|
HPV-positive Oropharyngeal Cancer
Human papillomavirus-positive oropharyngeal cancer (HPV-positive OPC or HPV+OPC), is a cancer (squamous cell carcinoma) of the throat caused by the human papillomavirus type 16 virus (HPV16). In the past, cancer of the oropharynx (throat) was associated with the use of alcohol or tobacco or both, but the majority of cases are now associated with the HPV virus, acquired by having oral contact with the genitals (oral-genital sex) of a person who has a genital HPV infection. Risk factors include having a large number of sexual partners, a history of oral-genital sex or anal–oral sex, having a female partner with a history of either an abnormal Pap smear or cervical dysplasia, having chronic periodontitis, and, among men, younger age at first intercourse and a history of genital warts. HPV-positive OPC is considered a separate disease from HPV-negative oropharyngeal cancer (also called HPV negative-OPC and HPV-OPC). HPV-positive OPC presents in one of four ways: as an asympt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisible to the eye unless aided by a microscope. There are many types of microscopes, and they may be grouped in different ways. One way is to describe the method an instrument uses to interact with a sample and produce images, either by sending a beam of light or electrons through a sample in its optical path, by detecting photon emissions from a sample, or by scanning across and a short distance from the surface of a sample using a probe. The most common microscope (and the first to be invented) is the optical microscope, which uses lenses to refract visible light that passed through a thinly sectioned sample to produce an observable image. Other major types of microscopes are the fluorescence microscope, electron microscope (both the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
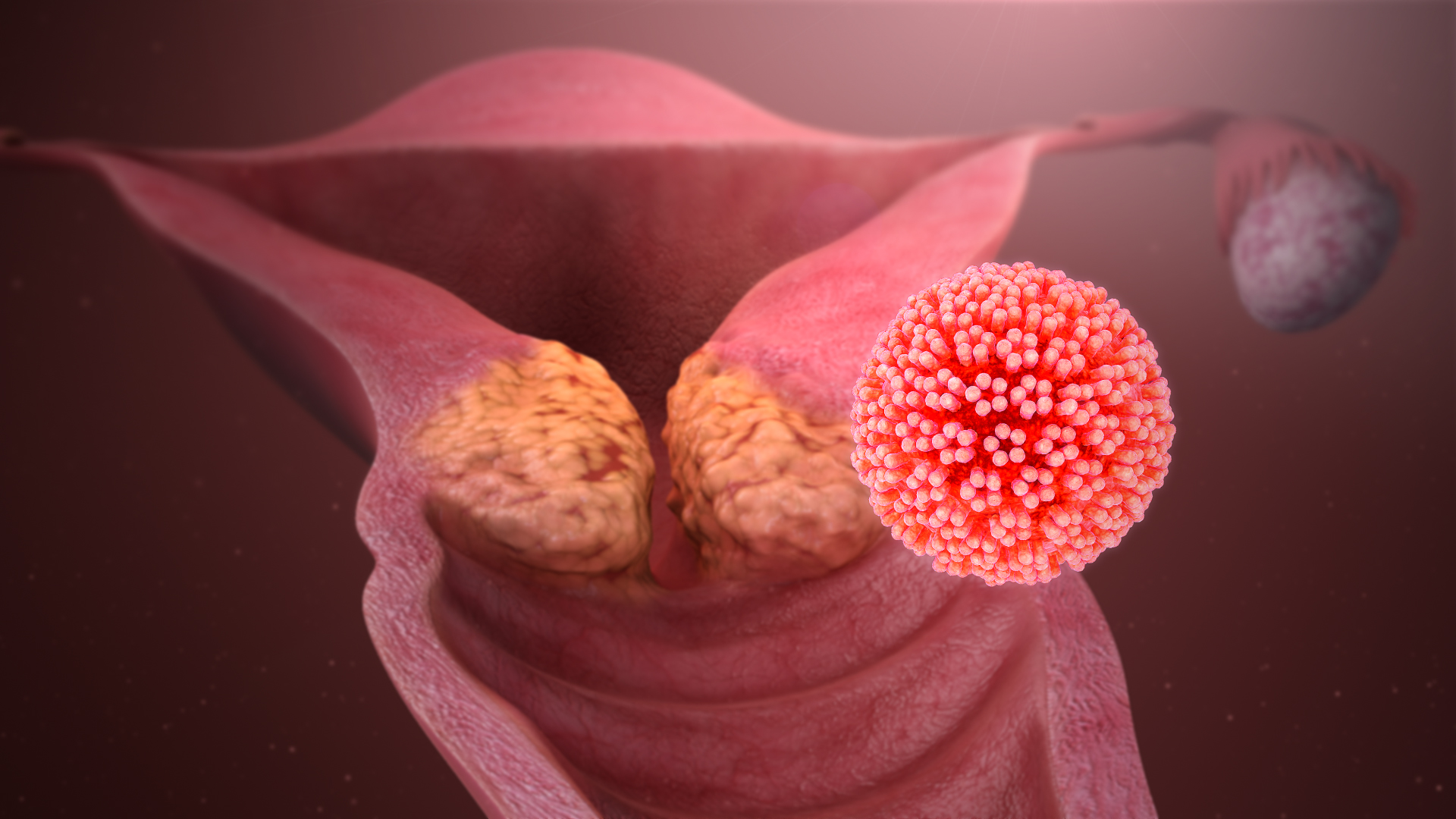
Human Papillomavirus
Human papillomavirus infection (HPV infection) is caused by a DNA virus from the '' Papillomaviridae'' family. Many HPV infections cause no symptoms and 90% resolve spontaneously within two years. In some cases, an HPV infection persists and results in either warts or precancerous lesions. These lesions, depending on the site affected, increase the risk of cancer of the cervix, vulva, vagina, penis, anus, mouth, tonsils, or throat. Nearly all cervical cancer is due to HPV and two strains – HPV16 and HPV18 – account for 70% of cases. HPV16 is responsible for almost 90% of HPV-positive oropharyngeal cancers. Between 60% and 90% of the other cancers listed above are also linked to HPV. HPV6 and HPV11 are common causes of genital warts and laryngeal papillomatosis. An HPV infection is caused by ''human papillomavirus'', a DNA virus from the papillomavirus family. Over 170 types have been described. An individual can become infected with more than one type of HPV, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AJCC
{{Short description, Organization standardising cancer staging The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) is an organization best known for defining and popularizing cancer staging standards, officially the AJCC staging system. The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) was established in 1959 to formulate and publish systems of classification of cancer, including staging and end results reporting, which will be acceptable to and used by the medical profession for selecting the most effective treatment, determining prognosis, and continuing evaluation of cancer control measures. Membership The AJCC has 20 member organizations. Membership is reserved for those organizations whose missions or goals are consistent with or complementary to those of the AJCC. These organizations generally demonstrate involvement or activity in one or more of the following areas: cancer epidemiology, patient care, cancer control, cancer registration, professional education, research, or biostati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staging System
Cancer staging is the process of determining the extent to which a cancer has developed by growing and spreading. Contemporary practice is to assign a number from I to IV to a cancer, with I being an isolated cancer and IV being a cancer that has spread to the limit of what the assessment measures. The stage generally takes into account the size of a tumor, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many regional (nearby) lymph nodes it has spread to (if any), and whether it has appeared in more distant locations (metastasized). The staging system is not applicable to astrocytoma, which is instead expressed as "grade I–IV". Grade IV astrocytoma, more commonly referred to as glioblastoma multiforme, is a universally fatal primary brain cancer most commonly seen in the seventh decade of life. TNM staging system Cancer staging can be divided into a clinical stage and a pathologic stage. In the TNM (Tumor, Node, Metastasis) system, clinical stage and pathologic stage are deno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P16 (gene)
p16 (also known as p16INK4a, cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2A, CDKN2A, multiple tumor suppressor 1 and numerous other synonyms), is a protein that slows cell division by slowing the progression of the cell cycle from the G1 phase to the S phase, thereby acting as a tumor suppressor. It is encoded by the ''CDKN2A'' gene. A deletion (the omission of a part of the DNA sequence during replication) in this gene can result in insufficient or non-functional p16, accelerating the cell cycle and resulting in many types of cancer. p16 can be used as a biomarker to improve the histological diagnostic accuracy of grade 3 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). p16 is also implicated in the prevention of melanoma, oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, cervical cancer, vulvar cancer and esophageal cancer. p16 was discovered in 1993. It is a protein with 148 amino acids and a molecular weight of 16 kDa that comprises four ankyrin repeats. The name of p16 is derived from its mole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumour Suppressor Protein
A tumor suppressor gene (TSG), or anti-oncogene, is a gene that regulates a cell during cell division and replication. If the cell grows uncontrollably, it will result in cancer. When a tumor suppressor gene is mutated, it results in a loss or reduction in its function. In combination with other genetic mutations, this could allow the cell to grow abnormally. The loss of function for these genes may be even more significant in the development of human cancers, compared to the activation of oncogenes. TSGs can be grouped into the following categories: caretaker genes, gatekeeper genes, and more recently landscaper genes. Caretaker genes ensure stability of the genome via DNA repair and subsequently when mutated allow mutations to accumulate. Meanwhile, gatekeeper genes directly regulate cell growth by either inhibiting cell cycle progression or inducing apoptosis. Lastly landscaper genes regulate growth by contributing to the surrounding environment, when mutated can cause an envir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
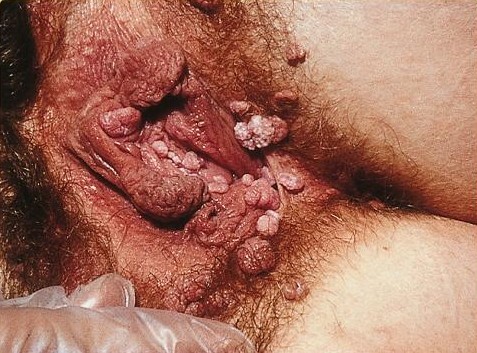
Genital Warts
Genital warts are a sexually transmitted infection caused by certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV). They are generally pink in color and project out from the surface of the skin. Usually they cause few symptoms, but can occasionally be painful. Typically they appear one to eight months following exposure. Warts are the most easily recognized symptom of genital HPV infection. HPV types 6 and 11 are responsible for causing majority of genital warts whereas HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, and 35 are also occasionally found. It is spread through direct skin-to-skin contact, usually during oral, genital, or anal sex with an infected partner. Diagnosis is generally based on symptoms and can be confirmed by biopsy. The types of HPV that cause cancer are not the same as those that cause warts. Some HPV vaccines can prevent genital warts as may condoms. Treatment options include creams such as podophyllin, imiquimod, and trichloroacetic acid. Cryotherapy or surgery may also be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main cause of tooth loss for adults worldwide.V. Baelum and R. Lopez, “Periodontal epidemiology: towards social science or molecular biology?,”Community Dentistry and Oral Epidemiology, vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 239–249, 2004.Nicchio I, Cirelli T, Nepomuceno R, et al. Polymorphisms in Genes of Lipid Metabolism Are Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Periodontitis, as Comorbidities, and with the Subjects' Periodontal, Glycemic, and Lipid Profiles Journal of Diabetes Research. 2021 Jan;2021. PMCID: PMC8601849. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or fall out. Bad breath may also occur. Periodontal disease is generally due to bacteria in the mout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Dysplasia
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN), also known as cervical dysplasia, is the abnormal growth of cells on the surface of the cervix that could potentially lead to cervical cancer. More specifically, CIN refers to the potentially precancerous transformation of cells of the cervix. CIN most commonly occurs at the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix, a transitional area between the squamous epithelium of the vagina and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. It can also occur in vaginal walls and vulvar epithelium. CIN is graded on a 1–3 scale, with 3 being the most abnormal (see classification section below). Human papillomavirus ( HPV) infection is necessary for the development of CIN, but not all with this infection develop cervical cancer. Many women with HPV infection never develop CIN or cervical cancer. Typically, HPV resolves on its own. However, those with an HPV infection that lasts more than one or two years have a higher risk of developing a higher grade of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pap Smear
The Papanicolaou test (abbreviated as Pap test, also known as Pap smear (AE), cervical smear (BE), cervical screening (BE), or smear test (BE)) is a method of cervical screening used to detect potentially precancerous and cancerous processes in the cervix (opening of the uterus or womb) or colon (in both men and women). Abnormal findings are often followed up by more sensitive diagnostic procedures and, if warranted, interventions that aim to prevent progression to cervical cancer. The test was independently invented in the 1920s by Georgios Papanikolaou and Aurel Babeș and named after Papanikolaou. A simplified version of the test was introduced by Anna Marion Hilliard in 1957. A Pap smear is performed by opening the vagina with a speculum and collecting cells at the outer opening of the cervix at the transformation zone (where the outer squamous cervical cells meet the inner glandular endocervical cells), using an Ayre spatula or a cytobrush. A similar method is used to co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anal–oral Sex
Anilingus (from the Latin ''anus'' + ''-lingus'', from ''lingere'', "to lick", variantly spelled "analingus") is the oral and anal sex act in which a person stimulates the anus of another by using the mouth, including lips, tongue, or teeth. It is also called anal–oral contact and anal–oral sex, and is additionally known by slang names. Health risks include fecal–oral transmission of diseases. Etymology and alternative names The term ''anilingus'' entered English through the 1899 F. J. Rebman translation of Edition 10 of sexologist Richard von Krafft-Ebing's 1886 book ''Psychopathia sexualis''. Colloquial names include "rimming", "rim job", "eating ass", or "tossing the salad". Practice General Pleasure for the giver during anilingus is usually based more on the principle of the act. The anus has a relatively high concentration of nerve endings and can be an erogenous zone, and the recipient may receive pleasure from external anal stimulation. The person receiving ani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral-genital Sex
Oral sex, sometimes referred to as oral intercourse, is sexual activity involving the stimulation of the genitalia of a person by another person using the mouth (including the lips, tongue, or teeth) and the throat. Cunnilingus is oral sex performed on the vulva or vagina, while fellatio is oral sex performed on the penis. Anilingus, another form of oral sex, is oral stimulation of the anus. Oral sex may be performed as foreplay to incite sexual arousal before other sexual activities (such as vaginal or anal intercourse), or as an erotic and physically intimate act in its own right. Like most forms of sexual activity, oral sex can pose a risk for contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs/STDs). However, the transmission risk for oral sex, especially HIV transmission, is significantly lower than for vaginal or anal sex. Oral sex is often regarded as taboo, but most countries do not have laws which ban the practice. Commonly, people do not regard oral sex as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_EM_(new_version).jpg)