|
Passio (Pärt)
''Passio Domini Nostri Jesu Christi secundum Joannem'' ( en, The Passion of Our Lord Jesus Christ According to John, also known as the ''St. John Passion'' or simply Passio, 1989) is a passion setting by Arvo Pärt for solo baritone (Jesus), solo tenor (Pilate), solo vocal quartet (Evangelist), choir, violin, oboe, cello, bassoon and organ. The work lasts approximately 70 minutes and is a setting of the Latin text from the Gospel of John, chapters 18 and 19, plus a brief introduction and conclusion. History When Pärt left Estonia for Austria in 1980, he took with him the first sketches for the ''St. John Passion,'' which would become the culmination of the tintinnabuli style. He eventually finished the work in 1982 and it was published in 1989. Since then, it has been recorded four times, and remains one of his most popular works. In much the same way that Pärt was inspired by medieval music in his creation of tintinnabuli, here too he is inspired by the earliest monophonic se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arvo Pärt
Arvo Pärt (; born 11 September 1935) is an Estonian composer of contemporary classical music. Since the late 1970s, Pärt has worked in a minimalist style that employs tintinnabuli, a compositional technique he invented. Pärt's music is in part inspired by Gregorian chant. His most performed works include ''Fratres'' (1977), ''Spiegel im Spiegel'' (1978), and ''Für Alina'' (1976). From 2011 to 2018, Pärt was the most performed living composer in the world, and the second most performed in 2019—after John Williams. The Arvo Pärt Centre, in Laulasmaa, was opened to the public in 2018. Early life, family and education Pärt was born in Paide, Järva County, Estonia, and was raised by his mother and stepfather in Rakvere in northern Estonia. He began to experiment with the top and bottom notes of the family's piano as the middle register was damaged. Pärt's musical education began at the age of seven when he began attending music school in Rakvere. By his early teenage ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous city and state. A landlocked country, Austria is bordered by Germany to the northwest, the Czech Republic to the north, Slovakia to the northeast, Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the west. The country occupies an area of and has a population of 9 million. Austria emerged from the remnants of the Eastern and Hungarian March at the end of the first millennium. Originally a margraviate of Bavaria, it developed into a duchy of the Holy Roman Empire in 1156 and was later made an archduchy in 1453. In the 16th century, Vienna began serving as the empire's administrative capital and Austria thus became the heartland of the Habsburg monarchy. After the dissolution of the H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Relation
A false relation (also known as cross-relation, non-harmonic relation) is the name of a type of dissonance that sometimes occurs in polyphonic music, most commonly in vocal music of the Renaissance. The term describes a "chromatic contradiction" between two notes sounding simultaneously (or in close proximity) in two different voices or parts; or alternatively, in music written before 1600, the occurrence of a tritone between two notes of adjacent chords. In the above example, a chromatic false relation occurs in two adjacent voices sounding at the same time (shown in red). The tenor voice sings G while the bass sings G momentarily beneath it, producing the clash of an augmented unison. In this instance, the false relation is less pronounced: the contradicting E (soprano voice) and E (bass voice) (diminished octave) do not sound simultaneously. Here the false relation occurs because the top voice is descending in a minor key, and therefore takes the notes of the melodic min ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
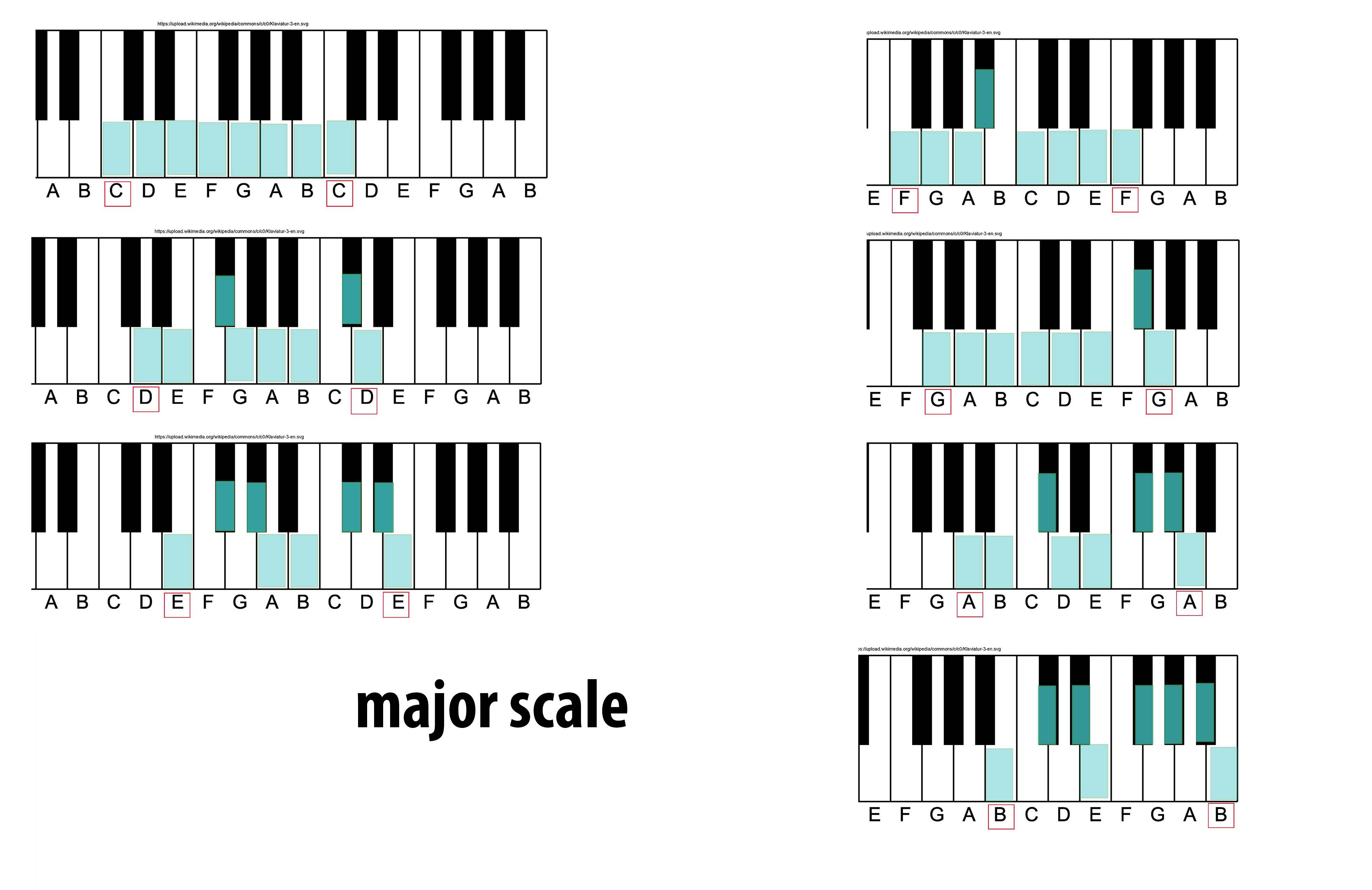
Major Scale
The major scale (or Ionian mode) is one of the most commonly used musical scales, especially in Western music. It is one of the diatonic scales. Like many musical scales, it is made up of seven notes: the eighth duplicates the first at double its frequency so that it is called a higher octave of the same note (from Latin "octavus", the eighth). The simplest major scale to write is C major, the only major scale not requiring sharps or flats: The major scale had a central importance in Western music, particularly in the common practice period and in popular music. In Carnatic music, it is known as '' Sankarabharanam''. In Hindustani classical music, it is known as '' Bilaval''. Structure A major scale is a diatonic scale. The sequence of intervals between the notes of a major scale is: : whole, whole, half, whole, whole, whole, half where "whole" stands for a whole tone (a red u-shaped curve in the figure), and "half" stands for a semitone (a red angled line in the figu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrygian Mode
The Phrygian mode (pronounced ) can refer to three different musical modes: the ancient Greek ''tonos'' or ''harmonia,'' sometimes called Phrygian, formed on a particular set of octave species or scales; the Medieval Phrygian mode, and the modern conception of the Phrygian mode as a diatonic scale, based on the latter. Ancient Greek Phrygian The octave species (scale) underlying the ancient-Greek Phrygian ''tonos'' (in its diatonic genus) corresponds to the medieval and modern Dorian mode. The terminology is based on the '' Elements'' by Aristoxenos (fl. c. 335 BC), a disciple of Aristotle. The Phrygian ''tonos'' or ''harmonia'' is named after the ancient kingdom of Phrygia in Anatolia. In Greek music theory, the ''harmonia'' given this name was based on a ''tonos'', in turn based on a scale or octave species built from a tetrachord which, in its diatonic genus, consisted of a series of rising intervals of a whole tone, followed by a semitone, followed by a whole tone. : In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Hillier
Paul Douglas Hillier OBE (born 9 February 1949) is an English conductor, music director and baritone. He specializes in both early and contemporary classical music, especially that by composers Steve Reich and Arvo Pärt. He was a co-founder of the Hilliard Ensemble and directed the Estonian Philharmonic Chamber Choir for numerous years. He has been Chief Conductor of Ars Nova (Copenhagen) since 2003, and Artistic Director and Chief Conductor of the National Chamber Choir of Ireland since 2008. Ensembles Hillier was born in Dorchester, England in 1949, where he attended Hardye's Grammar School. In 1967 he became a music student at the Guildhall School of Music & Drama, studying voice. In 1974 he co-founded the Hilliard Ensemble along with fellow vicar-choral Paul Elliott, tenor, and counter-tenor David James. His concert debut was in 1974 in London's Purcell Room. Hillier remained the director of the ensemble until 1990, when he founded Theatre of Voices. In addition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfect Fifth
In music theory, a perfect fifth is the Interval (music), musical interval corresponding to a pair of pitch (music), pitches with a frequency ratio of 3:2, or very nearly so. In classical music from Western culture, a fifth is the interval from the first to the last of five consecutive Musical note, notes in a diatonic scale. The perfect fifth (often abbreviated P5) spans seven semitones, while the Tritone, diminished fifth spans six and the augmented fifth spans eight semitones. For example, the interval from C to G is a perfect fifth, as the note G lies seven semitones above C. The perfect fifth may be derived from the Harmonic series (music), harmonic series as the interval between the second and third harmonics. In a diatonic scale, the dominant (music), dominant note is a perfect fifth above the tonic (music), tonic note. The perfect fifth is more consonance and dissonance, consonant, or stable, than any other interval except the unison and the octave. It occurs above the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitch (music)
Pitch is a perceptual property of sounds that allows their ordering on a frequency-related scale, or more commonly, pitch is the quality that makes it possible to judge sounds as "higher" and "lower" in the sense associated with musical melodies. Pitch is a major auditory attribute of musical tones, along with duration, loudness, and timbre. Pitch may be quantified as a frequency, but pitch is not a purely objective physical property; it is a subjective psychoacoustical attribute of sound. Historically, the study of pitch and pitch perception has been a central problem in psychoacoustics, and has been instrumental in forming and testing theories of sound representation, processing, and perception in the auditory system. Perception Pitch and frequency Pitch is an auditory sensation in which a listener assigns musical tones to relative positions on a musical scale based primarily on their perception of the frequency of vibration. Pitch is closely related to frequency, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhythm
Rhythm (from Greek , ''rhythmos'', "any regular recurring motion, symmetry") generally means a " movement marked by the regulated succession of strong and weak elements, or of opposite or different conditions". This general meaning of regular recurrence or pattern in time can apply to a wide variety of cyclical natural phenomena having a periodicity or frequency of anything from microseconds to several seconds (as with the riff in a rock music song); to several minutes or hours, or, at the most extreme, even over many years. Rhythm is related to and distinguished from pulse, meter, and beats: In the performance arts, rhythm is the timing of events on a human scale; of musical sounds and silences that occur over time, of the steps of a dance, or the meter of spoken language and poetry. In some performing arts, such as hip hop music, the rhythmic delivery of the lyrics is one of the most important elements of the style. Rhythm may also refer to visual presentation, as "timed mov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declamation
Declamation (from the Latin: ''declamatio'') is an artistic form of public speaking. It is a dramatic oration designed to express through articulation, emphasis and gesture the full sense of the text being conveyed. History In Ancient Rome, declamation was a genre of ancient rhetoric and a mainstay of the Roman higher education system. It was separated into two component subgenres, the ''controversia'', speeches of defense or prosecution in fictitious court cases, and the ''suasoria'', in which the speaker advised a historical or legendary figure as to a course of action. Roman declamations survive in four corpora: the compilations of Seneca the Elder and Calpurnius Flaccus, as well as two sets of ''controversiae'', the ''Major Declamations'' and ''Minor Declamations'' spuriously attributed to Quintilian. Declamation had its origin in the form of preliminary exercises for Greek students of rhetoric: works from the Greek declamatory tradition survive in works such as the collectio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evangelism
In Christianity, evangelism (or witnessing) is the act of preaching the gospel with the intention of sharing the message and teachings of Jesus Christ. Christians who specialize in evangelism are often known as evangelists, whether they are in their home communities or living as missionaries in the field, although some Christian traditions refer to such people as ''missionaries'' in either case. Some Christian traditions consider evangelists to be in a leadership position; they may be found preaching to large meetings or in governance roles. In addition, Christian groups who encourage evangelism are sometimes known as evangelistic or ''evangelist''. Etymology The word ''evangelist'' comes from the Koine Greek word (transliterated as ''euangelion'') via Latinised ''evangelium'' as used in the canonical titles of the Four Gospels, authored by (or attributed to) Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John (also known as the Four Evangelists). The Greek word originally meant a reward given ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pilate
Pontius Pilate (; grc-gre, Πόντιος Πιλᾶτος, ) was the fifth governor of the Roman province of Judaea, serving under Emperor Tiberius from 26/27 to 36/37 AD. He is best known for being the official who presided over the trial of Jesus and ultimately ordered his crucifixion. Pilate's importance in modern Christianity is underscored by his prominent place in both the Apostles' and Nicene Creeds. Due to the Gospels' portrayal of Pilate as reluctant to execute Jesus, the Ethiopian Church believes that Pilate became a Christian and venerates him as both a martyr and a saint, a belief which is historically shared by the Coptic Church. Although Pilate is the best-attested governor of Judaea, few sources regarding his rule have survived. Nothing is known about his life before he became governor of Judaea, and nothing is known about the circumstances that led to his appointment to the governorship. Coins that he minted have survived from Pilate's governorship, as well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |