|
Papillomas
A papilloma (plural papillomas or papillomata) ('' papillo-'' + '' -oma'') is a benign epithelial tumor growing exophytically (outwardly projecting) in nipple-like and often finger-like fronds. In this context, papilla refers to the projection created by the tumor, not a tumor on an already existing papilla (such as the nipple). When used without context, it frequently refers to infections (squamous cell papilloma) caused by human papillomavirus (HPV), such as warts. Human papillomavirus infection is a major cause of cervical cancer, vulvar cancer, vaginal cancer, penis cancer, anal cancer, and HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancer, HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Most Wart, viral warts are caused by human papillomavirus infection (HPV), of which there are nearly 200 distinct human papillomaviruses (HPVs), and many HPV types are Carcinogenic virus, carcinogenic. There are, however, a number of other conditions that cause papilloma, as well as many cases in which there is no known c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
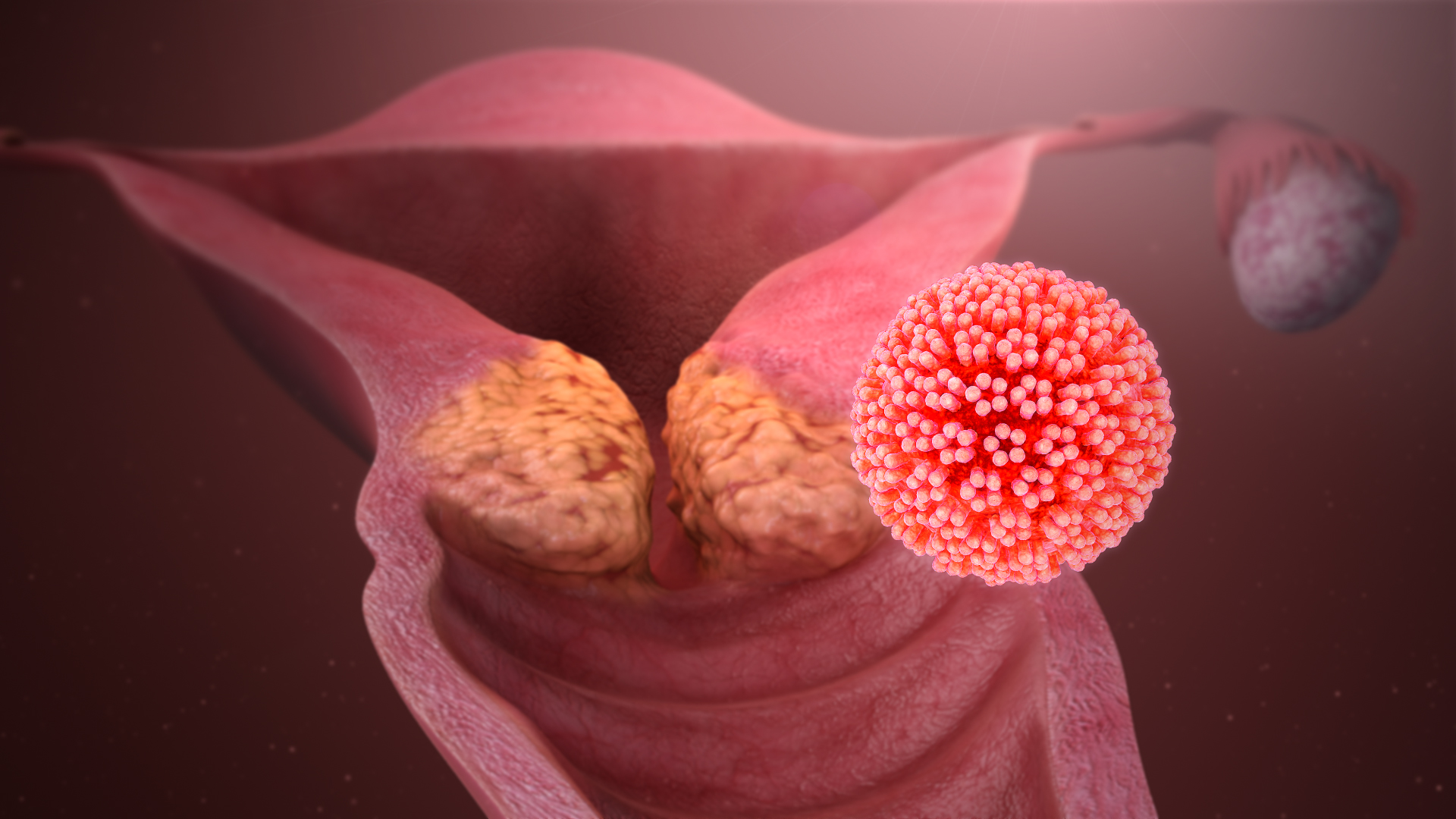
Wart
Warts are typically small, rough, hard growths that are similar in color to the rest of the skin. They typically do not result in other symptoms, except when on the bottom of the feet, where they may be painful. While they usually occur on the hands and feet, they can also affect other locations. One or many warts may appear. They are not cancerous. Warts are caused by infection with a type of human papillomavirus (HPV). Factors that increase the risk include use of public showers and pools, working with meat, eczema and a weak immune system. The virus is believed to enter the body through skin that has been damaged slightly. A number of types exist, including "common warts", plantar warts, " filiform warts", and genital warts. Genital warts are often sexually transmitted. Without treatment, most types of warts resolve in months to years. A number of treatments may speed resolution, including salicylic acid applied to the skin and cryotherapy. In those who are otherwise he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the ''Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, and the dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wart
Warts are typically small, rough, hard growths that are similar in color to the rest of the skin. They typically do not result in other symptoms, except when on the bottom of the feet, where they may be painful. While they usually occur on the hands and feet, they can also affect other locations. One or many warts may appear. They are not cancerous. Warts are caused by infection with a type of human papillomavirus (HPV). Factors that increase the risk include use of public showers and pools, working with meat, eczema and a weak immune system. The virus is believed to enter the body through skin that has been damaged slightly. A number of types exist, including "common warts", plantar warts, " filiform warts", and genital warts. Genital warts are often sexually transmitted. Without treatment, most types of warts resolve in months to years. A number of treatments may speed resolution, including salicylic acid applied to the skin and cryotherapy. In those who are otherwise he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intraductal Papilloma
Intraductal papillomas of the breast are benign lesions with an incidence of approximately 2-3% in humans. They result from abnormal proliferation of the epithelial cells lining the breast ducts. Two types of intraductal papillomas are generally distinguished. The central type develops near the nipple. They are usually solitary and often arise in the years nearing menopause. On the other hand, the peripheral type are often multiple papillomas arising at the peripheral ducts, and are usually found in younger women. The peripheral type are associated with a higher risk of malignancy. They are the most common cause of bloody nipple discharge in women age 20-40 and generally do not show up on mammography due to their small size. They may be detectable on ultrasound. A galactogram is the most definitive test but is somewhat invasive. The masses are often too small to be palpate Palpation is the process of using one's hands to check the body, especially while perceiving/diagnosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HPV-positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (HPV-positive OPC or HPV+OPC), is a cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the throat caused by the human papillomavirus type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the oropharynx (throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV virus, acquired by having oral contact with the genitals (oral-genital sex) of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal Pap smear or cervical dysplasia, having chronic periodontitis, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of genital warts. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease from HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer (also called HPV negative-OPC and HPV-OPC). HPV-positive OPC presents in one of four ways: as an asymptoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoperoxidase
Immunoperoxidase is a type of immunostain used in molecular biology, medical research, and clinical diagnostics. In particular, immunoperoxidase reactions refer to a sub-class of immunohistochemical or immunocytochemical procedures in which the antibodies are visualized via a peroxidase-catalyzed reaction. Immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry are methods used to determine in which cells or parts of cells a particular protein or other macromolecule are located. These stains use ''antibodies'' to bind to specific ''antigens'', usually of protein or glycoprotein origin. Since antibodies are normally invisible, special strategies must be employed to detect these bound antibodies. In an immunoperoxidase procedure, an enzyme known as a peroxidase is used to catalyze a chemical reaction to produce a coloured product. Simply, a very thin slice of tissue is fixed onto glass, incubated with antibody or a series of antibodies, the last of which is chemically linked to peroxidase. Aft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uvula
The palatine uvula, usually referred to as simply the uvula, is a conic projection from the back edge of the middle of the soft palate, composed of connective tissue containing a number of racemose glands, and some muscular fibers. It also contains many serous glands, which produce thin saliva. It is only found in human beings. Structure Muscle The muscular part of the uvula () shortens and broadens the uvula. This changes the contour of the posterior part of the soft palate. This change in contour allows the soft palate to adapt closely to the posterior pharyngeal wall to help close the nasopharynx during swallowing. Its muscles are controlled by the pharyngeal branch of the vagus nerve. Variation A bifid or bifurcated uvula is a split or cleft uvula. Newborns with cleft palate often also have a split uvula. The bifid uvula results from incomplete fusion of the palatine shelves but it is considered only a slight form of clefting. Bifid uvulas have less muscle in them th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity. A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separated. The palate is divided into two parts, the anterior, bony hard palate and the posterior, fleshy soft palate (or velum). Structure Innervation The maxillary nerve branch of the trigeminal nerve supplies sensory innervation to the palate. Development The hard palate forms before birth. Variation If the fusion is incomplete, a cleft palate results. Function When functioning in conjunction with other parts of the mouth, the palate produces certain sounds, particularly velar, palatal, palatalized, postalveolar, alveolopalatal, and uvular consonants. History Etymology The English synonyms palate and palatum, and also the related adjective palatine (as in palatine bone), are all from the Latin ''palatum'' via Old French ''palat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
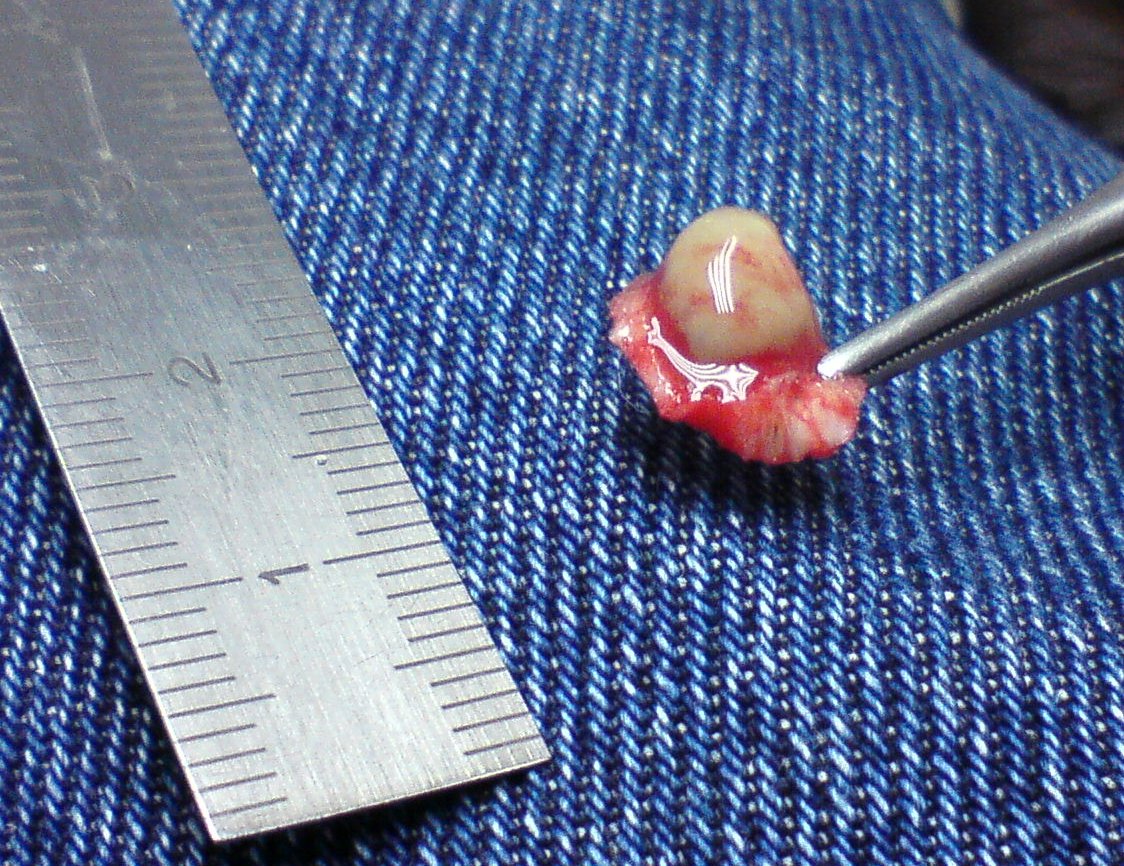
Sessility (medicine)
A peduncle is an elongated stalk of tissue. Sessility is the state of not having a peduncle; a sessile mass or structure lacks a stalk. In medicine, a mass such as a cyst or polyp is said to be ''pedunculated'' if it is supported by a peduncle. There are in total three types of peduncles in the cerebellum of the human brain, known as superior cerebellar peduncle, middle cerebellar peduncle, and inferior cerebellar peduncle. Pedunculated eyes are also the defining attribute of the Stylophthalmine trait found in certain fish larvae. The caudal peduncle is a slightly narrowed part of a fish where the caudal fin meets the spine. See also *Peduncle (botany) In botany, a peduncle is a stalk supporting an inflorescence or a solitary flower, or, after fecundation, an infructescence or a solitary fruit. The peduncle sometimes has bracts (a type of cataphylls) at nodes. The main axis of an inflorescenc ... References Gross pathology {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedunculated
A peduncle is an elongated stalk of tissue. Sessility is the state of not having a peduncle; a sessile mass or structure lacks a stalk. In medicine, a mass such as a cyst or polyp is said to be ''pedunculated'' if it is supported by a peduncle. There are in total three types of peduncles in the cerebellum of the human brain, known as superior cerebellar peduncle, middle cerebellar peduncle, and inferior cerebellar peduncle. Pedunculated eyes are also the defining attribute of the Stylophthalmine trait found in certain fish larvae. The caudal peduncle is a slightly narrowed part of a fish where the caudal fin meets the spine. See also *Peduncle (botany) In botany, a peduncle is a stalk supporting an inflorescence or a solitary flower, or, after fecundation, an infructescence or a solitary fruit. The peduncle sometimes has bracts (a type of cataphylls) at nodes. The main axis of an infloresce ... References Gross pathology {{anatomy-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mucous Membrane
A mucous membrane or mucosa is a membrane that lines various cavities in the body of an organism and covers the surface of internal organs. It consists of one or more layers of epithelial cells overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. It is mostly of endodermal origin and is continuous with the skin at body openings such as the eyes, eyelids, ears, inside the nose, inside the mouth, lips, the genital areas, the urethral opening and the anus. Some mucous membranes secrete mucus, a thick protective fluid. The function of the membrane is to stop pathogens and dirt from entering the body and to prevent bodily tissues from becoming dehydrated. Structure The mucosa is composed of one or more layers of epithelial cells that secrete mucus, and an underlying lamina propria of loose connective tissue. The type of cells and type of mucus secreted vary from organ to organ and each can differ along a given tract. Mucous membranes line the digestive, respiratory and reproductive trac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cauliflower
Cauliflower is one of several vegetables in the species ''Brassica oleracea'' in the genus ''Brassica'', which is in the Brassicaceae (or mustard) family. It is an annual plant that reproduces by seed. Typically, only the head is eaten – the edible white flesh sometimes called "curd" (with a similar appearance to cheese curd). The cauliflower head is composed of a white inflorescence meristem. Cauliflower heads resemble those in broccoli, which differs in having flower buds as the edible portion. ''Brassica oleracea'' also includes broccoli, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, collard greens, and kale, collectively called "cole" crops, though they are of different cultivar groups. History Pliny the Elder included ''cyma'' among cultivated plants he described in '' Natural History'': "''Ex omnibus brassicae generibus suavissima est cyma,''" ("Of all the varieties of cabbage the most pleasant-tasted is ''cyma''"). Pliny's description likely refers to the flowering heads of an earli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_EM_(new_version).jpg)

