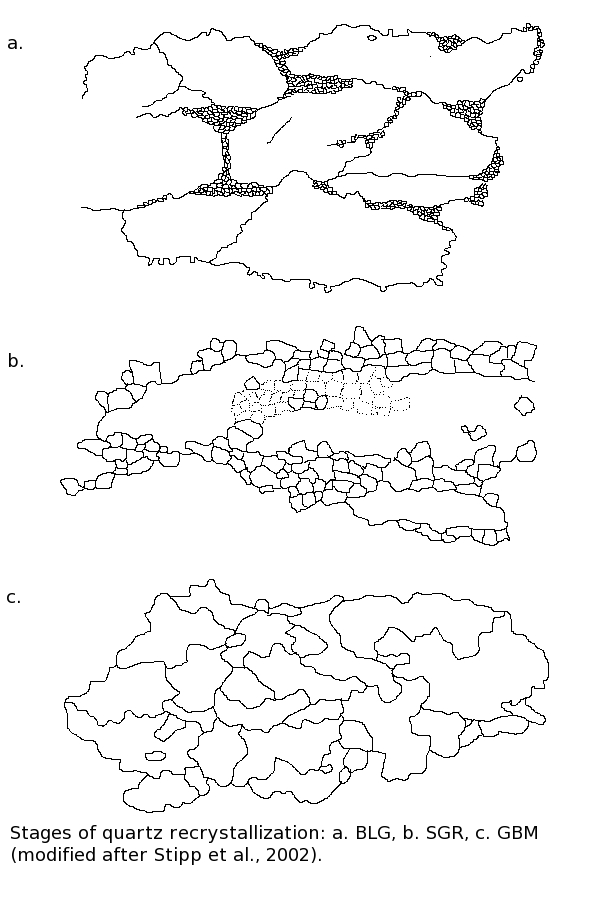
|
Dynamic Quartz Recrystallization
Quartz is the most abundant single mineral in the earth's crust (although behind the feldspar group when taken collectively), and as such is present in a very large proportion of rocks both as primary crystals and as detrital grains in sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. Dynamic recrystallization is a process of crystal regrowth under conditions of stress and elevated temperature, commonly applied in the fields of metallurgy and materials science. Dynamic quartz recrystallization happens in a relatively predictable way with relation to temperature, and given its abundance quartz recrystallization can be used to easily determine relative temperature profiles, for example in orogenic belts or near intrusions. Mechanisms of recrystallization Previous research has outlined several dislocation creep regimes present in experimental conditions. Two main mechanisms for altering grain boundaries have been defined. The first is the process by which quartz softens as temperature increases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stages Of Recrystallization
Stage or stages may refer to: Acting * Stage (theatre), a space for the performance of theatrical productions * Theatre, a branch of the performing arts, often referred to as "the stage" * ''The Stage'', a weekly British theatre newspaper * Stages Repertory Theatre, a theatre company in Houston, Texas Music * Stage, an American band featuring Ryan Star * ''Stage'', a 2002 book and DVD documenting Britney Spears' Dream Within a Dream Tour Albums * ''Stage'' (David Bowie album), 1978 * ''Stage'' (Great White album), 1995 * ''Stage'' (Keller Williams album), 2004 * ''Stage'', by Mónica Naranjo, 2009 * ''The Stage'' (album), by Avenged Sevenfold, or the title song (see below), 2016 * ''Stages'' (Cassadee Pope album), 2019 * ''Stages'' (Elaine Paige album), 1983 * ''Stages'' (Eric Clapton album), 1993 * ''Stages'' (Jimi Hendrix album), 1991 * ''Stages'' (Josh Groban album), 2015 * ''Stages'' (Melanie C album), 2012 * ''Stages'' (Triumph album), 1985 * ''Stages'' (Vede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strain Rate
In materials science, strain rate is the change in strain ( deformation) of a material with respect to time. The strain rate at some point within the material measures the rate at which the distances of adjacent parcels of the material change with time in the neighborhood of that point. It comprises both the rate at which the material is expanding or shrinking (expansion rate), and also the rate at which it is being deformed by progressive shearing without changing its volume ( shear rate). It is zero if these distances do not change, as happens when all particles in some region are moving with the same velocity (same speed and direction) and/or rotating with the same angular velocity, as if that part of the medium were a rigid body. The strain rate is a concept of materials science and continuum mechanics that plays an essential role in the physics of fluids and deformable solids. In an isotropic Newtonian fluid, in particular, the viscous stress is a linear function of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Solution
In structural geology and diagenesis, pressure solution or pressure dissolution is a deformation mechanism that involves the dissolution of minerals at grain-to-grain contacts into an aqueous pore fluid in areas of relatively high stress and either deposition in regions of relatively low stress within the same rock or their complete removal from the rock within the fluid. It is an example of diffusive mass transfer. The detailed kinetics of the process was reviewed by Rutter (1976), and since then such kinetics has been used in many applications in earth sciences. Occurrence Evidence for pressure solution has been described from sedimentary rocks that have only been affected by compaction. The most common example of this is bedding plane parallel stylolites developed in carbonates. In a tectonic manner, deformed rocks also show evidence of pressure solution including stylolites at a high angle to bedding. The process is also thought to be an important part of the developme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neomorphism
Neomorphism refers to the wet metamorphic process in which diagenetic alterations systematically transform minerals into either polymorphs or crystalline structures that are structurally identical to the rock(s) from which they developed. Coined by the late Robert L. Folk, ''neomorphism'' encompasses the functions of both recrystallization and inversion, which are geological processes that deal primarily with rock reformation. The neomorphic process, as it relates to geology and petrography, is one of the many major processes that sustain both carbonate minerals and limestone. Neomorphism is largely held accountable for the metastability of aragonite and magnesium-rich calcite, and when conditions permit, neomorphic reactions and interactions can result in texture loss and/or feature deformation of affected rock formations. Types of neomorphism Recrystallization The term "recrystallization" broadly refers to the many metamorphic processes that change the size and/or shape of cry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgrain Rotation Recrystallization
In metallurgy, materials science and structural geology, subgrain rotation recrystallization is recognized as an important mechanism for dynamic recrystallisation. It involves the rotation of initially low-angle sub-grain boundaries until the mismatch between the crystal lattices across the boundary is sufficient for them to be regarded as grain boundaries. This mechanism has been recognized in many minerals (including quartz, calcite, olivine, pyroxenes, micas, feldspars, halite, garnets and zircons) and in metals (various magnesium, aluminium and nickel alloys).Microtectonics by C.W.Passchier and R.A.J.Trouw, 2nd rev. and enlarged ed., 2005, XVI, 366 p., 322 illus., with CDEarth Structure: an introduction to structural geology and tectonics, B.A Van Der Pluijm & S. Marshak, 2nd edition, 2004, 656 p. Structure In metals and minerals, grains are ordered structures in different crystal orientations. Subgrains are defined as grains that are oriented at a BCC/Hexagonal crystal fam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tectonic compression within orogenic belts. Pure quartzite is usually white to grey, though quartzites often occur in various shades of pink and red due to varying amounts of hematite. Other colors, such as yellow, green, blue and orange, are due to other minerals. The term ''quartzite'' is also sometimes used for very hard but unmetamorphosed sandstones that are composed of quartz grains thoroughly cemented with additional quartz. Such sedimentary rock has come to be described as orthoquartzite to distinguish it from metamorphic quartzite, which is sometimes called metaquartzite to emphasize its metamorphic origins. Quartzite is very resistant to chemical weathering and often forms ridges and resistant hilltops. The nearly pure silica co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Undulose Extinction
Undulose extinction or undulatory extinction is a geological term referring to the type of extinction that occurs in certain minerals when examined in thin section under cross polarized light. As the microscope stage is rotated, individual mineral grains appear black when the polarization due to the mineral prevents any light from passing through. If a mineral is deformed plastically by dislocation processes without recovery, strain builds up within the crystal lattice causing it to warp. This means that different parts of a crystal reach extinction at slightly different angles, giving the crystal an irregular, mottled look. Undulose extinction is very common in quartz, so much so that it is often used as a diagnostic feature of that mineral, and feldspar Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shear Stress
Shear stress, often denoted by (Greek: tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross section. It arises from the shear force, the component of force vector parallel to the material cross section. '' Normal stress'', on the other hand, arises from the force vector component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts. General shear stress The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area.: : \tau = , where: : = the shear stress; : = the force applied; : = the cross-sectional area of material with area parallel to the applied force vector. Other forms Wall shear stress Wall shear stress expresses the retarding force (per unit area) from a wall in the layers of a fluid flowing next to the wall. It is defined as: \tau_w:=\mu\left(\frac\right)_ Where \mu is the dynamic viscosity, u the flow velocity and y the distance from the wall. It is used, for example, in the description of arterial blood flow in which case which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |