|
Paris Commune (1789–1795)
The Paris Commune during the French Revolution was the government of Paris from 1789 until 1795. Established in the '' Hôtel de Ville'' just after the storming of the Bastille, it consisted of 144 delegates elected by the 60 divisions of the city. Before its formal establishment, there had been much popular discontent on the streets of Paris over who represented the true Commune, and who had the right to rule the Parisian people. The first mayor was Jean Sylvain Bailly, a relatively moderate Feuillant who supported constitutional monarchy. He was succeeded in November 1791 by Pétion de Villeneuve after Bailly's unpopular use of the National Guard to disperse a riotous assembly in the Champ de Mars (17 July 1791). By 1792, the Commune was dominated by those Jacobins who were not in the Legislative Assembly due to the Self-Denying Ordinance. The new Commune meant that there was a genuinely revolutionary challenge to the Legislative Assembly, though its practical victories w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
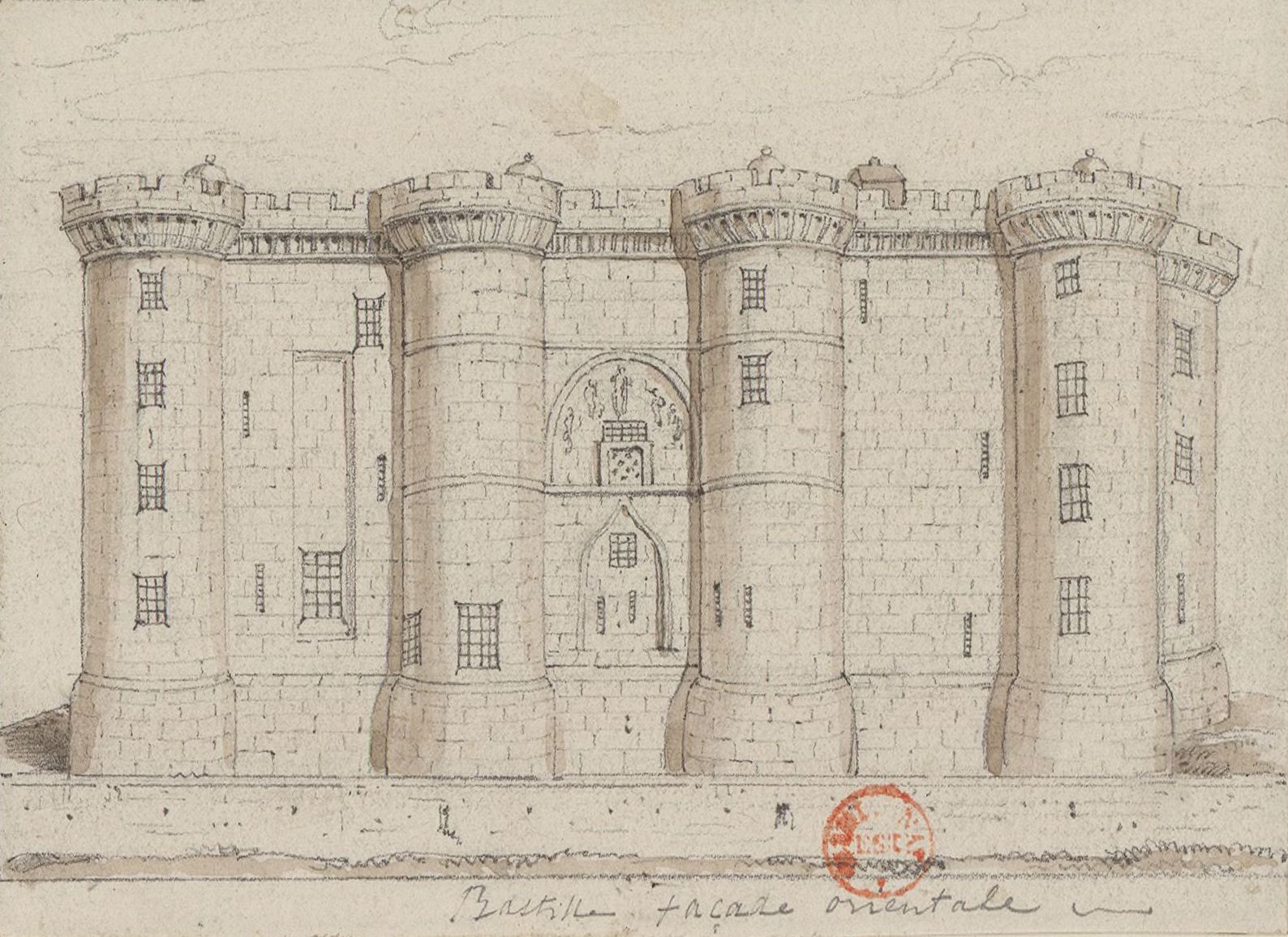
Bastille
The Bastille (, ) was a fortress in Paris, known formally as the Bastille Saint-Antoine. It played an important role in the internal conflicts of France and for most of its history was used as a state prison by the kings of France. It was stormed by a crowd on 14 July 1789, in the French Revolution, becoming an important symbol for the French Republican movement. It was later demolished and replaced by the Place de la Bastille. The castle was built to defend the eastern approach to the city from potential English attacks during the Hundred Years' War. Construction was underway by 1357, but the main construction occurred from 1370 onwards, creating a strong fortress with eight towers that protected the strategic gateway of the Porte Saint-Antoine heading out to the east. The innovative design proved influential in both France and England and was widely copied. The Bastille figured prominently in France's domestic conflicts, including the fighting between the rival factions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges Danton
Georges Jacques Danton (; 26 October 1759 – 5 April 1794) was a French lawyer and a leading figure in the French Revolution. He became a deputy to the Paris Commune, presided in the Cordeliers district, and visited the Jacobin club. In August 1792 he became French Minister of Justice and was responsible for inciting the September Massacres. In Spring 1793 he supported the foundation of a Revolutionary Tribunal and became the first president of the Committee of Public Safety. After the Insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793 he changed his mind on the use of force and lost his seat in the committee; Danton and Robespierre became rivals. In early October 1793, he left politics but was urged to return to Paris to plead, as a moderate, for an end to the Terror. Danton's continual criticism of the Committee of Public Safety provoked further counter-attacks. At the end of March 1794, Danton made a speech announcing the end of the Terror. Within a week he became embroiled in a sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunswick Manifesto
The Brunswick Manifesto was a proclamation issued by Charles William Ferdinand, Duke of Brunswick, commander of the Allied Army (principally Austrian and Prussian), on 25 July 1792 to the population of Paris, France during the War of the First Coalition. The manifesto threatened that if the French royal family were harmed, then French civilians would be harmed. It was said to have been a measure intended to intimidate Paris, but rather helped further spur the increasingly radical French Revolution and finally led to the war between revolutionary France and counter-revolutionary monarchies. Background On 20 April 1792, Revolutionary France declared war on Austria. On 28 April, France invaded the Austrian Netherlands (roughly present-day Belgium). Prussia joined the war against France. On 30 July, Austria and Prussia began an invasion of France, hoping to occupy Paris. Brunswick Manifesto On 25 July, the Duke of Brunswick issued the Brunswick Manifesto. The manifesto promi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constitutional Cabinet Of Louis XVI
The Kingdom of France (the remnant of the preceding absolutist Kingdom of France) was a constitutional monarchy that governed France from 3 September 1791 until 21 September 1792, when this constitutional monarchy was succeeded by the First Republic. On 3 September 1791, the National Constituent Assembly forced king Louis XVI to accept the French Constitution of 1791, thus turning the absolute monarchy into a constitutional monarchy. After the 10 August 1792 Storming of the Tuileries Palace, the Legislative Assembly on 11 August 1792 suspended this constitutional monarchy.Fraser, 454 The freshly elected National Convention abolished the monarchy on 21 September 1792, ending 203 years of consecutive Bourbon rule over France. Background France had been undergoing a revolution in its government and social orders. A National Assembly declared itself into being and promulgated their intention to provide France with a fair and liberal constitution. Louis XVI moved to Paris i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Girondin
The Girondins ( , ), or Girondists, were members of a loosely knit political faction during the French Revolution. From 1791 to 1793, the Girondins were active in the Legislative Assembly and the National Convention. Together with the Montagnards, they initially were part of the Jacobin movement. They campaigned for the end of the monarchy, but then resisted the spiraling momentum of the Revolution, which caused a conflict with the more radical Montagnards. They dominated the movement until their fall in the insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793, which resulted in the domination of the Montagnards and the purge and eventual mass execution of the Girondins. This event is considered to mark the beginning of the Reign of Terror. The Girondins were a group of loosely affiliated individuals rather than an organized political party and the name was at first informally applied because the most prominent exponents of their point of view were deputies to the Legislative Assembly from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Ten Brink
Jan ten Brink (15 June 1834 – 18 July 1901) was a Dutch writer. He was born in Appingedam, Netherlands. He studied in Leiden, went to Batavia for a few years, and in 1862 he became a teacher at a secondary school in The Hague. In 1884 he became professor in Dutch literature at the Leiden University. Ten Brink was a conservative writer. Conrad Busken Huet and, especially, the 'movement of 80', writers and poets who were far more progressive than Ten Brink, attacked him on several occasions in literary magazines such as '' De Gids'' and '' De Nieuwe Gids''. He died, aged 67, in Leiden. Works In total, Jan ten Brink wrote over 20 novels, including: * ''Gerbrand Adriaensen Brederoó'' (1859) * ''Dirck Volkertsen Coornhert en zijne Wellevenskunst'' (1860) * ''Oost-Indische dames en heeren'' (1866) * ''De schoonzoon van Mevrouw de Roggeveen'' (1871–1873) * ''Eene schitterende carrière'' (1879) * ''De familie Muller Belmonte'' (1880) He also wrote several books on the history ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Prosecutor
A prosecutor is a legal representative of the prosecution in states with either the common law adversarial system or the civil law inquisitorial system. The prosecution is the legal party responsible for presenting the case in a criminal trial against an individual accused of breaking the law. Typically, the prosecutor represents the state or the government in the case brought against the accused person. Prosecutor as a legal professional Prosecutors are typically lawyers who possess a law degree, and are recognised as suitable legal professionals by the court in which they are acting. This may mean they have been admitted to the bar, or obtained a comparable qualification where available - such as solicitor advocates in England and Wales. They become involved in a criminal case once a suspect has been identified and charges need to be filed. They are employed by an office of the government, with safeguards in place to ensure such an office can successfully pursue the pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Levasseur
René Levasseur, (27 May 1747 – 17 September 1834) was a French surgeon and politician, who was a Montagnard deputy in the National Convention during the First French Republic. Early life Levasseur was a surgeon and man-midwife under the Ancien Régime. He was disinherited by one of his uncles for his political radicalism. National Convention After the French Revolution, Levasseur served on the municipal government of Le Mans in 1790 and the district government in 1791. In the 1792 election to the new National Convention he won a seat representing the département of Sarthe. At the 1793 trial of Louis XVI , Levasseur voted in favour of his execution. He supported the creation of the Revolutionary Tribunal and was among the fiercest opponents of Modérantisme, especially in the insurrection of 31 May – 2 June 1793, supporting the arrest of all Girondins. He served in the Army of the North and his horse was shot from under him at the Battle of Hondschoote. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre-Joseph Cambon
Pierre-Joseph Cambon (, 10 June 1756 – 15 February 1820) was a French statesman. He is perhaps best known for speaking up against Maximilien Robespierre at the National Convention, sparking the end of Robespierre's reign. Born in Montpellier, Cambon was the son of a wealthy cotton merchant. In 1785, his father retired, leaving Pierre and his two brothers to run the business, but in 1788 Pierre entered politics, and was sent by his fellow-citizens as deputy suppliant to the Estates-General, where he was mostly a spectator. In January 1790 he returned to Montpellier, was elected a member of the municipality, co-founded the Jacobin Club in that city, and on the flight to Varennes of King Louis XVI in 1791, he drew up a petition to invite the National Constituent Assembly to proclaim a Republic —the first in date of such petitions. Elected to the Legislative Assembly, Cambon was viewed as independent, honest, and talented in the financial domain. He was the most active member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |