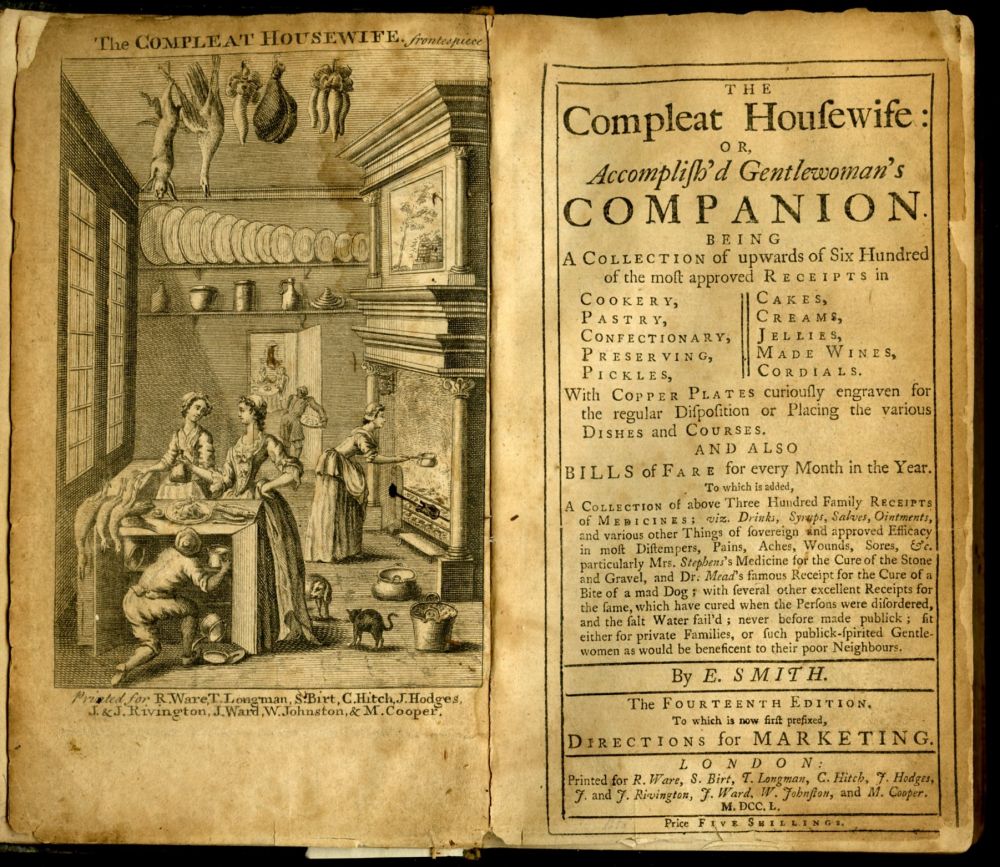
|
Paxamus
Paxamus, or Paxamos ( Greek: Πάξαμος), was an ancient Greek author from the Hellenistic period.... He composed a cookbook titled ''On Cooking'' and a text on farming titled ''On Farming''. Athenaeus, another Greek writer, mentioned Paxamus once in his work titled '' Deipnosophists''. Paxamus was perhaps the inventor of barley biscuits named after him called " paximathia". He was quoted in the ''Geoponica The ''Geoponica'' or ''Geoponika'' ( el, Γεωπονικά) is a twenty-book collection of agricultural lore, compiled during the 10th century in Constantinople for the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus. The Greek word ''Geoponic ...'', a Byzantine text on agriculture. References Citations Sources * * * Cookbook writers Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown {{Improve categories, date=July 2023 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paximathia
Paximathia ( el, παξιμάδια), also spelt paximadia (plural), or paximadi/paximathi (singular), is a hard bread of Greek origin, similar to rusk, that is prepared with whole wheat, chick pea or barley flour.... It has been referred to as being similar to biscotti or as a type of biscotti. Paximathia is a common food in Greece and many Greek bakeries sell the bread, which is often served as a breakfast food with marmalade or cheese.. Paximathia is purveyed also in Greek specialty stores in many areas of the United States. Etymology The name ''paximathia'' comes from the Greek term ''paximadion'' (Greek: παξιμάδιον), which is derived from , a 1st-century Greek author who wrote, among many things, a comprehensive cookbook. The word first appears in a recipe for laxative biscuits composed by the Greek physician Galen. History Paximadia were traditionally consumed by Greek farmers, as well as the Byzantine military and thrifty priests. Greek farmers would eat paximath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deipnosophists
The ''Deipnosophistae'' is an early 3rd-century AD ancient Greek, Greek work ( grc, Δειπνοσοφισταί, ''Deipnosophistaí'', lit. "The Dinner Sophists/Philosophers/Experts") by the Hellenistic period, Greek author Athenaeus of Naucratis. It is a long work of Greek literature, literary, Ancient history, historical, and Antiquarian#Antiquarianism in ancient Rome, antiquarian references set in Rome at a series of banquets held by the protagonist for an assembly of Grammarian (Greco-Roman world), grammarians, lexicographers, jurists, musicians, and hangers-on. Title The ancient Greek, Greek title ''Deipnosophistaí'' () derives from the combination of ' (, "dinner") and ''sophistḗs'' (, "expert, one knowledgeable in the arts of ~"). It and its English language, English derivative ''s'' thus describe people who are skilled at dining, particularly the refined conversation expected to accompany Greek symposium, symposia. However, the term is shaded by the harsh treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Language
Greek ( el, label=Modern Greek, Ελληνικά, Elliniká, ; grc, Ἑλληνική, Hellēnikḗ) is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages, native to Greece, Cyprus, southern Italy (Calabria and Salento), southern Albania, and other regions of the Balkans, the Black Sea coast, Asia Minor, and the Eastern Mediterranean. It has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning at least 3,400 years of written records. Its writing system is the Greek alphabet, which has been used for approximately 2,800 years; previously, Greek was recorded in writing systems such as Linear B and the Cypriot syllabary. The alphabet arose from the Phoenician script and was in turn the basis of the Latin, Cyrillic, Armenian, Coptic, Gothic, and many other writing systems. The Greek language holds a very important place in the history of the Western world. Beginning with the epics of Homer, ancient Greek literature includes many works of lasting impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, other countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. They also form a significant diaspora (), with Greek communities established around the world.. Greek colonies and communities have been historically established on the shores of the Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea, but the Greek people themselves have always been centered on the Aegean and Ionian seas, where the Greek language has been spoken since the Bronze Age.. Until the early 20th century, Greeks were distributed between the Greek peninsula, the western coast of Asia Minor, the Black Sea coast, Cappadocia in central Anatolia, Egypt, the Balkans, Cyprus, and Constantinople. Many of these regions coincided to a large extent with the borders of the Byzantine Empire of the late 11th cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellenistic Period
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 31 BC and the conquest of Ptolemaic Egypt the following year. The Ancient Greek word ''Hellas'' (, ''Hellás'') was gradually recognized as the name for Greece, from which the word ''Hellenistic'' was derived. "Hellenistic" is distinguished from "Hellenic" in that the latter refers to Greece itself, while the former encompasses all ancient territories under Greek influence, in particular the East after the conquests of Alexander the Great. After the Macedonian invasion of the Achaemenid Empire in 330 BC and its disintegration shortly after, the Hellenistic kingdoms were established throughout south-west Asia ( Seleucid Empire, Kingdom of Pergamon), north-east Africa ( Ptolemaic Kingdom) and South Asia ( Greco-Bactrian Kingdom, Indo-Greek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cookbook
A cookbook or cookery book is a kitchen reference containing recipes. Cookbooks may be general, or may specialize in a particular cuisine or category of food. Recipes in cookbooks are organized in various ways: by course (appetizer, first course, main course, dessert), by main ingredient, by cooking technique, alphabetically, by region or country, and so on. They may include illustrations of finished dishes and preparation steps; discussions of cooking techniques, advice on kitchen equipment, ingredients, and substitutions; historical and cultural notes; and so on. Cookbooks may be written by individual authors, who may be chefs, cooking teachers, or other food writers; they may be written by collectives; or they may be anonymous. They may be addressed to home cooks, to professional restaurant cooks, to institutional cooks, or to more specialized audiences. Some cookbooks are didactic, with detailed recipes addressed to beginners or people learning to cook particular dishes o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farming
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals (grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, meat, milk, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athenaeus
Athenaeus of Naucratis (; grc, Ἀθήναιος ὁ Nαυκρατίτης or Nαυκράτιος, ''Athēnaios Naukratitēs'' or ''Naukratios''; la, Athenaeus Naucratita) was a Greek rhetorician and grammarian, flourishing about the end of the 2nd and beginning of the 3rd century AD. The ''Suda'' says only that he lived in the times of Marcus Aurelius, but the contempt with which he speaks of Commodus, who died in 192, shows that he survived that emperor. He was a contemporary of Adrantus. Several of his publications are lost, but the fifteen-volume '' Deipnosophistae'' mostly survives. Publications Athenaeus himself states that he was the author of a treatise on the ''thratta'', a kind of fish mentioned by Archippus and other comic poets, and of a history of the Syrian kings. Both works are lost. The ''Deipnosophistae'' The '' Deipnosophistae'', which means "dinner-table philosophers", survives in fifteen books. The first two books, and parts of the third, eleventh and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley production is used as animal fodder, while 30% as a source of fermentable material for beer and certain distilled beverages, and as a component of various foods. It is used in soups and stews, and in barley bread of various cultures. Barley grains are commonly made into malt in a traditional and ancient method of preparation. In 2017, barley was ranked fourth among grains in quantity produced () behind maize, rice and wheat. Etymology The Old English word for barley was ', which traces back to Proto-Indo-European and is cognate to the Latin word ' "flour" (''see corresponding entries''). The direct ancestor of modern English ''barley'' in Old English was the derived adjective ''bærlic'', meaning "of barley". The first citation of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biscuit
A biscuit is a flour-based baked and shaped food product. In most countries biscuits are typically hard, flat, and unleavened. They are usually sweet and may be made with sugar, chocolate, icing, jam, ginger, or cinnamon. They can also be savoury, similar to crackers. Types of biscuit include sandwich biscuits, digestive biscuits, ginger biscuits, shortbread biscuits, chocolate chip cookies, chocolate-coated marshmallow treats, Anzac biscuits, '' biscotti'', and ''speculaas''. In most of North America, nearly all hard sweet biscuits are called " cookies", while the term " biscuit" is used for a soft, leavened quick bread similar to a less sweet version of a ''scone''. "Biscuit" may also refer to hard flour-based baked animal feed, as with dog biscuit. Variations in meaning * In most of the world outside North America, a biscuit is a small baked product that would be called either a " cookie" or a " cracker" in the United States and sometimes in Canada. Biscuits in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geoponica
The ''Geoponica'' or ''Geoponika'' ( el, Γεωπονικά) is a twenty-book collection of agricultural lore, compiled during the 10th century in Constantinople for the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogenitus. The Greek word ''Geoponica'' signifies "agricultural pursuits" in its widest sense. It is the only surviving Byzantine agricultural work. During the Macedonian Renaissance, the emperor Constantine VII assembled several compendia - compilations and excerpts of ancient writings - of which Geoponika was one. Around 50 manuscripts, dating from between the 10th and 16th centuries, have survived. ''Geoponika'' incorporated the work of Cassianus Bassus, which was compiled from an earlier work by Vindonius Anatolius. Sources The 10th century collection is sometimes (wrongly) ascribed to the 7th century author Cassianus Bassus, whose collection, also titled ''Geoponica'', was integrated into the extant work. Bassus drew heavily on the work of another agricultural compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |