|
Parvomai
Parvomay ( bg, Първомай ) is a town, part of the municipality of the same name ( Parvomay Municipality) in southern Bulgaria. It is located in Plovdiv Province, close to the towns Sadovo and Chirpan. The word literally means First of May, i.e., May Day, in English and is sometimes transliterated as Parvomai or Purvomai. As with many places in Bulgaria, the town has other names, such as its old name (up until 1947) of Borisovgrad (after Bulgaria's last Tsar, Boris to celebrate his birthday on 30 January 1894), as well as Borisovgrad, Borissograd, Borissovgrade, or Borissowgrad. Until 1894, it was known by its Turkish names of Hadzi Ejles (Bulgarian Хаджи Елес), Hadzi-Ele, Hadzi-Jeiles, Khadzhi Eiles, or Khadzhi-Eles ("Hacı İlyas" in Turkish). The Town The municipal centre town Parvomay is situated at 134 meters above sea level, with geographic coordinates 25о13`30`` East longitude and 42о06`00`` North latitude. The town is 180 km to the east of Sofia, 39 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedonia to the west, Greece and Turkey to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. Bulgaria covers a territory of , and is the sixteenth-largest country in Europe. Sofia is the nation's capital and largest city; other major cities are Plovdiv, Varna and Burgas. One of the earliest societies in the lands of modern-day Bulgaria was the Neolithic Karanovo culture, which dates back to 6,500 BC. In the 6th to 3rd century BC the region was a battleground for ancient Thracians, Persians, Celts and Macedonians; stability came when the Roman Empire conquered the region in AD 45. After the Roman state splintered, tribal invasions in the region resumed. Around the 6th century, these territories were settled by the early Slavs. The Bulgars, led by Asp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
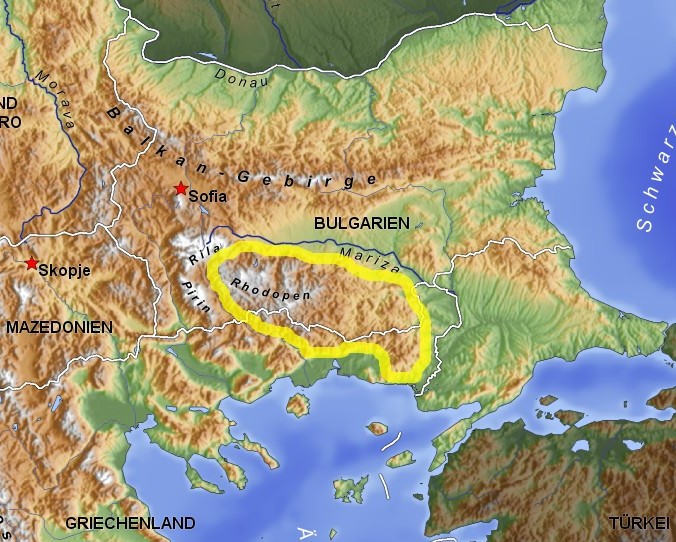
Rhodope Mountains
The Rhodopes (; bg, Родопи, ; el, Ροδόπη, ''Rodopi''; tr, Rodoplar) are a mountain range in Southeastern Europe, and the largest by area in Bulgaria, with over 83% of its area in the southern part of the country and the remainder in Greece. Golyam Perelik is its highest peak at . The mountain range gives its name to the terrestrial ecoregion Rodope montane mixed forests that belongs in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome and the Palearctic realm. The region is particularly notable for its karst areas with their deep river gorges, large caves and specific sculptured forms, such as the Trigrad Gorge. A significant part of Bulgaria's hydropower resources are located in the western areas of the range. There are a number of hydro-cascades and dams used for electricity production, irrigation, and as tourist destinations. In Greece, there are also the hydroelectric power plants of Thisavros and Platanovrysi. The Rhodopes have a rich cultural heritage including a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracians
The Thracians (; grc, Θρᾷκες ''Thrāikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European languages, Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied the area between northern Greece, southern Russia, and north-western Turkey. They shared the same language and culture... There may have been as many as a million Thracians, diveded among up to 40 tribes." Thracians resided mainly in the Balkans (mostly Present (time), modern day Bulgaria, Turkey and Greece) but were also located in Anatolia, Anatolia (Asia Minor) and other locations in Eastern Europe. The exact origin of Thracians is unknown, but it is believed that proto-Thracians descended from a purported mixture of Proto-Indo-Europeans and Early European Farmers, arriving from the rest of Asia and Africa through the Asia Minor (Anatolia). The proto-Thracian culture developed int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragoynovo
Dragoynovo ( bg, Драгойново) is a village in central southern Bulgaria, in the Parvomay municipality of Plovdiv Province. Geography The region of Dragoyna is located where the Maritsa valley merges with the high mountains of the Rhodopes. The Dragoyna peak has two summits - Golyama (Big) and Malka (Little) Dragoyna, with an attitude difference of some . They are connected by a saddle. As the highest point in the region, the peak has an extensive view. Population According to the 2020 census, the village of Dragoyna has 243 inhabitants. History The name of the village until 1906 was ''Kozluk''. In the 5th century BC, the powerful Odrysian kingdom was established in the Maritsa valley. The kingdom survived for centuries. The region of Dragoyna was probably a local centre of the Thracian aristocracy within the Odrysian kingdom. A high concentration of Thracian ''tumuli'' has been registered in the area. A golden ring has been found in Ezerovo near Dragoyna bearin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thracian Language
The Thracian language () is an extinct and poorly attested language, spoken in ancient times in Southeast Europe by the Thracians. The linguistic affinities of the Thracian language are poorly understood, but it is generally agreed that it was an Indo-European language with satem features. A contemporary, neighboring language, Dacian is usually regarded as closely related to Thracian. However, there is insufficient evidence with respect to either language to ascertain the nature of this relationship. The point at which Thracian became extinct is a matter of dispute. However, it is generally accepted that Thracian was still in use in the 6th century AD: Antoninus of Piacenza wrote in 570 that there was a monastery in the Sinai, at which the monks spoke Greek, Latin, Syriac, Egyptian, and Bessian – a Thracian dialect. Other theories about Thracian remain controversial. A classification put forward by some linguists, such as Harvey Mayer, suggests that Thracian (and Dacian) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumulus
A tumulus (plural tumuli) is a mound of earth and stones raised over a grave or graves. Tumuli are also known as barrows, burial mounds or ''kurgans'', and may be found throughout much of the world. A cairn, which is a mound of stones built for various purposes, may also originally have been a tumulus. Tumuli are often categorised according to their external apparent shape. In this respect, a long barrow is a long tumulus, usually constructed on top of several burials, such as passage graves. A round barrow is a round tumulus, also commonly constructed on top of burials. The internal structure and architecture of both long and round barrows has a broad range; the categorization only refers to the external apparent shape. The method of may involve a dolmen, a cist, a mortuary enclosure, a mortuary house, or a chamber tomb. Examples of barrows include Duggleby Howe and Maeshowe. Etymology The word ''tumulus'' is Latin for 'mound' or 'small hill', which is derived from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Bulgaria
The history of Bulgaria can be traced from the first settlements on the lands of Bulgaria, modern Bulgaria to its formation as a nation-state, and includes the history of the Bulgarians, Bulgarian people and their origin. The earliest evidence of hominid occupation discovered in what is today Bulgaria date from at least 1.4 million years ago. Around 5000 BC, a sophisticated civilization already existed which produced some of the first pottery, jewellery and golden artifacts in the world. After 3000 BC, the Thracians appeared on the Balkan Peninsula. In the late 6th century BC, parts of what is nowadays Bulgaria, in particular the eastern region of the country, came under the Achaemenid Empire, Persian Achaemenid Empire.Joseph Roisman,Ian Worthington"A companion to Ancient Macedonia"John Wiley & Sons, 2011. pp 135–138, pp 343–345 In the 470s BC, the Thracians formed the powerful Odrysian Kingdom which lasted until 46 BC, when it was finally conquered by the Roman Empi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinople. It survived the fragmentation and fall of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD and continued to exist for an additional thousand years until the fall of Constantinople to the Ottoman Empire in 1453. During most of its existence, the empire remained the most powerful economic, cultural, and military force in Europe. The terms "Byzantine Empire" and "Eastern Roman Empire" were coined after the end of the realm; its citizens continued to refer to their empire as the Roman Empire, and to themselves as Romans—a term which Greeks continued to use for themselves into Ottoman times. Although the Roman state continued and its traditions were maintained, modern historians prefer to differentiate the Byzantine Empire from Ancient Rome a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thrace
Thrace (; el, Θράκη, Thráki; bg, Тракия, Trakiya; tr, Trakya) or Thrake is a geographical and historical region in Southeast Europe, now split among Bulgaria, Greece, and Turkey, which is bounded by the Balkan Mountains to the north, the Aegean Sea to the south, and the Black Sea to the east. It comprises southeastern Bulgaria (Northern Thrace), northeastern Greece (Western Thrace), and the European part of Turkey ( East Thrace). The region's boundaries are based on that of the Roman Province of Thrace; the lands inhabited by the ancient Thracians extended in the north to modern-day Northern Bulgaria and Romania and to the west into the region of Macedonia. Etymology The word ''Thrace'' was first used by the Greeks when referring to the Thracian tribes, from ancient Greek Thrake (Θρᾴκη), descending from ''Thrāix'' (Θρᾷξ). It referred originally to the Thracians, an ancient people inhabiting Southeast Europe. The name ''Europe'' first referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Odrysian Kingdom
The Odrysian Kingdom (; Ancient Greek: ) was a state grouping many Thracian tribes united by the Odrysae, which arose in the early 5th century BC and existed at least until the late 1st century BC. It consisted mainly of present-day Bulgaria and parts of Southeastern Romania (Northern Dobruja), Northern Greece and European Turkey. Dominated by the eponymous Odrysian people, it was the largest and most powerful Thracian realm and the first larger political entity of the eastern Balkans. Before the foundation of Seuthopolis in the late 4th century it had no fixed capital. The Odrysian kingdom was founded by king Teres I, exploiting the collapse of the Persian presence in Europe due to failed invasion of Greece in 480–79. Teres and his son Sitalces pursued a policy of expansion, making the kingdom one of the most powerful of its time. Throughout much of its early history it remained an ally of Athens and even joined the Peloponnesian War on its side. By 400 the state showed first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deinotherium
''Deinotherium'' was a large elephant-like proboscidean that appeared in the Middle Miocene and survived until the Early Pleistocene. Although superficially resembling modern elephants, they had notably more flexible necks, limbs adapted to a more cursorial lifestyle as well as tusks that curved downwards and back. In addition, their tusks didn't emerge from the maxilla as in elephants but from the mandible. ''Deinotherium'' was a widespread genus, ranging from East Africa to the south to Europe and east to the Indian Subcontinent. They were browsing animals with a diet mainly consisting of leaves, and they most likely died out as forested areas were gradually replaced by open grassland during the latter half of the Neogene. History and naming ''Deinotherium'' has a long history, possibly dating back as early as the 17th century when a French surgeon named Matsorier found the bones of large animals in an area known as the "field of giants" near Lyon. Matsorier is said to have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byala Reka, Plovdiv Province
Byala Reka is a village in Parvomay Municipality, Plovdiv Province, Bulgaria Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedon .... In 2006, the population was 969. Villages in Plovdiv Province {{Plovdiv-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)