|
Penhallam
Penhallam is the site of a fortified manor house near Jacobstow in Cornwall, England. There was probably an earlier, 11th-century ringwork castle on the site, constructed by Tryold or his son, Richard fitz Turold in the years after the Norman invasion of 1066. Their descendants, in particular Andrew de Cardinham, created a substantial, sophisticated manor house at Penhallam between the 1180s and 1234, building a quadrangle of ranges facing onto an internal courtyard, surrounded by a moat and external buildings. The Cardinhams may have used the manor house for hunting expeditions in their nearby deer park. By the 14th century, the Cardinham male line had died out and the house was occupied by tenants. The surrounding manor was broken up and the house itself fell into decay and robbed for its stone. Archaeological investigations between 1968 and 1973 uncovered its foundations, unaltered since the medieval period, and the site is now managed by English Heritage and open to visit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Fitz Turold
Richard Fitz Turold (died after 1103–06) (''alias'' fitzThorold, fitzTurolf) was an eleventh-century Anglo-Norman landowner in Cornwall and Devon, mentioned in the Domesday Book. In the 13th century his estates formed part of the Feudal barony of Cardinham, Cornwall, and in 1166 as recorded in the Cartae Baronum his estates had been held as a separate fiefdom from Reginald, Earl of Cornwall. Origins As the prefix ''fitz'' in his surname suggests he was presumably the son of Turold/Thorold/Turolf. A certain "Turulf", presumably his father, witnessed a charter to the monastery of Mont Saint-Michel in Normandy, to which same monastery Richard also granted lands. Landholdings Cornwall Tenant of Count of Mortain He had a castle at Cardinham in Cornwall, in which county he was a major tenant and steward of Robert of Mortain, Count of Mortain, half-brother of King William the Conqueror. His holdings in Cornwall included the manor of Penhallam. Devon Tenant-in-chief His entry in the De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardinham Castle
Cardinham ( kw, Kardhinan) (the spelling 'Cardynham' is almost obsolete) is a civil parish and a village in mid Cornwall, England. The village is approximately three-and-a-half miles (6 km), east-northeast of Bodmin. The hamlets of Fletchersbridge, Millpool, Milltown, Mount, Old Cardinham Castle and Welltown are in the parish. Large areas which were once deciduous woodland are now plantations of conifers known as Cardinham Woods and managed by Forestry England. Edmund John Glynn, of Glynn House in the parish, rebuilt the house at Glynn in 1805 (it has a front of nine bays and a portico). Early history Richard Fitz Turold (Thorold) was an Anglo-Norman landowner of the eleventh century, mentioned in the Domesday Survey. He had a castle at Cardinham, where he was a major tenant and steward of Robert of Mortain. The holding included the manor of Penhallam. His son was William Fitz Richard of Cardinham. Restormel Castle belonged to the Cardinhams in the 12th century, until A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jacobstow
Jacobstow ( kw, Lannjago) is a civil parish and village in north Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. The village is located east of the A39 road approximately seven miles (11 km) south of Bude.Ordnance Survey: Landranger map sheet 190 ''Bude & Clovelly'' Penhallym in the north of the parish is mentioned (as ''Penhalun'') in the Domesday Book;GENUKI website; Jacobstow Retrieved May 2010 nearby is , site of a medieval manor. The name Jacobstow originates from Saxon times and derives from ''St James'' (Latin ''Jacobus'') and ''holy place''. As well as the church town, oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feudal Barony Of Cardinham
The Feudal barony of Cardinham (or Honour of Cardinham) is one of the three feudal baronies in Cornwall which existed during the medieval era. Its ''caput'' was at Cardinham Castle, Cornwall. The Barony was held in recent times by the Vivian family, the last being Nicholas Vivian, 6th Baron Vivian. Brigadier Nicholas Crespigny Laurence Vivian, 6th Baron Vivian (11 December 1935 - 28 February 2004), conveyed the title to John Anthony Vincent of Edifici Maxim's, Carrer General, Arsinal, Principat Andora, in 1995. Mr. Vincent was a member of the Manorial Society of Great Britain and died in Douglas, Isle of Man, on 31 March 2018. The Barony was then conveyed after the probate of his estate to an American citizen on 25 May 2019. Descent The manor of ''Cardinham'' (or ''Care Dynham '') is not mentioned in the Domesday Book (1086) and may thus have acquired its name from its later holders the ''de Dynham'' (or ''Dinham'') family which took its name from Dinan in Brittany. The ''de Cardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle Chapel
Castle chapels (german: Burgkapellen) in European architecture are chapels that were built within a castle. They fulfilled the religious requirements of the castle lord and his retinue, while also sometimes serving as a burial site. Because the construction of such church edifices was expensive for the lord of the castle, separate chapels are not found at every seat of the nobility. Often, a secondary room furnished with an altar had to suffice. According to historian Sarah Speight, "The religious role of chapels was as normal, as routine, and arguably, as integral to castles as any concern for symbolism and/or military strength." Castle chapels were usually consecrated to saints; especially those associated with knighthood, such as Saint George or Saint Gereon. In 1437, the chapel of Saint Mark at the castle in Braubach, Germany, gave the castle its present name: the Marksburg. Frequently, castle chapels were located near the gate or in the upper storey of the gate tower as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bakehouse
A bakery is an establishment that produces and sells flour-based food baked in an oven such as bread, cookies, cakes, donuts, pastries, and pies. Some retail bakeries are also categorized as cafés, serving coffee and tea to customers who wish to consume the baked goods on the premises. Confectionery items are also made in most bakeries throughout the world. History Baked goods have been around for thousands of years. The art of baking was developed early during the Roman Empire. It was a highly famous art as Roman citizens loved baked goods and demanded them frequently for important occasions such as feasts and weddings. Because of the fame of the art of baking, around 300 BC, baking was introduced as an occupation and respectable profession for Romans. Bakers began to prepare bread at home in an oven, using mills to grind grain into flour for their breads. The demand for baked goods persisted, and the first bakers' guild was established in 168 BC in Rome. The desire for bake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewhouse
A brewhouse is a building made for brewing beer and ale. This could be a part of a specialized brewery operation, but historically a brewhouse is a private building only meant for domestic production. Larger households, such as noble estates, often had dedicated brewhouses that could be quite elaborate using equipment not too different from that of commercial breweries. English country house An English country house is a large house or mansion in the English countryside. Such houses were often owned by individuals who also owned a town house. This allowed them to spend time in the country and in the city—hence, for these peopl ...s have detailed records of brewhouses. In ordinary farming households brewing was in some regions done outside, particularly in summer. The Baltic countries have a concept of a "summer kitchen", which is basically an outdoor area used for cooking and brewing in summer, but brewing could also be done outside in parts of Norway and Sweden as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pantry
A pantry is a room or cupboard where beverages, food, and sometimes dishes, household cleaning products, linens or provisions are stored within a home or office. Food and beverage pantries serve in an ancillary capacity to the kitchen. Etymology The word "pantry" derives from the same source as the Old French term ; that is from , the French form of the Latin , "bread". History in Europe and United States Late Middle Ages In a late medieval hall, there were separate rooms for the various service functions and food storage. The pantry was where bread was kept and food preparation was done. The head of the office responsible for this room was referred to as a pantler. There were similar rooms for storage of bacon and other meats (larder), alcoholic beverages ( buttery, known for the "buts" of barrels stored there), and cooking (kitchen). Colonial era In the United States, pantries evolved from early Colonial American " butteries", built in a cold north corner of a Coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buttery (room)
A buttery was originally a large cellar room under a monastery, in which food and drink were stored for the provisioning of strangers and passing guests. Nathan Bailey's ''An Universal Etymological English Dictionary'' gives "CELLARIST – one who keeps a Cella, or Buttery; the Butler in a religious House or Monastery." As the definition in John Stevens's ''The History of the Antient Abbeys'' shows, its initial function was to feed and water the guests rather than monks: "The Buttery; the Lodging for Guests". In a monastery a buttery was thus the place from which travellers would seek 'doles' of bread and weak ale, given at the exterior buttery door (and often via a small serving-hatch in the door, to prevent invasion of the stores by a crowd or by rough beggars). The task of doling out this free food and drink would be the role of the butterer. At larger monasteries there would also be a basic hostelry, where travellers could sleep for free. Later the term buttery was also ap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garderobe
Garderobe is a historic term for a room in a medieval castle. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' gives as its first meaning a store-room for valuables, but also acknowledges "by extension, a private room, a bed-chamber; also a privy". The word derives from the French , meaning "robes (or clothing) protector": thus, a closet or a toilet seat that would tend to prevent clothing from getting soiled. Its most common use now is as a term for a castle toilet. Store room is the French word for "wardrobe", a lockable place where clothes and other items are stored. According to medieval architecture scholar Frank Bottomley, garderobes were "Properly, not a latrine or privy but a small room or large cupboard, usually adjoining the chamber edroomor solar iving roomand providing safe-keeping for valuable clothes and other possessions of price: cloth, jewels, spices, plate and money." Toilet The term ''garderobe'' is also used to refer to a medieval or Renaissance toilet or a close stool ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caput Baroniae
In the customs of the kingdom of England, the ''caput baroniae'' (Latin, 'head of the barony') was the ancient, or chief seat or castle of a nobleman, which was not to be divided among the daughters upon his death, in case there be no son to inherit. Instead, it was to descend entirely to the eldest daughter, ''caeteris filiabus aliunde satisfactis'' (other daughters satisfied elsewhere). The central settlement in an Anglo-Saxon multiple estate was called a ''caput'',Michael Aston, ''Interpreting the Landscape'' (Routledge, reprinted 1998, page 34) (also short for ''caput baroniae''). The word is also used for the centre of administration of a hundred 100 or one hundred (Roman numeral: C) is the natural number following 99 and preceding 101. In medieval contexts, it may be described as the short hundred or five score in order to differentiate the English and Germanic use of "hundred" to de .... References English family law Feudalism in England English society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Crown
The Crown is the state in all its aspects within the jurisprudence of the Commonwealth realms and their subdivisions (such as the Crown Dependencies, overseas territories, provinces, or states). Legally ill-defined, the term has different meanings depending on context. It is used to designate the monarch in either a personal capacity, as Head of the Commonwealth, or as the king or queen of their realms (whereas the monarchy of the United Kingdom and the monarchy of Canada, for example, are distinct although they are in personal union). It can also refer to the rule of law; however, in common parlance 'The Crown' refers to the functions of government and the civil service. Thus, in the United Kingdom (one of the Commonwealth realms), the government of the United Kingdom can be distinguished from the Crown and the state, in precise usage, although the distinction is not always relevant in broad or casual usage. A corporation sole, the Crown is the legal embodiment of execut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
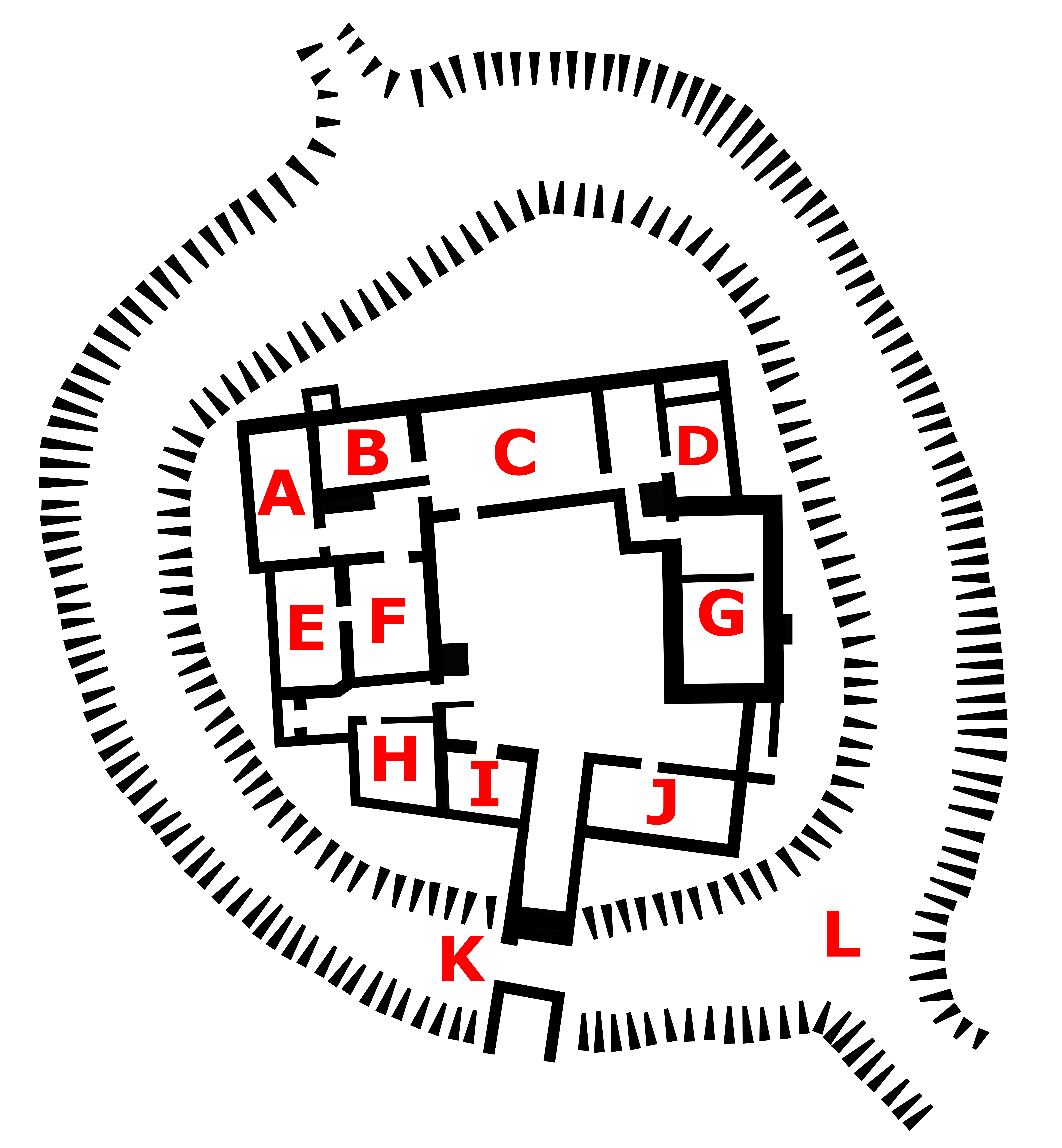







.jpg)

.jpg)