|
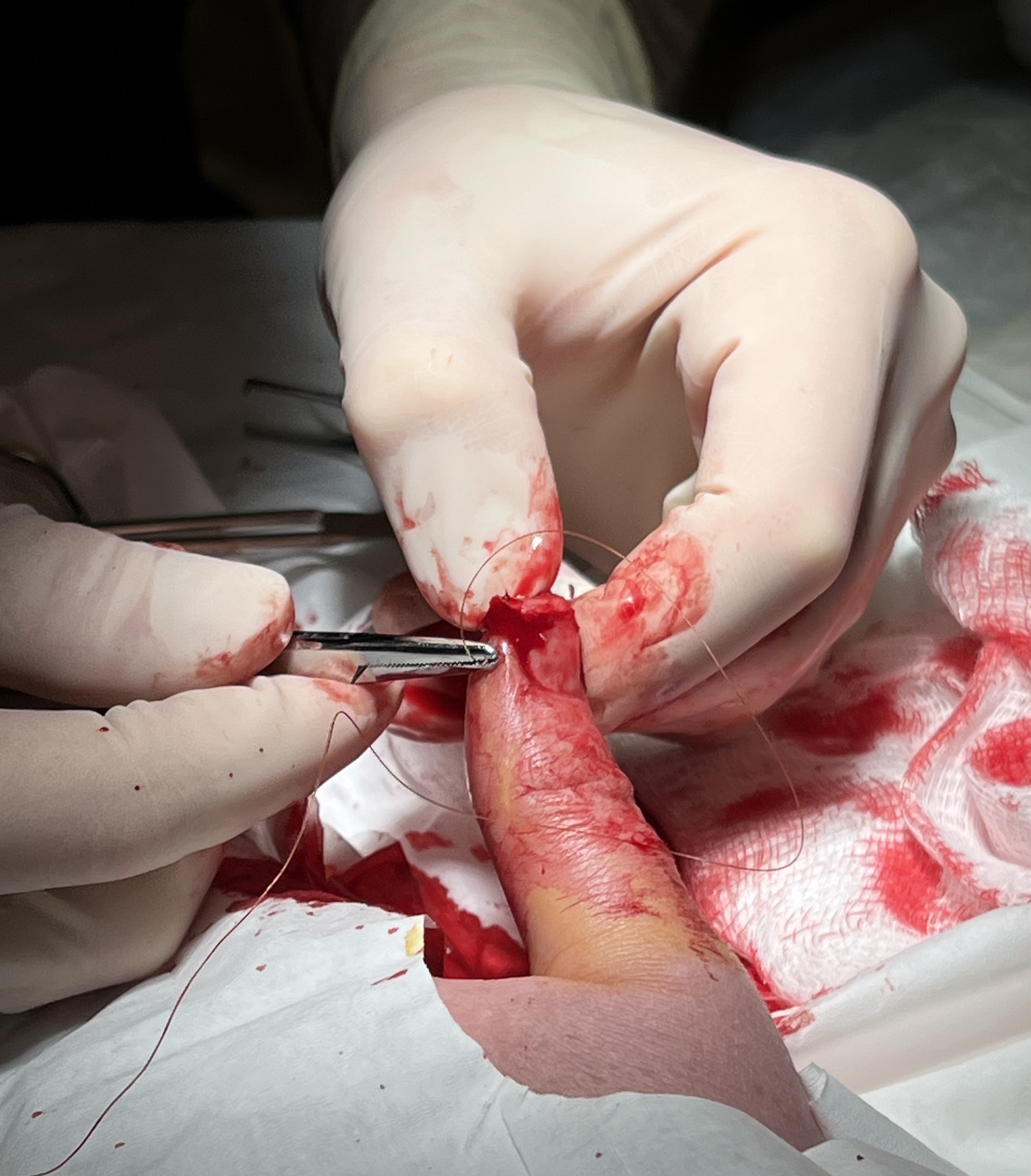
Patellar Tendon Rupture
Patellar tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon that connects the knee cap (patella) to the tibia. Often there is sudden onset of pain and walking is difficult. In a complete rupture, the ability to extend that knee is decreased. A pop may be felt when it occurs. Injury to the patellar tendon generally requires a significant force such as falling directly on the knee or jumping from a height. Risk factors include patellar tendinitis, kidney failure, diabetes, and corticosteroid, steroid or fluoroquinolone use. There are two main types of ruptures: partial and complete. In most cases, the patellar tendon tears at the point where it attaches to the knee cap. Diagnosis is based on symptoms, physical examination, examination, and medical imaging. Small tears may be treated with rest and orthopedic splinting, splinting, followed by physiotherapy. Larger tears typically require surgery within a couple of weeks. Outcomes are generally good. Rates in the general population are not clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial Tuberosity
The tuberosity of the tibia or tibial tuberosity or tibial tubercle is an elevation on the proximal, anterior aspect of the tibia, just below where the anterior surfaces of the lateral and medial tibial condyles end. Structure The tuberosity of the tibia gives attachment to the patellar ligament, which attaches to the patella from where the suprapatellar ligament forms the distal tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscles. The quadriceps muscles consist of the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These quadriceps muscles are innervated by the femoral nerve. KneeHipPain (1998) The tibial tuberosity thus forms the terminal part of the large structure that acts as a lever to extend the knee-joint and prevents the knee from collapsing when the foot strikes the ground. The t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Tendon
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified. Structure The patellar tendon is a strong, flat ligament, which originates on the apex of the patella distally and adjoining margins of the patella and the rough depression on its posterior surface; below, it inserts on the tuberosity of the tibia; its superficial fibers are continuous over the front of the patella with those of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris. It is about 4.5 cm long in adults (range from 3 to 6 cm). The medial and lateral portions of the quadriceps tendon pass down on either side of the patella to be inserted into the upper extremity of the tibia on either side of the tuberosity; these portions merge into the capsule, as stated above, forming the medial and lateral patellar retina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surgical Suture
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thread. There are numerous types of suture which differ by needle shape and size as well as thread material and characteristics. Selection of surgical suture should be determined by the characteristics and location of the wound or the specific body tissues being approximated. In selecting the needle, thread, and suturing technique to use for a specific patient, a medical care provider must consider the tensile strength of the specific suture thread needed to efficiently hold the tissues together depending on the mechanical and shear forces acting on the wound as well as the thickness of the tissue being approximated. One must also consider the elasticity of the thread and ability to adapt to different tissues, as well as the memory of the threa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, patient education, physical intervention, rehabilitation, disease prevention, and health promotion. Physical therapists are known as physiotherapists in many countries. In addition to clinical practice, other aspects of physical therapist practice include research, education, consultation, and health administration. Physical therapy is provided as a primary care treatment or alongside, or in conjunction with, other medical services. In some jurisdictions, such as the United Kingdom, physical therapists have the authority to prescribe medication. Overview Physical therapy addresses the illnesses or injuries that limit a person's abilities to move and perform functional activities in their daily lives. PTs use an individual's history and physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brace (orthopaedic)
Orthotics ( el, Ορθός, translit=ortho, lit=to straighten, to align) is a medical specialty that focuses on the design and application of orthoses, or braces. An is "an externally applied device used to influence the structural and functional characteristics of the neuromuscular and skeletal system". Orthotists are professionals who specialize in the provision of orthoses. Classification Orthotic devices are classified into four areas of the body according to the international classification system (ICS): orthotics of the lower extremities, orthotics of the upper extremities, orthotics for the trunk, and orthotics for the head. Orthoses are also classified by function: paralysis orthoses, relief orthoses, and soft braces. Under the International Standard terminology, orthoses are classified by an acronym describing the anatomical joints which they contain. For example, a knee-ankle-foot orthosis (English abbreviation: KAFO for Knee-ankle-foot orthoses) spans the kne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Cast
An orthopedic cast, or simply cast, is a shell, frequently made from plaster or fiberglass, that encases a limb (or, in some cases, large portions of the body) to stabilize and hold anatomical structures—most often a broken bone (or bones), in place until healing is confirmed. It is similar in function to a splint. Plaster bandages consist of a cotton bandage that has been combined with plaster of paris, which hardens after it has been made wet. Plaster of Paris is calcined gypsum (roasted gypsum), ground to a fine powder by milling. When water is added, the more soluble form of calcium sulfate returns to the relatively insoluble form, and heat is produced. :2 (CaSO4·½ H2O) + 3 H2O → 2 (CaSO4.2H2O) + Heat The setting of unmodified plaster starts about 10 minutes after mixing and is complete in about 45 minutes; however, the cast is not fully dry for 72 hours. Current bandages of synthetic materials are often used, often knitted fiberglass bandages impregnated with polyu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insall And Salvati Method biologist
{{surname ...
People with the surname Insall include: * Donald Insall (born 1926), British architect, conservationist and author * Gilbert Stuart Martin Insall (1894–1972), British pilot in the Royal Flying Corps and Royal Air Force * John Insall (1930–2000), pioneering English orthopaedic surgeon who spent most of his career in the United States * Robert Insall (born 1965), British cell & computational Computation is any type of arithmetic or non-arithmetic calculation that follows a well-defined model (e.g., an algorithm). Mechanical or electronic devices (or, historically, people) that perform computations are known as ''computers''. An espe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patella Alta
Attenuated patella alta is an extremely rare condition affecting mobility and leg strength. It is characterized by an unusually small knee cap (patella) that develops out of and above the joint. Typically, as the knee cap sits in the joint, it is stimulated to growth by abrasion from the opposing bones. When not situated properly in the joint, the knee cap does not experience such stimulation and remains small and undeveloped. Note that the cartilage under and around the kneecap is eight times smoother than ice, so "abrasion" may not be the best term. A similar condition, patella alta, can occur as the result of a sports injury, though the large majority of the time it is a congenital/developmental condition that is unrelated to trauma. A kneecap in an "alta" position sits above the "trochlear groove" and therefore is less stable. The "patellar tendon" that connects the kneecap to the tibia (shinbone) is elongated (longer than normal). This cannot happen by way of trauma, unle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadriceps Muscle
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur. The name derives . Structure Parts The quadriceps femoris muscle is subdivided into four separate muscles (the 'heads'), with the first superficial to the other three over the femur (from the trochanters to the condyles): *The rectus femoris muscle occupies the middle of the thigh, covering most of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originates on the ilium. It is named for its straight course. *The vastus lateralis muscle is on the ''lateral side'' of the femur (i.e. on the outer side of the thigh). *The vastus medialis muscle is on the ''medial side'' of the femur (i.e. on the inner part thigh). *The vastus intermedius muscle lies between vastus lateralis and vastus mediali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibial Tubercle
The tuberosity of the tibia or tibial tuberosity or tibial tubercle is an elevation on the proximal, anterior aspect of the tibia, just below where the anterior surfaces of the lateral and medial tibial condyles end. Structure The tuberosity of the tibia gives attachment to the patellar ligament, which attaches to the patella from where the suprapatellar ligament forms the distal tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscles. The quadriceps muscles consist of the rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, and vastus intermedius. These quadriceps muscles are innervated by the femoral nerve. KneeHipPain (1998) The tibial tuberosity thus forms the terminal part of the large structure that acts as a lever to extend the knee-joint and prevents the knee from collapsing when the foot strikes the ground. The tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patellar Ligament
The patellar tendon is the distal portion of the common tendon of the quadriceps femoris, which is continued from the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It is also sometimes called the patellar ligament as it forms a bone to bone connection when the patella is fully ossified. Structure The patellar tendon is a strong, flat ligament, which originates on the apex of the patella distally and adjoining margins of the patella and the rough depression on its posterior surface; below, it inserts on the tuberosity of the tibia; its superficial fibers are continuous over the front of the patella with those of the tendon of the quadriceps femoris. It is about 4.5 cm long in adults (range from 3 to 6 cm). The medial and lateral portions of the quadriceps tendon pass down on either side of the patella to be inserted into the upper extremity of the tibia on either side of the tuberosity; these portions merge into the capsule, as stated above, forming the medial and lateral patellar retina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |