|
Palaeoloxodon Falconeri
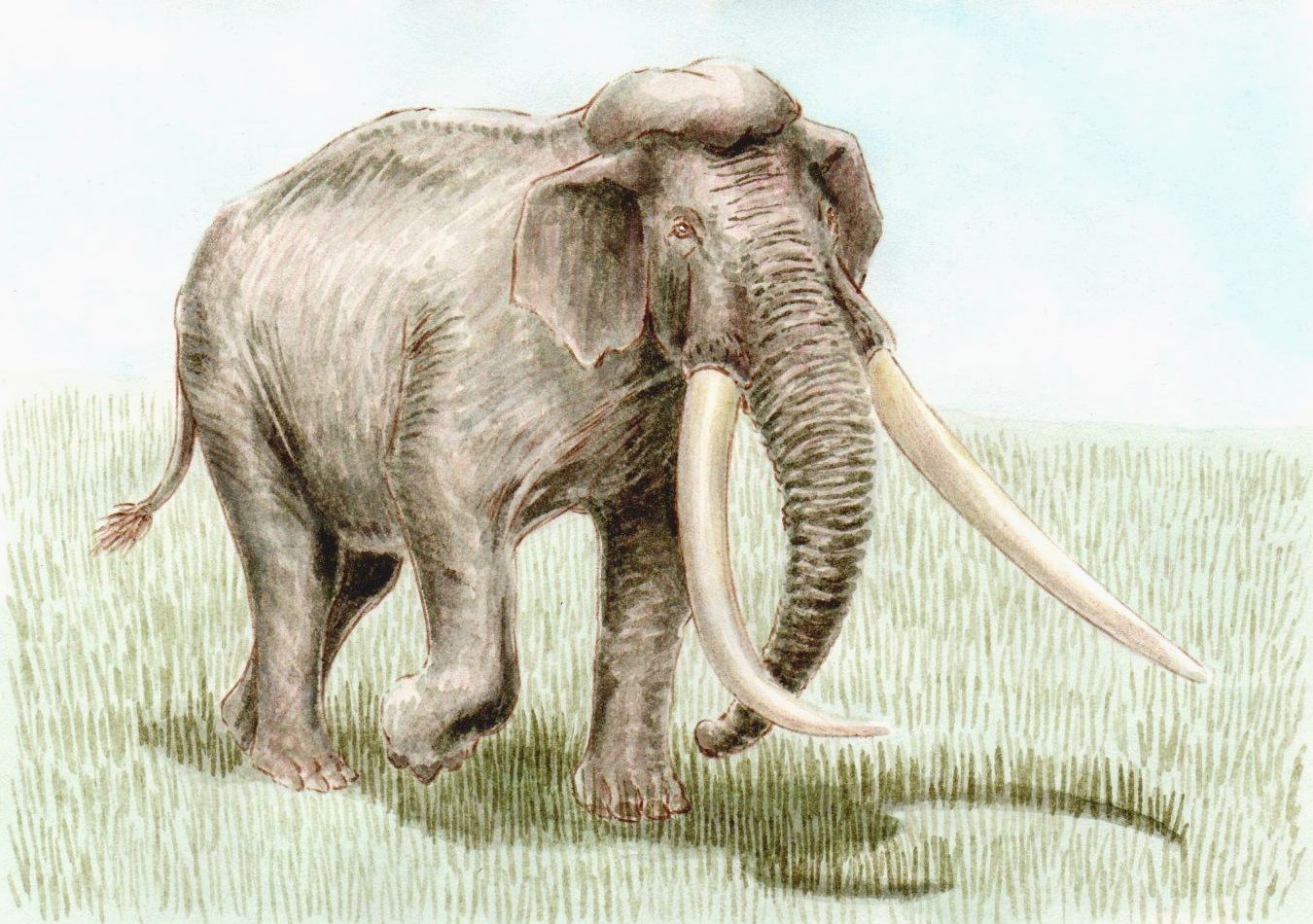
''Palaeoloxodon falconeri'', also known as the pygmy elephant, Maltese pygmy elephant, or Sicilian dwarf elephant, is an extinct Siculo- Maltese species of elephant that was derived from the straight-tusked elephant. It is amongst the smallest of all dwarf elephants. Chronology ''Palaeoloxodon'' ''falconeri'' derives from the 4 metre tall straight-tusked elephant (''P''. ''antiquus''), which arrived in Europe approximately 800,000 years ago. The oldest radiometrically dated fossils of ''Palaeoloxodon'' on Sicily date to around 500,000 years ago while the ones found in Għar Dalam on Malta date to around 450,000 years ago. ''P. falconeris ancestors most likely reached Sicily from the Italian mainland, likely via a series of islands that now form part of the southern Calabrian peninsula. The chronology of the species compared to that of the larger endemic species of ''Palaeoloxodon'' on Sicily, the tall '' Palaeoloxodon mnaidriensis'', is somewhat uncertain. It is generally thou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pleistocene
The Chibanian, widely known by its previous designation of Middle Pleistocene, is an age in the international geologic timescale or a stage in chronostratigraphy, being a division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. The Chibanian name was officially ratified in January 2020. It is currently estimated to span the time between 0.770 Ma (770,000 years ago) and 0.126 Ma (126,000 years ago), also expressed as 770–126 ka. It includes the transition in palaeoanthropology from the Lower to the Middle Palaeolithic over 300 ka. The Chibanian is preceded by the Calabrian and succeeded by the proposed Tarantian. The beginning of the Chibanian is the Brunhes–Matuyama reversal, when the Earth's magnetic field last underwent reversal. It ends with the onset of the Eemian interglacial period (Marine Isotope Stage 5). The term Middle Pleistocene was in use as a provisional or "quasi-formal" designation by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS). W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1867
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Species
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Proboscideans
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaeoloxodon
''Palaeoloxodon'' is an extinct genus of elephant. The genus originated in Africa during the Pliocene era, and expanded into Eurasia during the Pleistocene era. The genus contains some of the largest known species of elephants, over four metres tall at the shoulders, including the European straight-tusked elephant (''Palaeoloxodon antiquus''), and the southern Asian ''Palaeoloxodon namadicus'', the latter of which was possibly the Largest land mammal, largest known land mammal based on fragmentary remains, but this requires proper reexamination. In contrast, the genus also contains many species of Dwarf elephant, dwarf elephants that evolved via insular dwarfism on islands in the Mediterranean, some only a metre in height, making them the smallest elephants known. The genus has a long and complex taxonomic history, and at various times, it has been considered to belong to ''Loxodonta'' or ''Elephas'', but today is usually considered a valid and separate genus in its own right. Tax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Elephant
Dwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes (around ) in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example of insular dwarfism, the phenomenon whereby large terrestrial vertebrates (usually mammals) that colonize islands evolve dwarf forms, a phenomenon attributed to adaptation to resource-poor environments and selection for early maturation and reproduction. Some modern populations of Asian elephants have also undergone size reduction on islands to a lesser degree, resulting in populations of pygmy elephants. Fossil remains of dwarf elephants have been found on the Mediterranean islands of Cyprus, Malta (at Għar Dalam), Crete (in Chania at Vamos, Stylos and in a now-underwater cave on the coast), Sicily, Sardinia, the Cyclades Islands and the Dodecanese Islands. Other islands where dwarf ''Stegodon'' have been found are Sulawesi, Flores, Ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trento
Trento ( or ; Ladin and lmo, Trent; german: Trient ; cim, Tria; , ), also anglicized as Trent, is a city on the Adige River in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol in Italy. It is the capital of the autonomous province of Trento. In the 16th century, the city was the location of the Council of Trent. Formerly part of Austria and Austria-Hungary, it was annexed by Italy in 1919. With 118,142 inhabitants, Trento is the third largest city in the Alps and second largest in the historical region of Tyrol. Trento is an educational, scientific, financial and political centre in Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol, in Tyrol and Northern Italy in general. The city contains a picturesque Medieval and Renaissance historic centre, with ancient buildings such as Trento Cathedral and the Castello del Buonconsiglio. Together with other Alpine towns Trento engages in the Alpine Town of the Year Association for the implementation of the Alpine Convention to achieve sustainable development in the Alpin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MUSE - Science Museum
The Museo delle Scienze (MUSE) is a science museum in Trento, Italy. The museum was designed by architect Renzo Piano Renzo Piano (; born 14 September 1937) is an Italian architect. His notable buildings include the Centre Georges Pompidou in Paris (with Richard Rogers, 1977), The Shard in London (2012), the Whitney Museum of American Art in New York City ( ... and opened in 2013. References Science museums in Italy {{Italy-museum-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Museo Civico Di Storia Naturale Di Milano
The Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano (Milan Natural History Museum) is a museum in Milan, Italy. It was founded in 1838 when naturalist Giuseppe de Cristoforis donated his collections to the city. Its first director was Giorgio Jan. The Museum is located within a 19th-century building in the Indro Montanelli Garden, near the historic city gate of Porta Venezia. The structure was built between 1888 and 1893 in Neo-Romanesque style with Gothic elements. The museum is divided into five different permanent sections: Mineralogy (with a large collection of minerals from all over the world); Paleontology (with several fossils of dinosaurs and other prehistoric organisms); Natural History of Man (dedicated to the origins and evolution of humans with a particular attention to the relationship of the latter with the environment); Invertebrate Zoology (dedicated to mollusks, arthropods and entomology); and Vertebrate Zoology (dedicated to vertebrates, both exotic and Europea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleohistology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is distinct from the intentional creation of dwarf breeds, called dwarfing. This process has occurred many times throughout evolutionary history, with examples including dinosaurs, like '' Europasaurus'' and ''Magyarosaurus dacus'', and modern animals such as elephants and their relatives. This process, and other "island genetics" artifacts, can occur not only on islands, but also in other situations where an ecosystem is isolated from external resources and breeding. This can include caves, desert oases, isolated valleys and isolated mountains ("sky islands"). Insular dwarfism is one aspect of the more general "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |