|
Pameridea Marlothi
''Pameridea'' is a genus of insects comprising two species, ''P. roridulae'' and ''P. marlothii'', that live in symbiosis, symbiotic relationships with carnivorous plants in the genus ''Roridula''. ''Pameridea marlothii'' only occurs on ''R. dentata'', while ''P. roridulae'' exists on both ''R. dentata'' and ''R. gorgonias''. Life cycle ''Pameridea roridulae'' can only live on ''Roridula'', where it feeds on insects that the plant captures with its resin-tipped trichomes.Voigt, D. and Gorb S. (2008) An insect trap as habitat: cohesion-failure mechanism prevents adhesion of ''Pameridea roridulae'' bugs to the sticky surface of the plant ''Roridula gorgonias''. The Journal of Experimental Biology 211, 2647-2657. After devouring the captured arthropods, bugs in the genus excrete waste, which the plant absorbs using glands, making it an example of symbiosis. ''Pameridea'' also mates while on the plant, and hatchlings continue to live on the ''Roridula'' plant. Conservation status Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pameridea Marlothi
''Pameridea'' is a genus of insects comprising two species, ''P. roridulae'' and ''P. marlothii'', that live in symbiosis, symbiotic relationships with carnivorous plants in the genus ''Roridula''. ''Pameridea marlothii'' only occurs on ''R. dentata'', while ''P. roridulae'' exists on both ''R. dentata'' and ''R. gorgonias''. Life cycle ''Pameridea roridulae'' can only live on ''Roridula'', where it feeds on insects that the plant captures with its resin-tipped trichomes.Voigt, D. and Gorb S. (2008) An insect trap as habitat: cohesion-failure mechanism prevents adhesion of ''Pameridea roridulae'' bugs to the sticky surface of the plant ''Roridula gorgonias''. The Journal of Experimental Biology 211, 2647-2657. After devouring the captured arthropods, bugs in the genus excrete waste, which the plant absorbs using glands, making it an example of symbiosis. ''Pameridea'' also mates while on the plant, and hatchlings continue to live on the ''Roridula'' plant. Conservation status Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pameridea
''Pameridea'' is a genus of insects comprising two species, ''P. roridulae'' and ''P. marlothii'', that live in symbiotic relationships with carnivorous plants in the genus ''Roridula''. ''Pameridea marlothii'' only occurs on ''R. dentata'', while ''P. roridulae'' exists on both ''R. dentata'' and ''R. gorgonias''. Life cycle ''Pameridea roridulae'' can only live on ''Roridula'', where it feeds on insects that the plant captures with its resin-tipped trichomes.Voigt, D. and Gorb S. (2008) An insect trap as habitat: cohesion-failure mechanism prevents adhesion of ''Pameridea roridulae'' bugs to the sticky surface of the plant ''Roridula gorgonias''. The Journal of Experimental Biology 211, 2647-2657. After devouring the captured arthropods, bugs in the genus excrete waste, which the plant absorbs using glands, making it an example of symbiosis. ''Pameridea'' also mates while on the plant, and hatchlings continue to live on the ''Roridula'' plant. Conservation status Since it is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
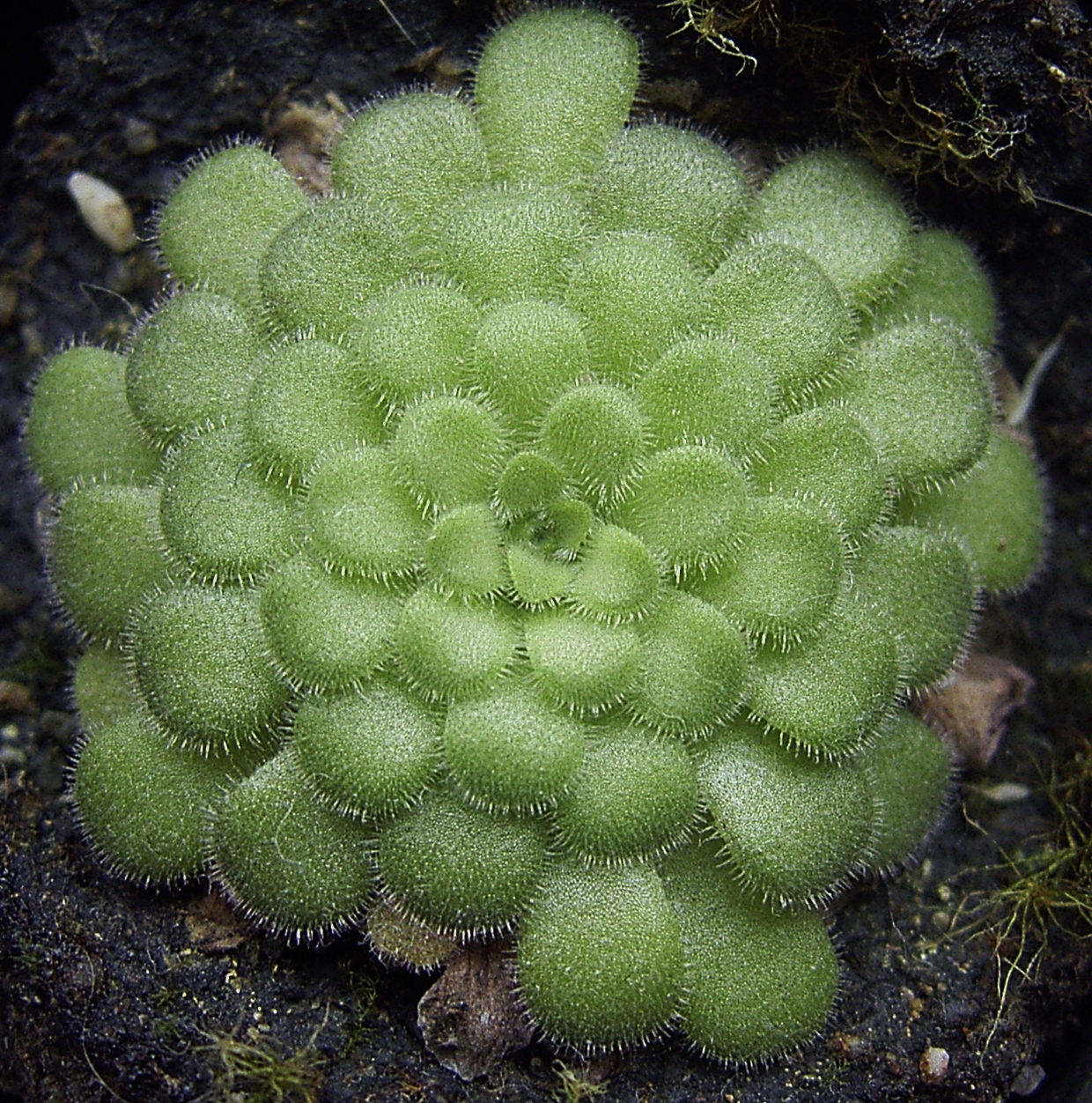
Darlingtonia Californica
''Darlingtonia californica'' , also called the California pitcher plant, cobra lily, or cobra plant, is a species of carnivorous plant. It is the sole member of the genus ''Darlingtonia'' in the family Sarraceniaceae. This pitcher plant is native to Northern California and Oregon, US, growing in bogs and seeps with cold running water usually on serpentine soils. This plant is designated as uncommon due to its rarity in the field. The name "cobra lily" stems from the resemblance of its tubular leaves to a rearing cobra, complete with a forked leaf – ranging from yellow to purplish-green – that resemble fangs or a serpent's tongue. The plant was discovered in 1841 by the botanist William D. Brackenridge at Mount Shasta. In 1853 it was described by John Torrey, who named the genus ''Darlingtonia'' after the Philadelphian botanist William Darlington (1782–1863). In cultivation in the UK this plant has gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit. Biology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthropods
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a Segmentation (biology), segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and Arthropod cuticle, cuticle made of chitin, often Mineralization (biology), mineralised with calcium carbonate. The arthropod body plan consists of segments, each with a pair of appendages. Arthropods are bilaterally symmetrical and their body possesses an exoskeleton, external skeleton. In order to keep growing, they must go through stages of moulting, a process by which they shed their exoskeleton to reveal a new one. Some species have wings. They are an extremely diverse group, with up to 10 million species. The haemocoel, an arthropod's internal cavity, through which its haemolymph – analogue of blood – circulates, accommodates its interior Organ (anatomy), organs; it has an open circulatory system. Like their exteriors, the internal or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarracenia Purpurea
''Sarracenia purpurea'', the purple pitcher plant, northern pitcher plant, turtle socks, or side-saddle flower, is a carnivorous plant in the family Sarraceniaceae. Description Like other species of ''Sarracenia'', ''S. purpurea'' obtains most of its nutrients through prey capture. However, prey acquisition is said to be inefficient, with less than 1% of the visiting prey captured within the pitcher. Even so, anecdotal evidence by growers often shows that pitchers quickly fill up with prey during the warm summer months. Prey fall into the pitcher and drown in the rainwater that collects in the base of each leaf. Prey items, such as flies, ants, spiders, and even moths or hornets, are then digested by an invertebrate community, made up mostly by the mosquito ''Wyeomyia smithii'' and the midge ''Metriocnemus knabi''. The relationship between ''W. smithii'' and ''S. purpurea'' is an example of commensalism. ''S. purpurea'' also traps juvenile spotted salamanders with enough reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protocarnivorous
A protocarnivorous plant (sometimes also paracarnivorous, subcarnivorous, or borderline carnivore), according to some definitions, traps and kills insects or other animals but lacks the ability to either directly digest or absorb nutrients from its prey like a carnivorous plant. The morphological adaptations such as sticky trichomes or pitfall traps of protocarnivorous plants parallel the trap structures of confirmed carnivorous plants. Some authors prefer the term "protocarnivorous" because it implies that these plants are on the evolutionary path to true carnivory, whereas others oppose the term for the same reason. The same problem arises with "subcarnivorous". Donald Schnell, author of the book ''Carnivorous Plants of the United States and Canada'', prefers the term "paracarnivorous" for a less rigid definition of carnivory that can include many of the possible carnivorous plants.Schnell, 2002 The demarcation between carnivorous and protocarnivorous is blurred by the lack of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nepenthes
''Nepenthes'' () is a genus of carnivorous plants, also known as tropical pitcher plants, or monkey cups, in the monotypic family Nepenthaceae. The genus includes about 170 species, and numerous natural and many cultivated hybrids. They are mostly liana-forming plants of the Old World tropics, ranging from South China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines; westward to Madagascar (two species) and the Seychelles (one); southward to Australia (four) and New Caledonia (one); and northward to India (one) and Sri Lanka (one). The greatest diversity occurs on Borneo, Sumatra, and the Philippines, with many endemic species. Many are plants of hot, humid, lowland areas, but the majority are tropical montane plants, receiving warm days but cool to cold, humid nights year round. A few are considered tropical alpine, with cool days and nights near freezing. The name "monkey cups" refers to the fact that monkeys were once thought to drink rainwater from the pitchers. Description ''N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinguicula
''Pinguicula'', commonly known as the butterworts, is a genus of carnivorous flowering plants in the family Lentibulariaceae. They use sticky, glandular leaves to lure, trap, and digest insects in order to supplement the poor mineral nutrition they obtain from the environment. Of the roughly 80 currently known species, 13 are native to Europe, 9 to North America, and some to northern Asia. The largest number of species is in South and Central America. Etymology The name ''Pinguicula'' is derived from a term coined by Conrad Gesner, who in his 1561 work entitled ''Horti Germaniae'' commented on the glistening leaves: ''"propter pinguia et tenera folia…"'' (Latin ''pinguis'', "fat"). The common name "butterwort" reflects this characteristic. Characteristics The majority of ''Pinguicula'' are perennial plants. The only known annuals are ''P. sharpii'', ''P. takakii'', ''P. crenatiloba'', and ''P. pumila''. All species form stemless rosettes. Habitat Butterworts can be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drosera
''Drosera'', which is commonly known as the sundews, is one of the largest genus, genera of carnivorous plants, with at least 194 species. 2 volumes. These members of the family Droseraceae lure, capture, and digest insects using stalked mucilage, mucilaginous glands covering their leaf surfaces. The insects are used to supplement the poor mineral nutrition of the soil in which the plants grow. Various species, which vary greatly in size and form, are native to every continent except Antarctica.McPherson, S.R. 2008. ''Glistening Carnivores''. Redfern NaturalHistory Productions Ltd., Poole. Charles Darwin performed much of the early research into ''Drosera'', engaging in a long series of experiments with Drosera rotundifolia which were the first to confirm carnivory in plants. In an 1860 letter, Darwin wrote, “…at the present moment, I care more about ''Drosera'' than the origin of all the species in the world.” Both the botanical name (from the Ancient Greek, Greek δρ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionaea Muscipula
The Venus flytrap (''Dionaea muscipula'') is a carnivorous plant native to subtropical wetlands on the East Coast of the United States in North Carolina and South Carolina. It catches its prey—chiefly insects and arachnids—with a trapping structure formed by the terminal portion of each of the plant's leaves, which is triggered by tiny hairs (called "trigger hairs" or "sensitive hairs") on their inner surfaces. When an insect or spider crawling along the leaves contacts a hair, the trap prepares to close, snapping shut only if another contact occurs within approximately twenty seconds of the first strike. Triggers may occur with a tenth of a second of contact. The requirement of redundant triggering in this mechanism serves as a safeguard against wasting energy by trapping objects with no nutritional value, and the plant will only begin digestion after five more stimuli to ensure it has caught a live bug worthy of consumption. ''Dionaea'' is a monotypic genus closely relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Cultivation
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae exclude the fungi and some algae, as well as the prokaryotes (the archaea and bacteria). By one definition, plants form the clade Viridiplantae (Latin name for "green plants") which is sister of the Glaucophyta, and consists of the green algae and Embryophyta (land plants). The latter includes the flowering plants, conifers and other gymnosperms, ferns and their allies, hornworts, liverworts, and mosses. Most plants are multicellular organisms. Green plants obtain most of their energy from sunlight via photosynthesis by primary chloroplasts that are derived from endosymbiosis with cyanobacteria. Their chloroplasts contain chlorophylls a and b, which gives them their green color. Some plants are parasitic or mycotrophic and have lost the ability ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pameridea Roridulae
''Pameridea roridulae'' is a species of jumping tree bug in the family Miridae. It has a symbiotic relationship with ''Roridula ''Roridula'' (; from Latin ''roridus'' "dewy") is a genus of evergreen, insect-trapping shrubs, with two species, of about 1⅓–2 m (4–6⅔ ft). It is the only genus in the family Roridulaceae. It has thin, woody, shyly branching, upright, in ...'', where it feeds on trapped insects and its excretions are absorbed through the leaves of the ''Roridula'', giving the plant much needed nutrients and nitrogen. Juvenile ''P. roridulae'' also pollinate the plant. References Further reading * Miridae Articles created by Qbugbot Insects described in 1907 {{hemiptera-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |