|
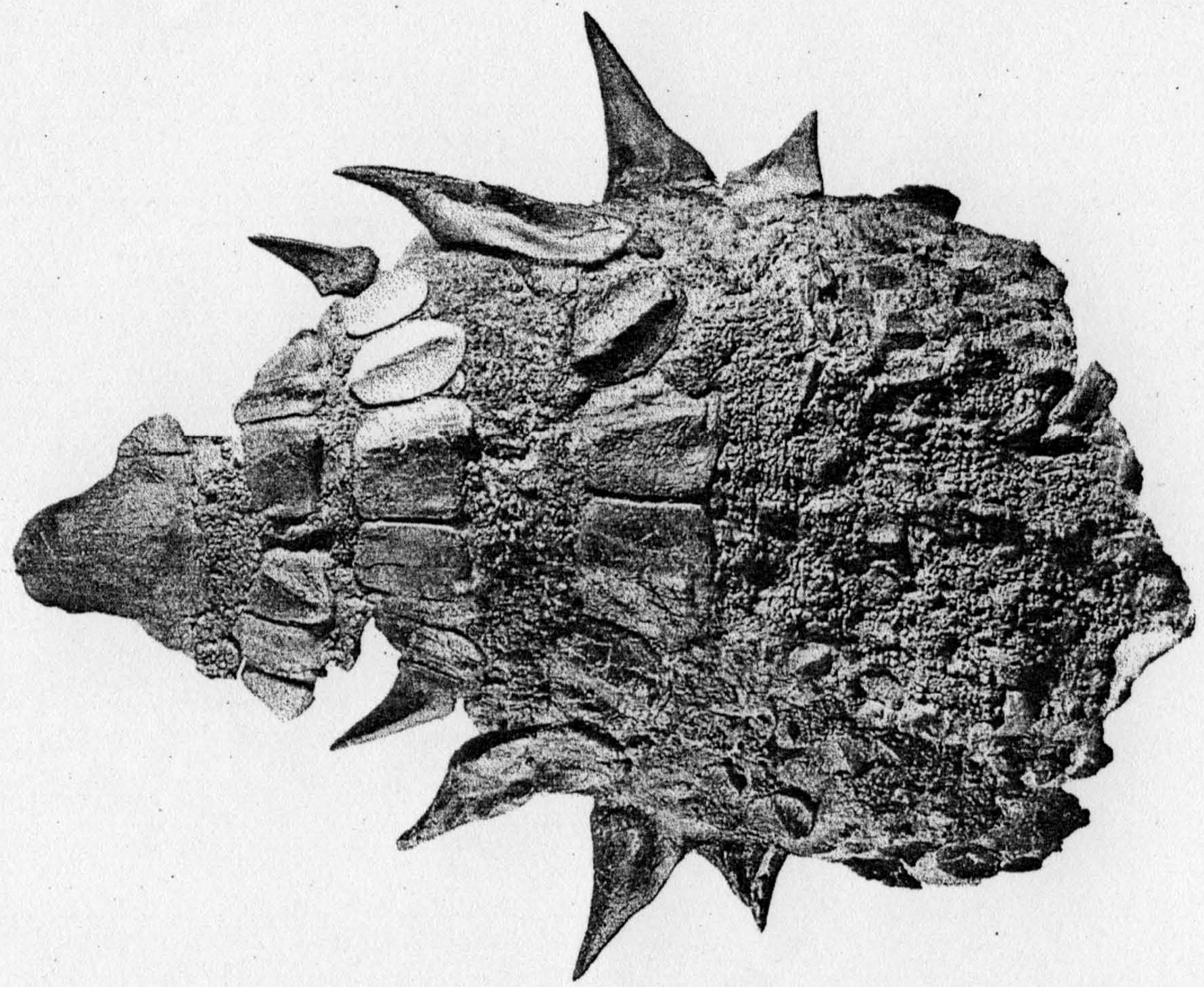
Panoplosaurus
''Panoplosaurus'' is a genus of armoured dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada. Few specimens of the genus are known, all from the middle Campanian of the Dinosaur Park Formation, roughly 76 to 75 million years ago. It was first discovered in 1917, and named in 1919 by Lawrence Lambe, named for its extensive armour, meaning "well-armoured lizard". ''Panoplosaurus'' has at times been considered the proper name for material otherwise referred to as ''Edmontonia'', complicating its phylogenetic and ecological interpretations, at one point being considered to have existed across Alberta, New Mexico and Texas, with specimens in institutions from Canada and the United States. The skull and skeleton of ''Panoplosaurus'' are similar to its relatives, but have a few significant differences, such as the lumpy form of the skull osteoderms, a completely fused shoulder blade, and regularly shaped plates on its neck and body lacking prominent spines. It was a quadrupedal animal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmontonia
''Edmontonia'' is a genus of panoplosaurin nodosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Period. It is part of the Nodosauridae, a family within Ankylosauria. It is named after the Edmonton Formation (now the Horseshoe Canyon Formation in Canada), the unit of rock where it was found. Description Size and general build ''Edmontonia'' was bulky, broad and tank-like. Its length has been estimated at about 6.6 m (22 ft). In 2010, Gregory S. Paul considered both main ''Edmontonia'' species, ''E. longiceps'' and ''E. rugosidens'', to be equally long at six metres and weigh three tonnes.Paul, G.S., 2010, ''The Princeton Field Guide to Dinosaurs'', Princeton University Press p. 238 ''Edmontonia'' had small, oval ridged bony plates on its back and head and many sharp spikes along its sides. The four largest spikes jutted out from the shoulders on each side, the second of which was split into subspines in ''E. rugosidens'' specimens. Its skull had a pear-like shape when viewed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panoplosaurinae
Panoplosaurini (derived from ''Panoplosaurus'', "all shield reptile") is a clade of nodosaurid ankylosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and South America. The group is defined as the largest clade containing ''Panoplosaurus mirus'', but not '' Nodosaurus textilis'' or '' Struthiosaurus austriacus'', and was named in 2021 by Madzia and colleagues for the group found in many previous analyses, both morphological and phylogenetic. Panoplosaurini includes not only the Late Cretaceous ''Panoplosaurus'', ''Denversaurus'' and ''Edmontonia'', but also the mid Cretaceous ''Animantarx'' and ''Texasetes'', as well as ''Patagopelta''. However, in the study describing it, its authors only placed it as a nodosaurine outside Panoplosaurini. The approximately equivalent clade Panoplosaurinae, named in 1929 by Franz Nopcsa, but was not significantly used until Robert Bakker reused the name in 1988, alongside the new clades Edmontoniinae and Edmontoniidae, which were considered to unite ''Pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panoplosaurini
Panoplosaurini (derived from ''Panoplosaurus'', "all shield reptile") is a clade of nodosaurid ankylosaurs from the Cretaceous of North America and South America. The group is defined as the largest clade containing ''Panoplosaurus mirus'', but not '' Nodosaurus textilis'' or '' Struthiosaurus austriacus'', and was named in 2021 by Madzia and colleagues for the group found in many previous analyses, both morphological and phylogenetic. Panoplosaurini includes not only the Late Cretaceous ''Panoplosaurus'', ''Denversaurus'' and ''Edmontonia'', but also the mid Cretaceous ''Animantarx'' and ''Texasetes'', as well as ''Patagopelta''. However, in the study describing it, its authors only placed it as a nodosaurine outside Panoplosaurini. The approximately equivalent clade Panoplosaurinae, named in 1929 by Franz Nopcsa, but was not significantly used until Robert Bakker reused the name in 1988, alongside the new clades Edmontoniinae and Edmontoniidae, which were considered to unite ''Pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinosaur Park Formation
The Dinosaur Park Formation is the uppermost member of the Belly River Group (also known as the Judith River Group), a major geologic unit in southern Alberta. It was deposited during the Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous, between about 76.5 and 74.4 million years ago. It was deposited in alluvial and coastal plain environments, and it is bounded by the nonmarine Oldman Formation below it and the marine Bearpaw Formation above it.Eberth, D.A. 2005. The geology. In: Currie, P.J., and Koppelhus, E.B. (eds), Dinosaur Provincial Park: A Spectacular Ancient Ecosystem Revealed. Indiana University Press: Bloomington and Indianapolis, p.54-82. . The Dinosaur Park Formation contains dense concentrations of dinosaur skeletons, both articulated and disarticulated, which are often found with preserved remains of soft tissues. Remains of other animals such as fish, turtles, and crocodilians, as well as plant remains, are also abundant. The formation has been named after Dinosaur Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1919 In Paleontology
Expeditions, field work, and fossil discoveries * ''Summer:'' William Edmund Cutler resumed collecting dinosaur fossils in Dinosaur Provincial Park. One discovery was a disarticulated ceratopsian he identified as an "''Eoceratops''". He spent the remainder of the year excavating the specimen although his progress was hampered by illness and bad weather. Institutions and organizations Natural history museums Scientific organizations Scientific advances Paleoanthropology Paleobotany Evolutionary biology Exopaleontology Extinction research Micropaleontology Invertebrate paleozoology Trace fossils Vertebrate paleozoology Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Research techniques Fossil trade Law and politics Regulation of fossil collection, transport, or sale Fossil-related crime Official symbols Protected areas Ethics and practice Hoaxes Scandals Unethical practice People Births Awards and recognition Deaths Historiography a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodosauridae
Nodosauridae is a family of ankylosaurian dinosaurs, from the Late Jurassic to the Late Cretaceous period in what is now North America, South America, Europe, and Asia. Description Nodosaurids, like their close relatives the ankylosaurids, were heavily armored dinosaurs adorned with rows of bony armor nodules and spines (osteoderms), which were covered in keratin sheaths. All nodosaurids, like other ankylosaurians, were medium-sized to large, heavily built, quadrupedal, herbivorous dinosaurs, possessing small, leaf-shaped teeth. Unlike ankylosaurids, nodosaurids lacked mace-like tail clubs, instead having flexible tail tips. Many nodosaurids had spikes projecting outward from their shoulders. One particularly well-preserved nodosaurid "mummy", known as the Suncor nodosaur (''Borealopelta markmitchelli''), preserved a nearly complete set of armor in life position, as well as the keratin covering and mineralized remains of the underlying skin, which indicate reddish dorsal pigmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawrence Lambe
Lawrence Morris Lambe (August 27, 1863 – March 12, 1919) was a Canadian geologist, palaeontologist, and ecologist from the Geological Survey of Canada (GSC). His published work, describing the diverse and plentiful dinosaur discoveries from the fossil beds in Alberta, did much to bring dinosaurs into the public eye and helped usher in the ''Golden Age of Dinosaurs'' in the province. During this period, between the 1880s and World War I, dinosaur hunters from all over the world converged on Alberta. ''Lambeosaurus'', a well-known hadrosaur, was named after him as a tribute, in 1923. In addition to paleontology, Lambe discovered a number of invertebrate species ranging from Canada to the Pacific Northwest. Lambe's contemporary discoveries were published in works such as ''Sponges From the Atlantic Coast of Canada'' and ''Catalogue of the recent marine sponges of Canada and Alaska''. Early life and education Lambe was born in Montreal on August 27, 1863. Lambe studied at the Royal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaurs
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
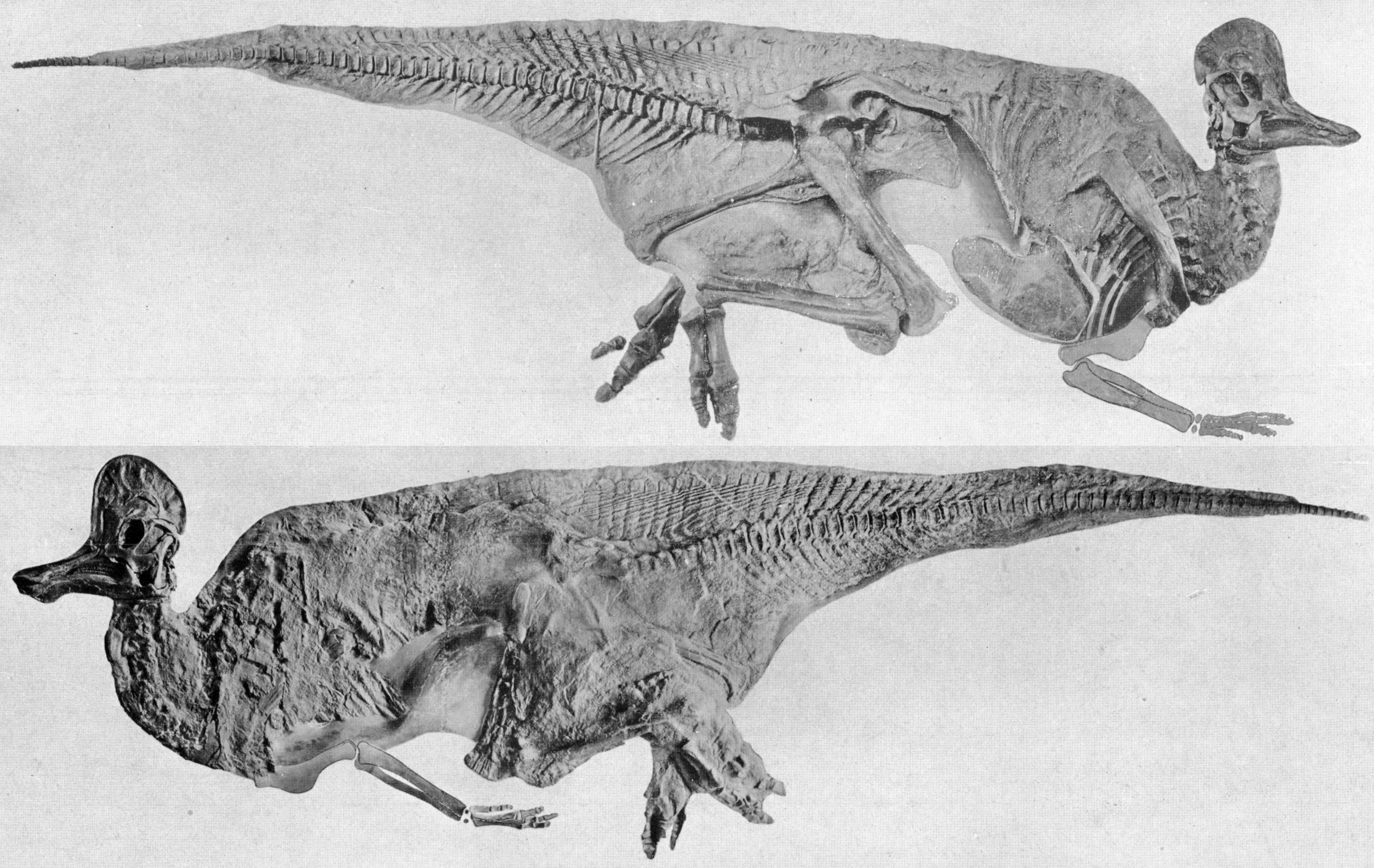
Corythosaurus
''Corythosaurus'' (; ) is a genus of hadrosaurid "duck-billed" dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous Period (geology), Period, about 77–75.7 million years ago. It lived in what is now North America. Its name means "helmet lizard", derived from Ancient Greek, Greek κόρυς. It was named and described in 1914 by Barnum Brown. ''Corythosaurus'' is now thought to be a Lambeosaurinae, lambeosaurine, related to ''Nipponosaurus'', ''Velafrons'', ''Hypacrosaurus'', and ''Olorotitan''. ''Corythosaurus'' has an estimated length of , and has a skull, including the crest, that is tall. ''Corythosaurus'' is known from many complete specimens, including the nearly complete holotype found by Brown in 1911. The holotype skeleton is only missing the last section of the tail, and part of the forelimbs, but was preserved with impressions of polygonal scales. ''Corythosaurus'' is known from many skulls with tall crests. The crests resemble the crests of the cassowary and a Corinthian helmet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nodosaurus
''Nodosaurus'' (meaning "knobbed lizard") is a genus of herbivorous nodosaurid ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous, the fossils of which are found exclusively in the Frontier Formation in Wyoming. Description ''Nodosaurus'' grew up to roughly long and it was an ornithischian dinosaur with bony dermal plates covering the top of its body, and it may have had spikes along its side as well. The dermal plates were arranged in bands along its body, with narrow bands over the ribs alternating with wider plates in between. These wider plates were covered in regularly arranged bony nodules, which give the animal its scientific name. In 2010 Paul estimated its length at 6 meters (20 ft) and its weight at 3.5 tonnes (3.85 short tons). It had four short legs, five-toed feet, a short neck, and a long, stiff, clubless tail. The head was narrow, with a pointed snout, powerful jaws, and small teeth. It perhaps ate soft plants, as it would have been unable to chew tough, fib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosaur
Ankylosauria is a group of herbivorous dinosaurs of the order Ornithischia. It includes the great majority of dinosaurs with armor in the form of bony osteoderms, similar to turtles. Ankylosaurs were bulky quadrupeds, with short, powerful limbs. They are known to have first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and persisted until the end of the Cretaceous Period. The two main families of Ankylosaurs, Nodosauridae and Ankylosauridae are primarily known from the Northern Hemisphere, but the more basal Parankylosauria are known from southern Gondwana during the Cretaceous. Ankylosauria was first named by Henry Fairfield Osborn in 1923.Osborn, H. F. (1923). "Two Lower Cretaceous dinosaurs of Mongolia." ''American Museum Novitates'', 95: 1–1/ref> In the Linnaean classification system, the group is usually considered either a suborder or an infraorder. It is contained within the group Thyreophora, which also includes the stegosaurs, armored dinosaurs known for their combination of plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hindlimb
A hindlimb or back limb is one of the paired articulated appendages (limbs) attached on the caudal ( posterior) end of a terrestrial tetrapod vertebrate's torso.http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/hind%20limb, Merriam Webster Dictionary-Hindlimb With reference to quadrupeds, the term hindleg or back leg is often used instead. In bipedal animals with an upright posture (e.g. humans and some primates), the term lower limb is often used. Location It is located on the limb of an animal. Hindlimbs are present in a large number of quadrupeds. Though it is a posterior limb, it can cause lameness in some animals. The way of walking through hindlimbs are called bipedalism. Benefits of hindlimbs Hindlimbs are helpful in many ways, some examples are: Frogs Frogs can easily adapt at the surroundings using hindlimbs. The main reason is it can jump high to easily escape to its predator and also to catch prey. It can perform some tricks using the hindlimbs such as the somersault and h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(18147021802).jpg)