|
Parahesperornis
''Parahesperornis'' is a genus of prehistoric flightless birds from the Late Cretaceous. Its range in space and time may have been extensive, but its remains are rather few and far between, at least compared with its contemporary relatives in ''Hesperornis''. Remains are known from central North America, namely the former shallows of the Western Interior Seaway in Kansas. Found only in the upper Niobrara Chalk, these are from around the Coniacian-Santonian boundary, 85-82 million years ago (mya). ''Parahesperornis alexi'' (Martin, 1984) was long lumped with specimen YPM 1478, described initially as ''Hesperornis gracilis'' and later moved to the monotypic genus ''Hargeria'' (Lucas, 1903). It then turned out that this genus' description actually referred to specimen KUVP 2287, which eventually became the holotype of ''P. alexi''. Nonetheless, the taxon description of ''Hargeria'' was about ''"Hesperornis" gracilis'' exclusively, and thus despite the misidentification it applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parahesperornis Alexi
''Parahesperornis'' is a genus of prehistoric flightless birds from the Late Cretaceous. Its range in space and time may have been extensive, but its remains are rather few and far between, at least compared with its contemporary relatives in ''Hesperornis''. Remains are known from central North America, namely the former shallows of the Western Interior Seaway in Kansas. Found only in the upper Niobrara Chalk, these are from around the Coniacian-Santonian boundary, 85-82 million years ago (mya). ''Parahesperornis alexi'' (Martin, 1984) was long lumped with specimen YPM 1478, described initially as ''Hesperornis gracilis'' and later moved to the monotypic genus ''Hargeria'' (Lucas, 1903). It then turned out that this genus' description actually referred to specimen KUVP 2287, which eventually became the holotype of ''P. alexi''. Nonetheless, the taxon description of ''Hargeria'' was about ''"Hesperornis" gracilis'' exclusively, and thus despite the misidentification it applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornitheans
Hesperornithes is an extinct and highly specialized group of aquatic avialans closely related to the ancestors of modern birds. They inhabited both marine and freshwater habitats in the Northern Hemisphere, and include genera such as ''Hesperornis'', ''Parahesperornis'', ''Baptornis'', ''Enaliornis'', and ''Potamornis'', all strong-swimming, predatory divers. Many of the species most specialized for swimming were completely flightless. The largest known hesperornithean, ''Canadaga arctica'', may have reached a maximum adult length of . Hesperornitheans were the only Mesozoic avialans to colonize the oceans. They were wiped out in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, along with enantiornitheans and all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other diverse plant and animal groups. Anatomy and ecology Most of what is known about this group rests on analyses of single species, as few provide sufficiently complete fossils for analysis. Although some of the smaller and more basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornithiformes
Hesperornithes is an extinct and highly specialized group of aquatic avialans closely related to the ancestors of modern birds. They inhabited both marine and freshwater habitats in the Northern Hemisphere, and include genera such as ''Hesperornis'', ''Parahesperornis'', ''Baptornis'', ''Enaliornis'', and ''Potamornis'', all strong-swimming, predatory divers. Many of the species most specialized for swimming were completely flightless. The largest known hesperornithean, ''Canadaga arctica'', may have reached a maximum adult length of . Hesperornitheans were the only Mesozoic avialans to colonize the oceans. They were wiped out in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, along with enantiornitheans and all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other diverse plant and animal groups. Anatomy and ecology Most of what is known about this group rests on analyses of single species, as few provide sufficiently complete fossils for analysis. Although some of the smaller and more basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornithes
Hesperornithes is an extinct and highly specialized group of aquatic avialans closely related to the ancestors of modern birds. They inhabited both marine and freshwater habitats in the Northern Hemisphere, and include genera such as ''Hesperornis'', ''Parahesperornis'', ''Baptornis'', ''Enaliornis'', and ''Potamornis'', all strong-swimming, predatory divers. Many of the species most specialized for swimming were completely flightless. The largest known hesperornithean, ''Canadaga arctica'', may have reached a maximum adult length of . Hesperornitheans were the only Mesozoic avialans to colonize the oceans. They were wiped out in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, along with enantiornitheans and all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other diverse plant and animal groups. Anatomy and ecology Most of what is known about this group rests on analyses of single species, as few provide sufficiently complete fossils for analysis. Although some of the smaller and more basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
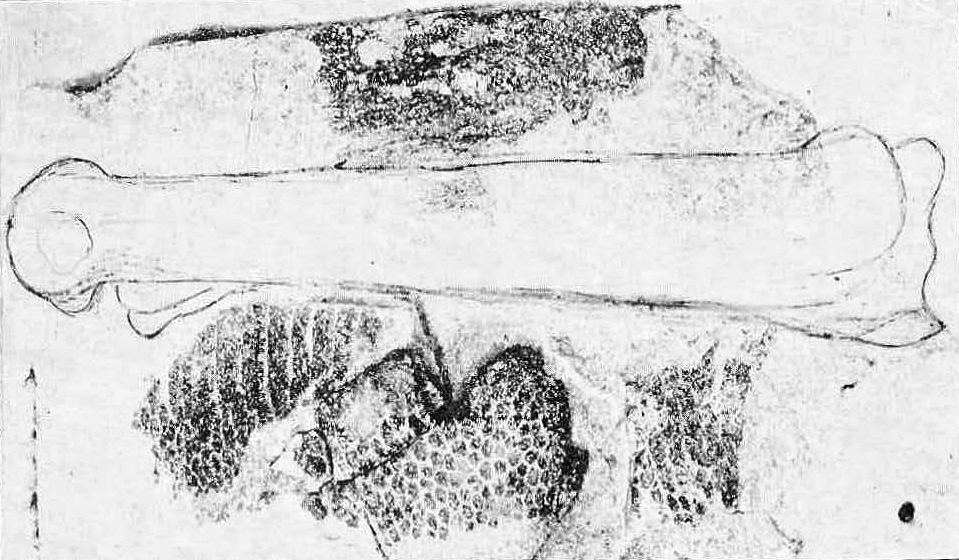
Hesperornis
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nemegt Formation
The Nemegt Formation (also known as Nemegtskaya Svita) is a geological formation in the Gobi Desert of Mongolia, dating to the Late Cretaceous. The formation consists of river channel sediments and contains fossils of fish, turtles, crocodilians, and a diverse fauna of dinosaurs, including birds. Description The Nemegt Formation is composed of mudstones and sandstones that were deposited by ancient lakes, streams, and flood plains. The Altan Uul locality was described by Michael Novacek as "a canyon carved out of a very rich series of sedimentary rocks" with "steep cliffs and narrow washes". The climate associated with it was wetter than when preceding formations were deposited; there seems to have existed at least some degree of forest cover. Fossilized trunks have been also found. These petrified wood, and the remains of Araucariaceae conifers indicate that the forests of the Nemegt were thickly wooded, with a high canopy formed by tall conifer trees. When examined, the rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastrichtian
The Maastrichtian () is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the latest age (uppermost stage) of the Late Cretaceous Epoch or Upper Cretaceous Series, the Cretaceous Period or System, and of the Mesozoic Era or Erathem. It spanned the interval from . The Maastrichtian was preceded by the Campanian and succeeded by the Danian (part of the Paleogene and Paleocene). The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event (formerly known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event) occurred at the end of this age. In this mass extinction, many commonly recognized groups such as non-avian dinosaurs, plesiosaurs and mosasaurs, as well as many other lesser-known groups, died out. The cause of the extinction is most commonly linked to an asteroid about wide colliding with Earth, ending the Cretaceous. Stratigraphic definitions Definition The Maastrichtian was introduced into scientific literature by Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1849, after studying rock strata of the Chalk Group c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsagaan Kushu
Tsagaan (Mongolian: цагаан, ''white'', zh, 查干) may refer to: People * Monguor people or ''Tsagaan mongghol'', a Mongol ethnic group in China * Okna Tsahan Zam (born 1957), a Kalmyk throat singer * Chagaan, 13th-century commander of the Mongol Empire Places in Mongolia * Baatsagaan, Bayankhongor * Bayantsagaan, Bayankhongor * Bayantsagaan, Töv * Buutsagaan, Bayankhongor * Erdenetsagaan, Sükhbaatar * Saintsagaan, Dundgovi * Tsagaanchuluut, Zavkhan * Tsagaandelger, Dundgovi * Tsagaankhairkhan, Uvs * Tsagaankhairkhan, Zavkhan * Tsagaan-Ovoo, Dornod * Tsagaan-Uul, Khövsgöl * Tsagaan-Üür, Khövsgöl Others * Tsagaan Sar, the Mongolian New Year festival * ''Tsaagan ''Tsaagan'' (meaning "white") is a genus of dromaeosaurid dinosaur from the Djadokhta Formation of the Late Cretaceous of Mongolia. Discovery and naming The holotype of ''Tsaagan'' was discovered in 1996 and first identified as a specimen of '' ...'', the dinosaur ''Tsaagan mangas'' (te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million, making it the world's most sparsely populated sovereign nation. Mongolia is the world's largest landlocked country that does not border a closed sea, and much of its area is covered by grassy steppe, with mountains to the north and west and the Gobi Desert to the south. Ulaanbaatar, the capital and largest city, is home to roughly half of the country's population. The territory of modern-day Mongolia has been ruled by various nomadic empires, including the Xiongnu, the Xianbei, the Rouran, the First Turkic Khaganate, and others. In 1206, Genghis Khan founded the Mongol Empire, which became the largest contiguous land empire in history. His grandson Kublai Khan conquered China proper and established the Yuan dynasty. After the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibiotarsus
The tibiotarsus is the large bone between the femur and the tarsometatarsus in the leg of a bird. It is the fusion of the proximal part of the tarsus with the tibia. A similar structure also occurred in the Mesozoic Heterodontosauridae. These small ornithischian dinosaurs were unrelated to birds and the similarity of their foot bones is best explained by convergent evolution. See also *Bird anatomy References * Proctor, Nobel S. ''Manual of Ornithology: Avian Structure and Function''. Yale University Press Yale University Press is the university press of Yale University. It was founded in 1908 by George Parmly Day, and became an official department of Yale University in 1961, but it remains financially and operationally autonomous. , Yale Universi .... (1993) Bird anatomy {{ornithology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anatomical Terms Of Location
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position provides a definition of what is at the front ("anterior"), behind ("posterior") and so on. As part of defining and describing terms, the body is described through the use of anatomical planes and anatomical axes. The meaning of terms that are used can change depending on whether an organism is bipedal or quadrupedal. Additionally, for some animals such as invertebrates, some terms may not have any meaning at all; for example, an animal that is radially symmetrical will have no anterior surface, but can still have a description that a part is close to the middle ("proximal") or further from the middle ("distal"). International organisations have determined vocabularies that are often used as standard vocabularies for subdisciplines of anatom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



