|
Paul Pfeiffer (chemist)
Paul Pfeiffer (21 April 1875 – 4 March 1951) was an influential German chemist. He received his Ph.D. at the University of Zurich, studying under Alfred Werner, the "father of coordination chemistry". His thesis, submitted in 1898, dealt with adducts of tin halides. Pfeiffer was considered Werner's most successful student and became Werner's assistant until, due to a dispute with his mentor, he left first for Rostock, then Karlsruhe, and finally Bonn. At Bonn, where he had studied as an undergraduate, he occupied Kekulé's chair. Pfeiffer's work spanned many themes. The Pfeiffer effect, which involves interactions between chiral solutes, is named after his discoveries. His group first made the salen ligands, which gave the first artificial oxygen carriers. He recognized that crystals, e.g. of zinc sulfide Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Zurich
The University of Zürich (UZH, german: Universität Zürich) is a public research university located in the city of Zürich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of theology, law, medicine which go back to 1525, and a new faculty of philosophy. Currently, the university has seven faculties: Philosophy, Human Medicine, Economic Sciences, Law, Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Theology and Veterinary Medicine. The university offers the widest range of subjects and courses of any Swiss higher education institution. History The University of Zurich was founded on April 29, 1833, when the existing colleges of theology, the ''Carolinum'' founded by Huldrych Zwingli in 1525, law and medicine were merged with a new faculty of Philosophy. It was the first university in Europe to be founded by the state rather than a monarch or church. In the university's early years, the 183 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Werner
Alfred Werner (12 December 1866 – 15 November 1919) was a Swiss chemist who was a student at ETH Zurich and a professor at the University of Zurich. He won the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1913 for proposing the octahedral configuration of transition metal complexes. Werner developed the basis for modern coordination chemistry. He was the first inorganic chemist to win the Nobel prize, and the only one prior to 1973.https://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/chemistry/laureates/1913/werner-bio.html Nobel Prize Retrieved 1 December 2012 Biography Werner was born in 1866 in Mulhouse, Alsace (which was then part of France, but which was annexed by Germany in 1871). He was raised as Roman Catholic. He was the fourth and last child of Jean-Adam Werner, a foundry worker, and his second wife, Salomé Jeanette Werner, who originated from a wealthy family. He went to Switzerland to study chemistry at the Swiss Federal Institute (Polytechnikum) in Zurich, but since this institute was n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemische Berichte
''Chemische Berichte'' (usually abbreviated as ''Ber.'' or ''Chem. Ber.'') was a German-language scientific journal of all disciplines of chemistry founded in 1868. It was one of the oldest scientific journals in chemistry, until it merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' in 1997. ''Chemische Berichte/Recueil'' was then merged with other European journals in 1998 to form ''European Journal of Inorganic Chemistry''. History Founded in 1868 as ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft'' (, CODEN BDCGAS), it operated under this title until 1928 (Vol. 61). The journal was then split into: * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, A: Vereins-Nachrichten'' (, CODEN BDCAAS), and * ''Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft, B: Abhandlungen'' (, CODEN BDCBAD). Vol. 78 and 79 (1945–1946) were omitted and not published due to World War II. The journal was renamed ''Chemische Berichte'' (, CODEN CHBEAM) in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich August Kekulé Von Stradonitz
Friedrich may refer to: Names * Friedrich (surname), people with the surname ''Friedrich'' * Friedrich (given name), people with the given name ''Friedrich'' Other * Friedrich (board game), a board game about Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War * ''Friedrich'' (novel), a novel about anti-semitism written by Hans Peter Richter * Friedrich Air Conditioning, a company manufacturing air conditioning and purifying products *, a German cargo ship in service 1941-45 See also * Friedrichs (other) * Frederick (other) * Nikolaus Friedreich {{disambig ja:フリードリヒ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfeiffer Effect
The Pfeiffer effect is an optical phenomenon whereby the presence of an optically active compound influences the optical rotation of a racemic mixture of a second compound. Racemic mixtures do not rotate plane polarized light, but the equilibrium concentration of the two enantiomers can shift from unity in the presence of a strongly interacting chiral species. Paul Pfeiffer, a student of Alfred Werner and inventor of the salen ligand, reported this phenomenon. The first example of the effect is credited to Eligio Perucca, who observed optical rotations in the visible part of the spectrum when crystals of sodium chlorate, which are chiral and colourless, were stained with a racemic In chemistry, a racemic mixture, or racemate (), is one that has equal amounts of left- and right-handed enantiomers of a chiral molecule or salt. Racemic mixtures are rare in nature, but many compounds are produced industrially as racemates. ... dye.Chemical & Engineering News, Vol. 86 No. 33, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salen Ligand
Salen refers to a tetradentate C2-symmetric ligand synthesized from salicylaldehyde (sal) and ethylenediamine (en). It may also refer to a class of compounds, which are structurally related to the classical salen ligand, primarily bis-Schiff bases. Salen ligands are notable for coordinating a wide range of different metals, which they can often stabilise in various oxidation states. For this reason salen-type compounds are used as metal deactivators. Metal salen complexes also find use as catalysts. Synthesis and properties H2salen may be synthesized by the condensation of ethylenediamine and salicylaldehyde. : Complexes of salen with metal cations may be made without isolating it from the reaction mixture. This is possible because the stability constant for the formation of the metal complexes are very high, due to the chelate effect. :H2L + Mn+ → ML(n−2)+ + 2 H+ where L stands for the ligand. The pyridine adduct of the cobalt(II) complex Co(salen)(py) ( salcomine) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Justus Liebig's Annalen Der Chemie
''Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie'' (often cited as just ''Liebigs Annalen'') was one of the oldest and historically most important journals in the field of organic chemistry worldwide. It was established in 1832 and edited by Justus von Liebig with Friedrich Wöhler and others until Liebig's death in 1873. In 1997 the journal merged with ''Recueil des Travaux Chimiques des Pays-Bas'' to form ''Liebigs Annalen/Recueil''. In 1998 it was absorbed by ''European Journal of Organic Chemistry'' by merger of a number of other national European chemistry journals. Title history * ''Annalen der Pharmacie'', 1832–1839 * ''Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie'', 1840–1873 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie und Pharmacie'', 1873–1874 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Justus Liebig's Annalen der Chemie'', 1874–1944 & 1947–1978 (, CODEN JLACBF) * ''Liebigs Annalen der Chemie'', 1979–1994 (, CODEN LACHDL) * ''Liebigs Annalen'', 1995–1996 (, CODEN LANAEM) * ''Liebi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
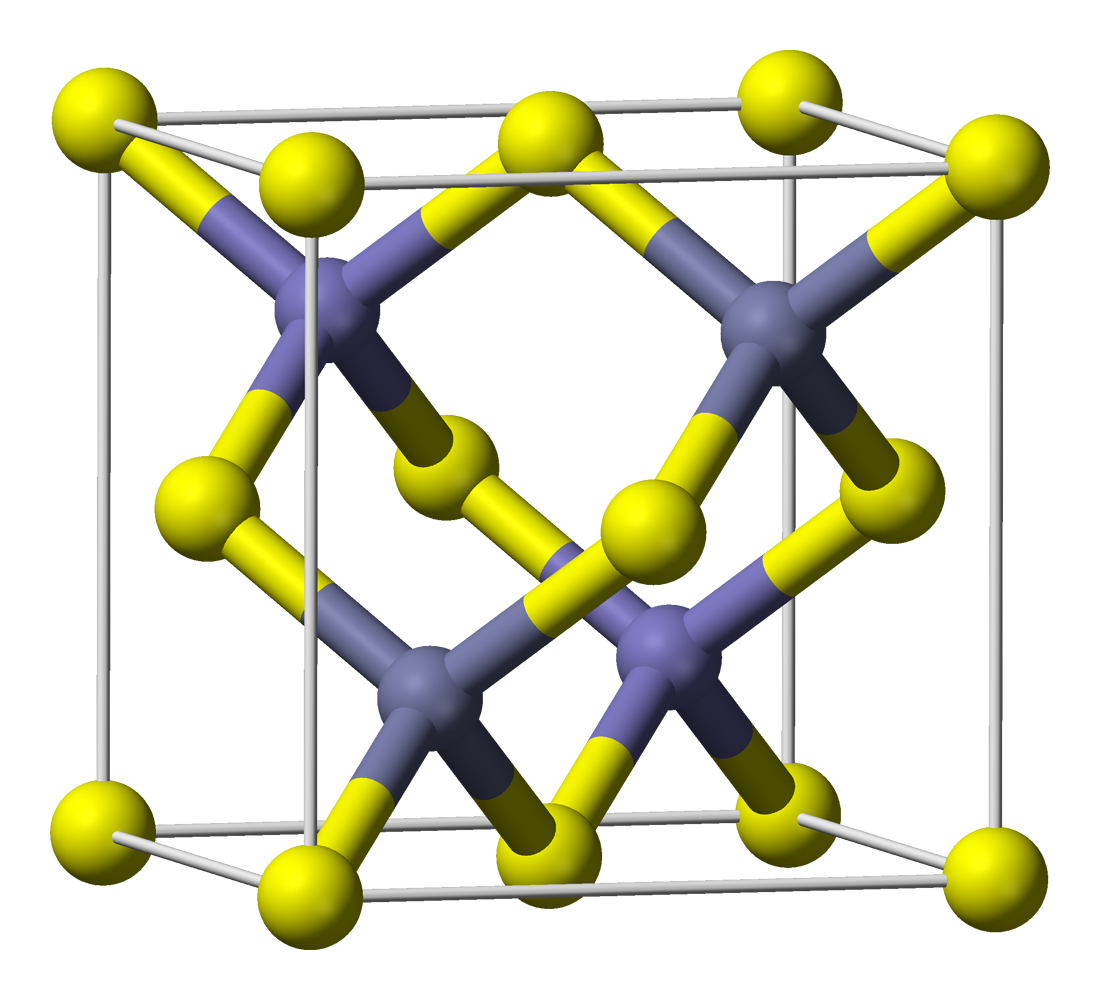
Zinc Sulfide
Zinc sulfide (or zinc sulphide) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula of ZnS. This is the main form of zinc found in nature, where it mainly occurs as the mineral sphalerite. Although this mineral is usually black because of various impurities, the pure material is white, and it is widely used as a pigment. In its dense synthetic form, zinc sulfide can be transparent, and it is used as a window for visible optics and infrared optics. Structure ZnS exists in two main crystalline forms. This dualism is an example of polymorphism. In each form, the coordination geometry at Zn and S is tetrahedral. The more stable cubic form is known also as zinc blende or sphalerite. The hexagonal form is known as the mineral wurtzite, although it also can be produced synthetically.. The transition from the sphalerite form to the wurtzite form occurs at around 1020 °C. A tetragonal form is also known as the very rare mineral called polhemusite, with the formula . Applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeitschrift Für Anorganische Und Allgemeine Chemie
The ''Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie'' (''Journal of Inorganic and General Chemistry'') is a semimonthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering inorganic chemistry, published by Wiley-VCH. The editors-in-chief are Thomas F. Fässler, Christian Limberg, Guodong Qian, and David Scheschkewitz. Originally the journal was published in German, but nowadays it is completely in English. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the following databases: According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as i ... of 1.414, ranking it 40th out of 46 journals in the category "Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear". References External links * Chemistry journals Wiley-VCH aca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1875 Births
Events January–March * January 1 – The Midland Railway of England abolishes the Second Class passenger category, leaving First Class and Third Class. Other British railway companies follow Midland's lead during the rest of the year (Third Class is renamed Second Class in 1956). * January 5 – The Palais Garnier, one of the most famous opera houses in the world, is inaugurated in Paris. * January 12 – Guangxu Emperor, Guangxu becomes the 11th Qing Dynasty Emperor of China at the age of 3, in succession to his cousin. * January 14 – The newly proclaimed King Alfonso XII of Spain (Queen Isabella II's son) arrives in Spain to restore the monarchy during the Third Carlist War. * February 3 – Third Carlist War – Battle of Lácar: Carlist commander Torcuato Mendiri, Torcuato Mendíri secures a brilliant victory, when he surprises and routs a Government force under General Enrique Bargés at Lácar, east of Estella, nearly capturing newly cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |