|
Hesperornithiformes
Hesperornithes is an extinct and highly specialized group of aquatic avialans closely related to the ancestors of modern birds. They inhabited both marine and freshwater habitats in the Northern Hemisphere, and include genera such as ''Hesperornis'', ''Parahesperornis'', ''Baptornis'', ''Enaliornis'', and ''Potamornis'', all strong-swimming, predatory divers. Many of the species most specialized for swimming were completely flightless. The largest known hesperornithean, ''Canadaga arctica'', may have reached a maximum adult length of . Hesperornitheans were the only Mesozoic avialans to colonize the oceans. They were wiped out in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, along with enantiornitheans and all other non-avian dinosaurs, and many other diverse plant and animal groups. Anatomy and ecology Most of what is known about this group rests on analyses of single species, as few provide sufficiently complete fossils for analysis. Although some of the smaller and more basal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornis BW (white Background)
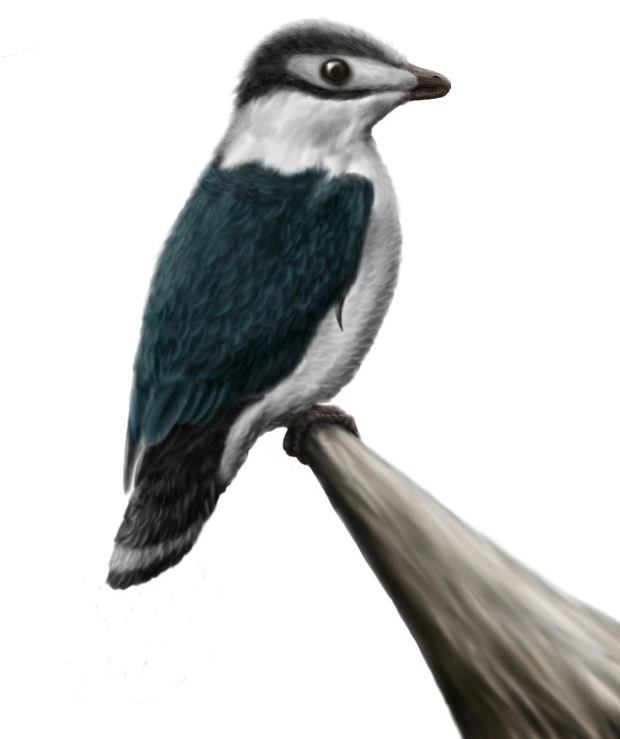
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornis Regalis
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperornis
''Hesperornis'' (meaning "western bird") is a genus of cormorant-like bird that spanned the first half of the Campanian age of the Late Cretaceous period (83.5–78 mya). One of the lesser-known discoveries of the paleontologist O. C. Marsh in the late 19th century Bone Wars, it was an early find in the history of avian paleontology. Locations for ''Hesperornis'' fossils include the Late Cretaceous marine limestones from Kansas and the marine shales from Canada. Nine species are recognised, eight of which have been recovered from rocks in North America and one from Russia. Description ''Hesperornis'' was a large bird, reaching up to in length. It had virtually no wings, and swam with its powerful hind legs. Studies on the feet initially indicated that ''Hesperornis'' and kin had lobed toes similar to modern-day grebes, as opposed to webbed toes as seen in most aquatic birds such as loons. More recent work looking at the morphometrics of the feet in hesperornithiformes and mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parahesperornis
''Parahesperornis'' is a genus of prehistoric flightless birds from the Late Cretaceous. Its range in space and time may have been extensive, but its remains are rather few and far between, at least compared with its contemporary relatives in ''Hesperornis''. Remains are known from central North America, namely the former shallows of the Western Interior Seaway in Kansas. Found only in the upper Niobrara Chalk, these are from around the Coniacian-Santonian boundary, 85-82 million years ago (mya). ''Parahesperornis alexi'' (Martin, 1984) was long lumped with specimen YPM 1478, described initially as ''Hesperornis gracilis'' and later moved to the monotypic genus ''Hargeria'' (Lucas, 1903). It then turned out that this genus' description actually referred to specimen KUVP 2287, which eventually became the holotype of ''P. alexi''. Nonetheless, the taxon description of ''Hargeria'' was about ''"Hesperornis" gracilis'' exclusively, and thus despite the misidentification it applies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bird
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweight skeleton. Birds live worldwide and range in size from the bee hummingbird to the ostrich. There are about ten thousand living species, more than half of which are passerine, or "perching" birds. Birds have whose development varies according to species; the only known groups without wings are the extinct moa and elephant birds. Wings, which are modified forelimbs, gave birds the ability to fly, although further evolution has led to the loss of flight in some birds, including ratites, penguins, and diverse endemic island species. The digestive and respiratory systems of birds are also uniquely adapted for flight. Some bird species of aquatic environments, particularly seabirds and some waterbirds, have further evolved for swimming. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brodavis
''Brodavis'' is a genus of freshwater hesperornithiform birds known from the Late Cretaceous (possibly Campanian and Maastrichtian stage) of North America and Asia. It was first described and named by Larry D. Martin, Evgeny N. Kurochkin and Tim T. Tokaryk in 2012 and assigned to a new monogeneric family, Brodavidae. Four species were described and assigned to ''Brodavis''. The type species, ''B. americanus'', is known from the holotype left metatarsal, RSM P 2315.1 which was collected in the Maastrichtian-age Frenchman Formation of Canada. ''B. baileyi'' is known from the holotype left metatarsal, UNSM 50665, which was collected in the Maastrichtian-age Hell Creek Formation of South Dakota, United States (dated to between 66.8 and 66 Ma agoLongrich, N.R., Tokaryk, T. and Field, D.J. (2011). "Mass extinction of birds at the Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) boundary." ''Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences'', 108(37): 15253-15257. ) ''B. mongoliensis'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chupkaornis
''Chupkaornis'' is a genus of prehistoric flightless birds from the Late Cretaceous (Coniacian-Santonian) Kashima Formation of Hokkaido, Japan. Description Diagnostic traits of ''Chupkaornis'' include a finger-like projected tibiofibular crest of femur, deep, emarginated lateral excavation with a sharply defined edge of the ventral margin of the thoracic vertebrae, and the heterocoelous articular surface of the thoracic vertebrae.Tomonori Tanaka, Yoshitsugu Kobayashi, Ken'ichi Kurihara, Anthony R. Fiorillo and Manabu Kano. 2017. The Oldest Asian Hesperornithiform from the Upper Cretaceous of Japan, and the Phylogenetic Reassessment of Hesperornithiformes. Journal of Systematic Palaeontology. Phylogeny ''Chupkaornis'' is recovered by Tanaka et al. (2017) as more derived than the Cenomanian-age form ''Pasquiaornis'', but less advanced than ''Brodavis'' and ''Baptornis ''Baptornis'' ("diving bird") is a genus of flightless, aquatic birds from the Late Cretaceous, some 87-80 mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fumicollis
''Fumicollis'' is a genus of prehistoric flightless birds from the Late Cretaceous (Coniacian-Santonian) Niobrara Chalk of Kansas. Description Diagnostic traits of ''Fumicollis'' include presacral vertebrae with expanded ventral processes, an elongate pelvis with reduced acetabulum (acetabulum width: pelvis length is approximately 0.096 meters), a femur with expanded lateral condyle (transverse extent of condyle over 75% of midshaft width) and moderately expanded trochanter. The genus name refers to the Smoky Hill Chalk Member of the Niobrara Chalk in which it was found.Bell A, Chiappe LM (2015) Identification of a New Hesperornithiform from the Cretaceous Niobrara Chalk and Implications for Ecologic Diversity among Early Diving Birds. PLoS ONE 10(11): e0141690. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0141690 Discovery The holotype of ''Fumicollis'', USNM 20030, was found by Harold Shepherd and George Sternberg in 1937 in the Smoky Hill Member of the Niobrara Chalk of Logan County, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretaceous–Paleogene Extinction Event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the exception of some ectothermic species such as sea turtles and crocodilians, no tetrapods weighing more than survived. It marked the end of the Cretaceous Period, and with it the Mesozoic era, while heralding the beginning of the Cenozoic era, which continues to this day. In the geologic record, the K–Pg event is marked by a thin layer of sediment called the K–Pg boundary, which can be found throughout the world in marine and terrestrial rocks. The boundary clay shows unusually high levels of the metal iridium, which is more common in asteroids than in the Earth's crust. As originally proposed in 1980 by a team of scientists led by Luis Alvarez and his son Walter, it is now generally thought that the K–Pg extinction was cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enantiornithes
The Enantiornithes, also known as enantiornithines or enantiornitheans in literature, are a group of extinct avialans ("birds" in the broad sense), the most abundant and diverse group known from the Mesozoic era. Almost all retained teeth and clawed fingers on each wing, but otherwise looked much like modern birds externally. Over eighty species of Enantiornithes have been named, but some names represent only single bones, so it is likely that not all are valid. The Enantiornithes became extinct at the Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary, along with Hesperornithes and all other non-avian dinosaurs. Discovery and naming The first Enantiornithes to be discovered were incorrectly referred to modern bird groups. For example, the first known species of Enantiornithes, ''Gobipteryx minuta'', was originally considered a paleognath related to ostriches and tinamou. The Enantiornithes were first recognized as a distinct lineage, or "subclass" of birds, by Cyril A. Walker in 1981. Walker mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)


.jpg)



