 |
Paleostress Inversion
Paleostress inversion refers to the determination of paleostress history from evidence found in rocks, based on the principle that past tectonic stress should have left traces in the rocks. Such relationships have been discovered from field studies for years: qualitative and quantitative analyses of deformation structures are useful for understanding the distribution and transformation of paleostress fields controlled by sequential tectonic events. Deformation ranges from microscopic to regional scale, and from brittle to ductile behaviour, depending on the rheology of the rock, orientation and magnitude of the stress etc. Therefore, detailed observations in outcrops, as well as in thin sections, are important in reconstructing the paleostress trajectories. Inversions require assumptions in order to simplify the complex geological processes. The stress field is assumed to be spatially uniform for a faulted rock mass and temporally stable over the concerned period of time when fau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Paleostress
Paleostress is a term used in geology (specifically in the fields of structural geology and tectonics) to indicate mechanical stress that has affected rock formations in the geological past. In practice, a paleostress tensor may be quantified based on the measurement of certain geological structures (e.g. faults), whose specific geometries and spatial organization are theoretically linked to the parameters of the tensor (see paleostress inversion). The latter are quantified through inversion of the structures measured in the field (or potentially on rock samples in the lab). Paleostress is a subset of mechanical stress within geology. Variations in stress fields within the Earth's crust can result in a variety of mechanical responses: *Microscopic: :*Crystal deformation, including twinning, :*Pressure solution :*Microfractures, :*Aligned fluid inclusions. *Macroscopic: :*Folding :*Fracturing :*Faulting (fracturing accompanied by offset of rock bodies on either side of the fract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Stress Vectors
Stress may refer to: Science and medicine * Stress (biology), an organism's response to a stressor such as an environmental condition * Stress (linguistics), relative emphasis or prominence given to a syllable in a word, or to a word in a phrase or sentence * Stress (mechanics), the internal forces that neighboring particles of a continuous material exert on each other * Occupational stress, stress related to one's job * Psychological stress, a feeling of strain and pressure * Surgical stress, systemic response to surgical injury Arts, entertainment, and media Music Groups and musicians * Stress (Brazilian band), a Brazilian heavy metal band * Stress (British band), a British rock band * Stress (pop rock band), an early 1980s melodic rock band from San Diego * Stress (musician) (born 1977), hip hop singer from Switzerland * Stress (record producer) (born 1979), artistic name of Can Canatan, Swedish musician and record producer Albums * ''Stress'' (Anonymus album), 1997 * ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Burgers Vector
In materials science, the Burgers vector, named after Dutch physicist Jan Burgers, is a vector, often denoted as , that represents the magnitude and direction of the lattice distortion resulting from a dislocation in a crystal lattice. The vector's magnitude and direction is best understood when the dislocation-bearing crystal structure is first visualized ''without'' the dislocation, that is, the ''perfect'' crystal structure. In this perfect crystal structure, a rectangle whose lengths and widths are integer multiples of (the unit cell edge length) is drawn ''encompassing'' the site of the original dislocation's origin. Once this encompassing rectangle is drawn, the dislocation can be introduced. This dislocation will have the effect of deforming, not only the perfect crystal structure, but the rectangle as well. The said rectangle could have one of its sides disjoined from the perpendicular side, severing the connection of the length and width line segments of the rectangle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Flow Stress
In materials science the flow stress, typically denoted as Yf (or \sigma_\text), is defined as the instantaneous value of stress required to continue plastically deforming a material - to keep it flowing. It is most commonly, though not exclusively, used in reference to metals. On a stress-strain curve, the flow stress can be found anywhere within the plastic regime; more explicitly, a flow stress can be found for any value of strain between and including yield point (\sigma_\text) and excluding fracture (\sigma_\text): \sigma_\text \leq Y_\text < \sigma_\text. The flow stress changes as deformation proceeds and usually increases as strain accumulates due to work hardening, although the flow stress could decrease due to any recovery process. In |
|
|
Grain Boundary
In materials science, a grain boundary is the interface between two grains, or crystallites, in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundaries are two-dimensional defects in the crystal structure, and tend to decrease the electrical and thermal conductivity of the material. Most grain boundaries are preferred sites for the onset of corrosion and for the precipitation of new phases from the solid. They are also important to many of the mechanisms of creep. On the other hand, grain boundaries disrupt the motion of dislocations through a material, so reducing crystallite size is a common way to improve mechanical strength, as described by the Hall–Petch relationship. High and low angle boundaries It is convenient to categorize grain boundaries according to the extent of misorientation between the two grains. ''Low-angle grain boundaries'' (''LAGB'') or ''subgrain boundaries'' are those with a misorientation less than about 15 degrees. Generally speaking they are composed o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Dislocation
In materials science, a dislocation or Taylor's dislocation is a linear crystallographic defect or irregularity within a crystal structure that contains an abrupt change in the arrangement of atoms. The movement of dislocations allow atoms to slide over each other at low stress levels and is known as ''glide'' or slip. The crystalline order is restored on either side of a ''glide dislocation'' but the atoms on one side have moved by one position. The crystalline order is not fully restored with a ''partial dislocation''. A dislocation defines the boundary between ''slipped'' and ''unslipped'' regions of material and as a result, must either form a complete loop, intersect other dislocations or defects, or extend to the edges of the crystal. A dislocation can be characterised by the distance and direction of movement it causes to atoms which is defined by the Burgers vector. Plastic deformation of a material occurs by the creation and movement of many dislocations. The number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
BLG Sub '', a genealogical publication
{{disambiguation ...
BLG may refer to: * Former ISO 639-3 code for Balau, a dialect of the Iban language. * Barlow Lyde & Gilbert, a British law firm * Belaga Airport, Sarawak, Malaysia * Beluga Airport, Alaska * Beta-lactoglobulin * Bilibili Gaming, a Chinese esports franchise * Borden Ladner Gervais, a Canadian law firm * ''Burke's Landed Gentry ''Burke's Landed Gentry'' (originally titled ''Burke's Commoners'') is a reference work listing families in Great Britain and Ireland who have owned rural estates of some size. The work has been in existence from the first half of the 19th cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Grain Growth
In materials science, grain growth is the increase in size of grains (crystallites) in a material at high temperature. This occurs when recovery and recrystallisation are complete and further reduction in the internal energy can only be achieved by reducing the total area of grain boundary. The term is commonly used in metallurgy but is also used in reference to ceramics and minerals. The behaviors of grain growth is analogous to the coarsening behaviors of grains, which implied that both of grain growth and coarsening may be dominated by the same physical mechanism. Importance of grain growth The practical performances of polycrystalline materials are strongly affected by the formed microstructure inside, which is mostly dominated by grain growth behaviors. For example, most materials exhibit the Hall–Petch effect at room-temperature and so display a higher yield stress when the grain size is reduced (assuming abnormal grain growth has not taken place). At high temperatures ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
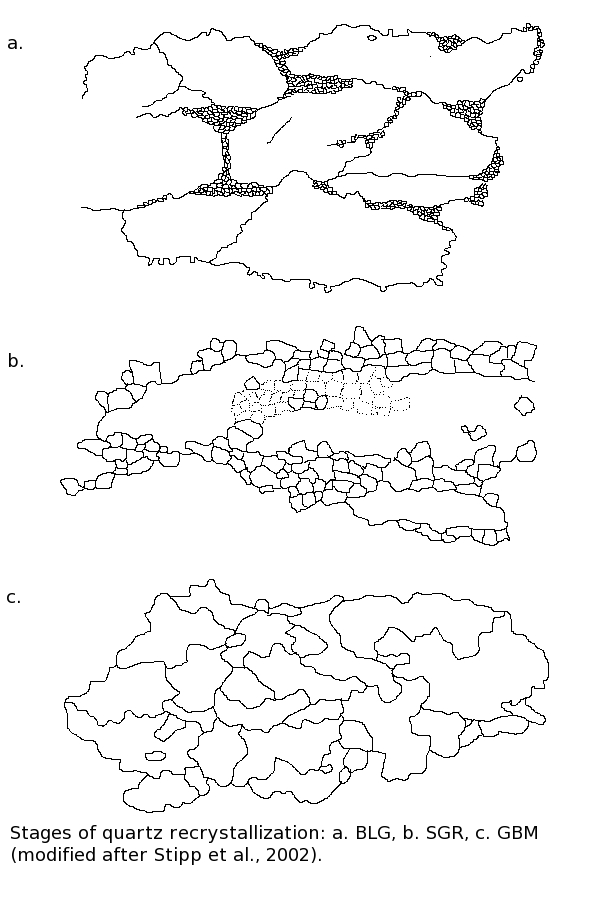 |
Dynamic Quartz Recrystallization
Quartz is the most abundant single mineral in the earth's crust (although behind the feldspar group when taken collectively), and as such is present in a very large proportion of rocks both as primary crystals and as detrital grains in sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Dynamic recrystallization is a process of crystal regrowth under conditions of stress and elevated temperature, commonly applied in the fields of metallurgy and materials science. Dynamic quartz recrystallization happens in a relatively predictable way with relation to temperature, and given its abundance quartz recrystallization can be used to easily determine relative temperature profiles, for example in orogenic belts or near intrusions. Mechanisms of recrystallization Previous research has outlined several dislocation creep regimes present in experimental conditions. Two main mechanisms for altering grain boundaries have been defined. The first is the process by which quartz softens as temperature increases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Upper Mantle (Earth)
The upper mantle of Earth is a very thick layer of rock inside the planet, which begins just beneath the crust (at about under the oceans and about under the continents) and ends at the top of the lower mantle at . Temperatures range from approximately at the upper boundary with the crust to approximately at the boundary with the lower mantle. Upper mantle material that has come up onto the surface comprises about 55% olivine, 35% pyroxene, and 5 to 10% of calcium oxide and aluminum oxide minerals such as plagioclase, spinel, or garnet, depending upon depth. Seismic structure The density profile through Earth is determined by the velocity of seismic waves. Density increases progressively in each layer, largely due to compression of the rock at increased depths. Abrupt changes in density occur where the material composition changes. The upper mantle begins just beneath the crust and ends at the top of the lower mantle. The upper mantle causes the tectonic plates to mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Grain Boundaries
In materials science, a grain boundary is the interface between two grains, or crystallites, in a polycrystalline material. Grain boundaries are two-dimensional defects in the crystal structure, and tend to decrease the electrical and thermal conductivity of the material. Most grain boundaries are preferred sites for the onset of corrosion and for the precipitation of new phases from the solid. They are also important to many of the mechanisms of creep. On the other hand, grain boundaries disrupt the motion of dislocations through a material, so reducing crystallite size is a common way to improve mechanical strength, as described by the Hall–Petch relationship. High and low angle boundaries It is convenient to categorize grain boundaries according to the extent of misorientation between the two grains. ''Low-angle grain boundaries'' (''LAGB'') or ''subgrain boundaries'' are those with a misorientation less than about 15 degrees. Generally speaking they are composed of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Deformation (mechanics)
In physics, deformation is the continuum mechanics transformation of a body from a ''reference'' configuration to a ''current'' configuration. A configuration is a set containing the positions of all particles of the body. A deformation can occur because of external loads, intrinsic activity (e.g. muscle contraction), body forces (such as gravity or electromagnetic forces), or changes in temperature, moisture content, or chemical reactions, etc. Strain is related to deformation in terms of ''relative'' displacement of particles in the body that excludes rigid-body motions. Different equivalent choices may be made for the expression of a strain field depending on whether it is defined with respect to the initial or the final configuration of the body and on whether the metric tensor or its dual is considered. In a continuous body, a deformation field results from a stress field due to applied forces or because of some changes in the temperature field of the body. The relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |