|
Pai Chang
Baizhang Huaihai (; pinyin: ''Bǎizhàng Huáihái''; Wade-Giles: ''Pai-chang Huai-hai''; ja, Hyakujō Ekai) (720–814) was a Zen Zen ( zh, t=禪, p=Chán; ja, text= 禅, translit=zen; ko, text=선, translit=Seon; vi, text=Thiền) is a school of Mahayana Buddhism that originated in China during the Tang dynasty, known as the Chan School (''Chánzong'' 禪宗), and ... master during the Tang Dynasty The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom .... A native of Fuzhou, he was a dharma heir In Chan and Zen Buddhism, dharma transmission is a custom in which a person is established as a "successor in an unbroken lineage of teachers and disciples, a spiritual 'bloodline' (''kechimyaku'') theoretically traced back to the Buddha himse ... of Mazu Daoyi Mazu Dao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Asian Yogācāra
East Asian Yogācāra (, "'Consciousness Only' school" or , "'Dharma Characteristics' school") refers to the traditions in East Asia which developed out of the Indian Buddhist Yogachara systems. The 4th-century Gandharan brothers, Asaṅga and Vasubandhu, are considered the classic philosophers and systematizers of this school, along with its other founder, Maitreya-natha.Siderits, Mark, ''Buddhism as philosophy'', 2017, p. 146. Asian Buddhist scholars such as Xuanzang and his students Kuiji, Woncheuk and Dōshō were also pivotal to the founding and development of the tradition in East Asia. Etymology The term ''Fǎxiàng'' itself was first applied to this tradition by the Huayan teacher Fazang ( zh, 法藏), who used it to characterize Consciousness Only teachings as provisional, dealing with the phenomenal appearances of the dharmas. Chinese proponents preferred the title ''Wéishí'' (), meaning "Consciousness Only" (Sanskrit ''Vijñaptimātra''). This school may also be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secular Buddhism
Secular Buddhism—sometimes also referred to as agnostic Buddhism, Buddhist agnosticism, ignostic Buddhism, atheistic Buddhism, pragmatic Buddhism, Buddhist atheism, or Buddhist secularism—is a broad term for a form of Buddhism based on humanist, skeptical, and agnostic values, valuing pragmatism and (often) naturalism, eschewing beliefs in the supernatural or paranormal. It can be described as the embrace of Buddhist rituals and philosophy for their secular benefits by people who are atheist or agnostic. Secular Buddhists interpret the teachings of the Buddha and the Buddhist texts in a rationalist and often evidentialist manner, considering the historical and cultural contexts of the times in which the Buddha lived and in which the various sutras and tantras were written. The secular Buddhist framework strips Buddhist doctrine of various traditional beliefs that could be considered superstitious, or that cannot be tested through empirical research, such as: supernatural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
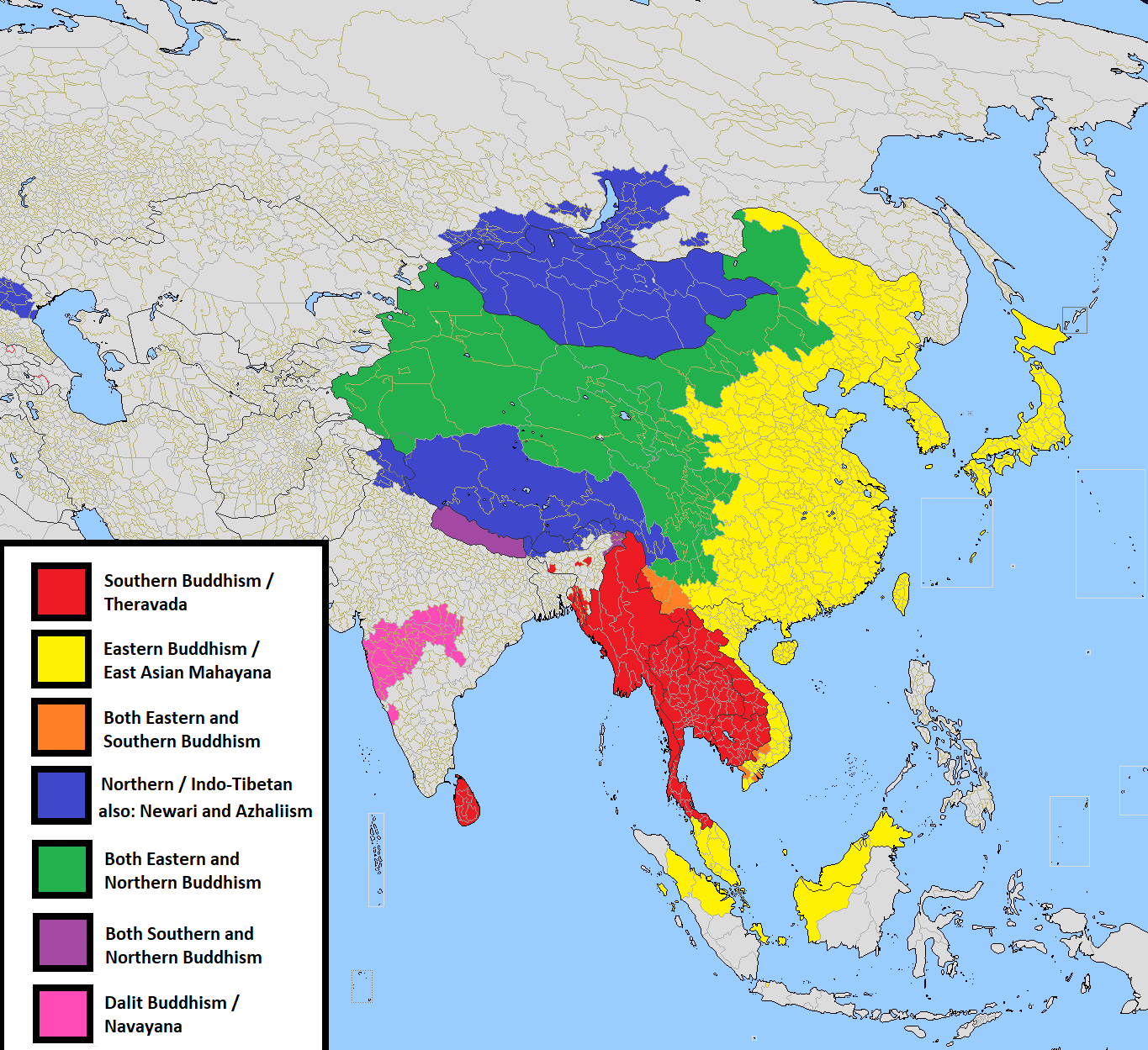
Schools Of Buddhism
The schools of Buddhism are the various institutional and doctrinal divisions of Buddhism that have existed from ancient times up to the present. The classification and nature of various doctrinal, philosophical or cultural facets of the schools of Buddhism is vague and has been interpreted in many different ways, often due to the sheer number (perhaps thousands) of different sects, subsects, movements, etc. that have made up or currently make up the whole of Buddhist traditions. The sectarian and conceptual divisions of Buddhist thought are part of the modern framework of Buddhist studies, as well as comparative religion in Asia. From a largely English-language standpoint, and to some extent in most of Western academia, Buddhism is separated into two groups: Theravāda, literally "the Teaching of the Elders" or "the Ancient Teaching," and Mahāyāna, literally the "Great Vehicle." The most common classification among scholars is threefold: Theravāda, Mahāyāna and Vajrayāna. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Buddhism-related Articles
0–9 * 22 Vows of Ambedkar A * Abhayagiri Buddhist Monastery * Abhayamudra * Abhibhavayatana * Abhidhajamahāraṭṭhaguru * Abhidhamma * Abhidhamma Pitaka * Abhijatabhivamsa * Abhijna * Acala * Acariya * Access to Insight * Achar (Buddhism) * Adam's Peak * Adhiṭṭhāna * Adi-Buddha * ''Ādittapariyāya Sutta'' * Adosa * Āgama * Agga Maha Pandita * '' Aggañña Sutta'' * Aggavamsa * ''Aggi-Vacchagotta Sutta'' * Ahimsa * Anne Hopkins Aitken * Robert Baker Aitken * Ajahn * Ajahn Amaro * Ajahn Brahm * Ajahn Candasiri * Ajahn Chah * Ajahn Fuang Jotiko * Ajahn Jayasāro * Ajahn Khemadhammo * Ajahn Lee * Ajahn Maha Bua * Ajahn Mun * Ajahn Pasanno * Ajahn Sao Kantasilo Mahathera * Ajahn Sobin S. Namto * Ajahn Sucitto * Ajahn Sujato * Ajahn Sumedho * Ajahn Sundara * Ajahn Suwat Suvaco * Ajahn Thate * Ajahn Waen Sujinno * Ajahn Viradhammo * Ajanta Caves * Ajari * Ajatasattu * Akasagarbha * Aksobhya * Alayavijnana * Alexandra David-Néel * Alobha * Alodawpyi Pagoda * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In China
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy, medicine and material culture. Chinese Buddhism is the largest institutionalized religion in Mainland China.Cook, Sarah (2017). The Battle for China's Spirit: Religious Revival, Repression, and Resistance under Xi Jinping.' Freedom House Report. Rowman & Littlefield. Currently, there are an estimated 185 to 250 million Chinese Buddhists in the People's Republic of China. It is also a major religion in Taiwan, Singapore, and Malaysia, as well as among the Chinese Diaspora. Buddhism was first introduced to China during the Han Dynasty (202 BCE–220 CE). The translation of a large body of Indian Buddhist scriptures into Chinese and the inclusion of these translations (along with Taoist and Confucian works) into a Chinese Buddhist canon had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Anti-Buddhist Persecution
The Huichang Persecution of Buddhism () was initiated by Emperor Wuzong (Li Chan) of the Tang dynasty during the Huichang era (841–845). Among its purposes were to appropriate war funds and to cleanse Tang China of foreign influences. As such, the persecution was directed not only towards Buddhism but also towards other religions, such as Zoroastrianism, Nestorian Christianity, and Manicheism. Rationale Emperor Wuzong's economic, social, and religious reasons for persecuting Buddhist organizations and temples throughout China were as follows: * ''Economic reasons'': In 843 the emperor's armies won a decisive battle against the Uyghur tribes at the cost of almost bankrupting the country. Wuzong's solution to the financial crisis was to go after the wealth that had been accumulated in the Buddhist monasteries. Buddhism had flourished greatly during the Tang period, and its monasteries enjoyed tax-exempt status. In 845, Wuzong closed many Buddhist shrines, confiscated their pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hsu Yun
Xuyun or Hsu Yun (; 5 September 1840? – 13 October 1959) was a renowned Chinese Chan Buddhist master and an influential Buddhist teacher of the 19th and 20th centuries. Early life Xuyun was purportedly born on 5 September 1840 in Fujian, Qing China. His original name was Xiao Guyan (). He was the son of Xiao Yutang () and his mother was surnamed Yan (). His mother died during childbirth. Guyan's grandmother insisted that her grandson take a wife. In order to continue both his and his uncle's lineage, Guyan was arranged to marry one woman from the Tian family and one from the Tan family. His first exposure to Buddhism was during the funeral of his grandmother. Soon afterward he began reading Buddhist sutras and later made a pilgrimage to Mount Heng, one of the most important Buddhist sites in China. When he was fourteen years old, he announced that he wished to renounce the material world in favour of monastic life. His father did not approve of Buddhism and had him ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taixu
Taixu (Tai Hsu) (), (January 8, 1890 – March 17, 1947) was a Buddhist modernist, activist and thinker who advocated for a reformation and revival of Chinese Buddhism by drawing upon eclectic domestic and foreign sources and ideologies. Biography Taixu was born in Hǎiníng (海寧) in Zhejiang province. His lay name was Lǚ Pèilín (呂沛林). His parents died when he was still young, and he was raised by his grandparents. At 16, he was ordained into the Linji school of Chan Buddhism in Xiao Jiǔhuá Temple (小九華寺) in Suzhou. Not long after being ordained he was given the Dharma name of Taixu, meaning Great Emptiness. In 1909, he traveled to Nanking to join the Sutra Carving Society established there by the lay Buddhist Yang Renshan. As a result of being exposed to the political writings of Kang Youwei, Liang Qichao, Tan Sitong and Zhang Taiyan, Taixu turned his mind to the reformation of Buddhism. In 1911 while in Guangzhou, he made contact with the revolutionarie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monk
A monk (, from el, μοναχός, ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a person who practices religious asceticism by monastic living, either alone or with any number of other monks. A monk may be a person who decides to dedicate their life to serving other people and serving God, or to be an ascetic who voluntarily chooses to leave mainstream society and live their life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many religions and in philosophy. In the Greek language, the term can apply to women, but in modern English it is mainly in use for men. The word ''nun'' is typically used for female monastics. Although the term ''monachos'' is of Christian origin, in the English language ''monk'' tends to be used loosely also for both male and female ascetics from other religious or philosophical backgrounds. However, being generic, it is not interchangeable with terms that denote particular kinds of monk, such as cenobite, hermit, anchor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wild Fox Koan
The wild fox kōan, also known as "Pai-chang 's fox" and "Hyakujō and a Fox", is an influential kōan story in the Zen tradition dating back as early as 1036, when it appeared in the Chinese biographical history ''T'ien-sheng kuang-teng lu''. It was also in ''The Gateless Gate'' (Mandarin: 無門關 ''Wúménguān''; Japanese: 無門関 ''Mumonkan''), a 13th-century collection of 48 kōans compiled by the Chinese monk Wumen, as case two. Overview The koan tells the story of a monk who, after denying that an enlightened person falls into cause and effect, was turned into a wild fox for five hundred lifetimes. He appears to Zen Master Baizhang ( Wade-Giles: ''Pai-chang''; Japanese: ''Hyakujō'') and demands a "turning word," a phrase intended to prompt one to realization, to be freed from his animal form. After Baizhang tells him not to ignore cause and effect, the monk confirms that he has been released from his wild fox body and asks to be given a monk's funeral rites. Later, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Cleary
Thomas Cleary (24 April 1949 – 20 June 2021) was an American translator and writer of more than 80 books related to Buddhist, Taoist, Confucian, and Muslim classics, and of ''The Art of War'', a treatise on management, military strategy, and statecraft. He has translated books from Pali, Sanskrit, Arabic, Chinese language, Chinese, Japanese language, Japanese, and Old Irish into English. Cleary lived in Oakland, California. Life and work Cleary became interested in Buddhism when he was a teenager; his researches into Buddhist thought began with a desire to learn during this time of his life. When he began translating, he chose either untranslated works or—as in the case of Sun Tzu's ''The Art of War''—books whose extant translations were "too limited". Cleary earned a Ph.D. in EALC, East Asian Languages and Civilizations from Harvard University, and a JD from the Boalt Hall School of Law at the University of California, Berkeley. After completing his doctoral studies, Clea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |