|
Parazoa
Parazoa (Parazoa, gr. Παρα-, para, "next to", and ζωα, zoa, "animals") is an obsolete subkingdom that is located at the base of the phylogenetic tree of the animal kingdom in opposition to the subkingdom Eumetazoa; they group together the most primitive forms, characterized by not having proper tissues or where, in any case, these tissues are only partially differentiated. It generally includes a single phylum, Porifera, which lack muscles, nerves and internal organs, which in many cases resembles a cell colony rather than a multicellular organism itself. All other animals are eumetazoans and agnotozoans (Agnotozoans are possibly paraphyletic or even nonexistent in studies), which do have differentiated tissues. On occasion, Parazoa reunites Porifera with Archaeocyatha, a group of extinct sponges sometimes considered a separate phylum. In other cases, Placozoa is included, depending on the authors. Porifera and Archaeocyatha Porifera and Archaeocyatha show similari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eumetazoa
Eumetazoa (), also known as Epitheliozoa or Histozoa, is a proposed basal animal subkingdom as a sister group of Porifera (sponges). The basal eumetazoan clades are the Ctenophora and the ParaHoxozoa. Placozoa is now also seen as a eumetazoan in the ParaHoxozoa. The competing hypothesis is the Myriazoa clade. The subkingdom Parazoa and Agnotozoa are the other taxa, and agnotozoa may be fake or even nonexistent at studies. Parazoa or Agnotozoa are a main sister group to eumetazoans, forming clade Blastozoa/Diploblastozoa. Alternatively, Parazoa was considered as a sister group to Agnotozoa(now considered polyphyletic). Several other extinct or obscure life forms, such as '' Iotuba'' and '' Thectardis'', appear to have emerged in the group. Characteristics of eumetazoans include true tissues organized into germ layers, the presence of neurons and muscles, and an embryo that goes through a gastrula stage. Some phylogenists once speculated the sponges and eumetazoans evolv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
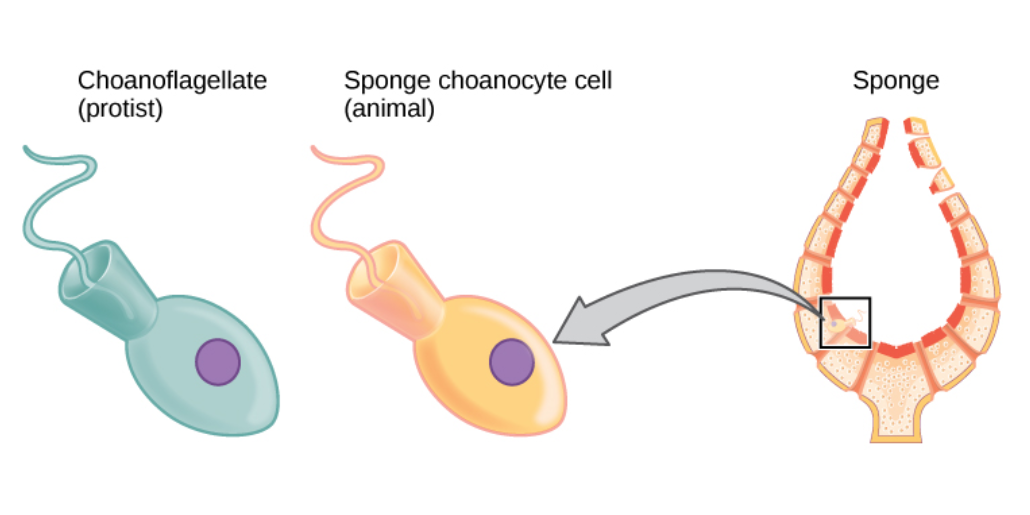
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important sponge reef , reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cell (biology) , cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can cellular differentiation , transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous system , nervous, digestive system , digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Traditionally, textbooks from Canada and the United States have used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria or Eubacteria), while textbooks in other parts of the world, such as Bangladesh, Brazil, Greece, India, Pakistan, Spain, and the United Kingdom have used five kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, '' funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agnotozoa
Agnotozoa is a subkingdom of simple animals that is sometimes used. It is one of the three "traditional" animal subkingdoms, along with Parazoa and Eumetazoa. On some classifications, it is nearly synonymous with Mesozoa. Agnotozoa was first used as one of the branches of the subkingdom Metazoa. It was then considered to contain only one group, Mesozoa. More recently, some have used the name to refer to a subkingdom of three small phyla of simple animals without organs, Placozoa, Orthonectida, and Rhombozoa Dicyemida, also known as Rhombozoa, is a phylum of tiny parasites that live in the renal appendages of cephalopods. Taxonomy Classification is controversial. Traditionally, dicyemids have been grouped with the Orthonectida in the phylum Mes .... They are known as "simple" though they have differentiated tissue, because that tissue is only organized in simple ways; for example, by being layered. The Orthonectida and Rhombozoa are grouped into the Mesozoa. Biologists t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placozoa
Placozoa ( ; ) is a phylum of free-living (non-parasitic) marine invertebrates. They are blob-like animals composed of aggregations of cells. Moving in water by ciliary motion, eating food by Phagocytosis, engulfment, reproducing by Fission (biology), fission or budding, placozoans are described as "the simplest animals on Earth." Structural and molecular analyses have supported them as among the most basal animals, thus, constituting a primitive metazoan phylum. The first known placozoan, ''Trichoplax adhaerens'', was discovered in 1883 by the German zoologist Franz Eilhard Schulze (1840–1921).F. E. Schulze "''Trichoplax adhaerens'' n. g., n. s.", ''Zoologischer Anzeiger'' (Elsevier, Amsterdam and Jena) 6 (1883), p. 92. Describing the uniqueness, another German, Karl Gottlieb Grell (1912–1994), erected a new phylum, Placozoa, for it in 1971. Remaining a monotypic phylum for over a century, new species began to be added since 2018. So far, three other extant species have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom (biology)
In biology, a kingdom is the second highest taxonomic rank, just below domain. Kingdoms are divided into smaller groups called phyla (singular phylum). Traditionally, textbooks from Canada and the United States have used a system of six kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista, Archaea/Archaebacteria, and Bacteria or Eubacteria), while textbooks in other parts of the world, such as Bangladesh, Brazil, Greece, India, Pakistan, Spain, and the United Kingdom have used five kingdoms (Animalia, Plantae, Fungi, Protista and Monera). Some recent classifications based on modern cladistics have explicitly abandoned the term ''kingdom'', noting that some traditional kingdoms are not monophyletic, meaning that they do not consist of all the descendants of a common ancestor. The terms ''flora'' (for plants), ''fauna'' (for animals), and, in the 21st century, '' funga'' (for fungi) are also used for life present in a particular region or time. Definition and associated terms Whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otavia
''Otavia antiqua'' is an ancient sponge-like multicellular organism found in the Otavi Group (the generic name being the namesake) in the Etosha National Park, Namibia. It is claimed to be the oldest animal fossil, being found in rock aged between 760 and 550 million years ago. The oldest ''Otavia'' fossils are from the Tonian period, before the Cryogenian glaciations, but the latest found were from the Nama Group rocks of the Ediacaran The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last ... period. The shape of ''Otavia'' fossils is irregular but rounded, and the size varies from one-third of a millimetre to . They are hollow inside, and have many small, osculum-like holes connecting the interior to the outside, similar in body plan to most poriferans. The material of the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylum
In biology, a phylum (; : phyla) is a level of classification, or taxonomic rank, that is below Kingdom (biology), kingdom and above Class (biology), class. Traditionally, in botany the term division (taxonomy), division has been used instead of phylum, although the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants accepts the terms as equivalent. Depending on definitions, the animal kingdom Animalia contains about 31 phyla, the plant kingdom Plantae contains about 14 phyla, and the fungus kingdom Fungi contains about eight phyla. Current research in phylogenetics is uncovering the relationships among phyla within larger clades like Ecdysozoa and Embryophyta. General description The term phylum was coined in 1866 by Ernst Haeckel from the Greek (, "race, stock"), related to (, "tribe, clan"). Haeckel noted that species constantly evolved into new species that seemed to retain few consistent features among themselves and therefore few features that distinguishe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nerves
A nerve is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of nerve fibers (called axons). Nerves have historically been considered the basic units of the peripheral nervous system. A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses called action potentials that are transmitted along each of the axons to peripheral organs or, in the case of sensory nerves, from the periphery back to the central nervous system. Each axon is an extension of an individual neuron, along with other supportive cells such as some Schwann cells that coat the axons in myelin. Each axon is surrounded by a layer of connective tissue called the endoneurium. The axons are bundled together into groups called fascicles, and each fascicle is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the perineurium. The entire nerve is wrapped in a layer of connective tissue called the epineurium. Nerve cells (often called neurons) are further classified as either sensory or motor. In the central nervous system, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. There are two forms of reproduction: Asexual reproduction, asexual and Sexual reproduction, sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to unicellular organism, single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes.John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two specialized reproductive cells, called gametes, which contain half t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |