven institutions. Together with the Council of the European Union (known as the Council and informally as the Council of Ministers), it adop .... St Mary's Church is located a short distance east of the village. It was built in 1831, replacing an earlier church of c.1760 on the same site. The Church is a Gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan Evaporation
Pan evaporation is a measurement that combines or integrates the effects of several climate elements: temperature, humidity, rain fall, drought dispersion, solar radiation, and wind. Evaporation is greatest on hot, windy, dry, sunny days; and is greatly reduced when clouds block the sun and when air is cool, calm, and humid. Pan evaporation measurements enable farmers and ranchers to understand how much water their crops will need. Evaporation pan An evaporation pan is used to hold water during observations for the determination of the quantity of evaporation at a given location. Such pans are of varying sizes and shapes, the most commonly used being circular or square. The best known of the pans are the "Class A" evaporation pan and the "Sunken Colorado Pan". In Europe, India and South Africa, a Symon's Pan (or sometimes Symon's Tank) is used. Often the evaporation pans are automated with water level sensors and a small weather station is located nearby. Standard methods A va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relative Humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present. Humidity depends on the temperature and pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. A related parameter is the dew point. The amount of water vapor needed to achieve saturation increases as the temperature increases. As the temperature of a parcel of air decreases it will eventually reach the saturation point without adding or losing water mass. The amount of water vapor contained within a parcel of air can vary significantly. For example, a parcel of air near saturation may contain 28 g of water per cubic metre of air at , but only 8 g of water per cubic metre of air at . Three primary measurements of humidity are widely employed: absolute, relative, and specific. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychrometric Constant
The psychrometric constant \gamma relates the partial pressure of water in air to the air temperature. This lets one interpolate actual vapor pressure from paired dry and wet thermometer bulb temperature readings. :: \gamma =\frac : \gamma = psychrometric constant Pa °C−1 : P = atmospheric pressure Pa : \lambda_v = latent heat of water vaporization, 2.45 J kg−1 : c_p = specific heat of air at constant pressure, J kg−1 °C−1 : MW_ = ratio molecular weight of water vapor/dry air = 0.622. Both \lambda_v and MW_ are constants. Since atmospheric pressure, P, depends upon altitude, so does \gamma. At higher altitude water evaporates and boils at lower temperature. Although \left( c_p \right)_ is constant, varied air composition results in varied \left( c_p \right)_ . Thus on average, at a given location or altitude, the psychrometric constant is approximately constant. Still, it is worth remembering that weather impacts both atmospheric pressure a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latent Heat Of Vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. The enthalpy of vaporization is a function of the pressure at which that transformation takes place. The enthalpy of vaporization is often quoted for the normal boiling temperature of the substance. Although tabulated values are usually corrected to 298 K, that correction is often smaller than the uncertainty in the measured value. The heat of vaporization is temperature-dependent, though a constant heat of vaporization can be assumed for small temperature ranges and for reduced temperature T_r \ll 1. The heat of vaporization diminishes with increasing temperature and it vanishes completely at a certain point called the critical temperature (T_r = 1). Above the critical temperature, the liquid and vapor phases are indistinguishable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Howard Penman
Howard Latimer Penman (1909 – 1984) was a British meteorologist. He formulated Penman’s Formula, which is used worldwide by meteorologists and agricultural scientists to assess evaporation rates in different setups (lakes and ponds, lawns, cropped fields) and locations in the world. With John Monteith he formulated the Penman–Monteith equation which is used to calculate evapotranspiration and the need for crop irrigation. Penman was a distinguished Rothamsted Research scientist and government advisor, and a well-known local figure in Harpenden. Early life Howard Penman was born in County Durham and studied at Durham University where he graduated in Physics in 1930. While working for the British Cotton Research Association in Manchester he worked on his thesis for his Ph.D., which was awarded by Durham University in 1938. Bored by the work on cotton dyes he applied in 1937 for a post in the Soil Physics Department at Rothamsted Research, headed by Bernard Keen, for a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |