|
Pacman Conjecture
{{refimprove, date=May 2008 The Pacman conjecture holds that durable-goods monopolists have complete market power and so can exercise perfect price discrimination, thus extracting the total surplus.Coase versus Pacman: Who Eats Whom in the Durable Goods Monopoly? Author(s): Nils-Henrik Morch von der Fehr and Kai-Uwe Kuhn Source: The Journal of Political Economy, Vol. 103, No. 4, (Aug., 1995), pp. 785–812 Published by: The University of Chicago Press This is in contrast to the Coase conjecture which holds that a durable goods monopolist has ''no'' market power, and so price is equal to the competitive market price. In a December 1989 journal article Bagnoli, M., Salant, S.W., & Swierzbinski, J.E. "Durable-Goods Monopoly with Discrete Demand". '' The Journal of Political Economy'', 97.6 (December 1989), pp. 1459–1478.JSTOR Mark Bagnoli, Stephen W. Salant, and Joseph E. Swierzbinski theorized that if each consumer could be relied upon to buy a good as soon as its price dipped b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durable-goods Monopolist
In industrial organization and in particular monopoly theory, a durapolist or durable good monopolist is a producer that manipulates the durability of its product. The term was coined by antitrust scholar Barak Orbach. The concept is used to explain how durable good manufacturers overcome the durability problem of their products and persuade consumers to purchase new goods. The concept utilizes a monopolist to simplify explanations regarding product durability.Orbach, Barak (2004). "The Durapolist Puzzle: Monopoly Power in Durable-Goods Market". Yale Journal on Regulation (21): 67–118. Overview Once a durable-good manufacturer sells a product to a consumer, it faces a challenge to convince this consumer to purchase another good. A consumer needs one refrigerator, one razor, a limited number of shirts, and so forth. Durability, therefore, may mean limited prospects for businesses. Ronald Coase argued that because of the durability problem a durable-good monopolist may not be able to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pac-Man
originally called ''Puck Man'' in Japan, is a 1980 maze video game, maze action game, action video game developed and released by Namco for Arcade game, arcades. In North America, the game was released by Midway Manufacturing as part of its licensing agreement with Namco America. The player controls Pac-Man (character), Pac-Man, who must eat all the dots inside an enclosed maze while avoiding four colored Ghosts (Pac-Man), ghosts. Eating large flashing dots called "Power Pellets" causes the ghosts to temporarily turn blue, allowing Pac-Man to eat them for bonus points. Game development began in early 1979, directed by Toru Iwatani with a nine-man team. Iwatani wanted to create a game that could appeal to women as well as men, because most video games of the time had themes of war or sports. Although the inspiration for the Pac-Man character was the image of a pizza with a slice removed, Iwatani has said he also rounded out the Japanese character for mouth, kuchi ( ja, wiktiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly (economics)
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a specific person or company, enterprise is the only supplier of a particular thing. This contrasts with a monopsony which relates to a single entity's control of a Market (economics), market to purchase a good or service, and with oligopoly and duopoly which consists of a few sellers dominating a market. Monopolies are thus characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce the good (economics), good or Service (economics), service, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anti-competitive Practices
Anti-competitive practices are business or government practices that prevent or reduce competition in a market. Antitrust laws differ among state and federal laws to ensure businesses do not engage in competitive practices that harm other, usually smaller, businesses or consumers. These laws are formed to promote healthy competition within a free market by limiting the abuse of monopoly power. Competition allows companies to compete in order for products and services to improve; promote innovation; and provide more choices for consumers. In order to obtain greater profits, some large enterprises take advantage of market power to hinder survival of new entrants. Anti-competitive behavior can undermine the efficiency and fairness of the market, leaving consumers with little choice to obtain a reasonable quality of service. Anti-competitive behaviour is used by business and governments to lessen competition within the markets so that monopolies and dominant firms can generate superno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
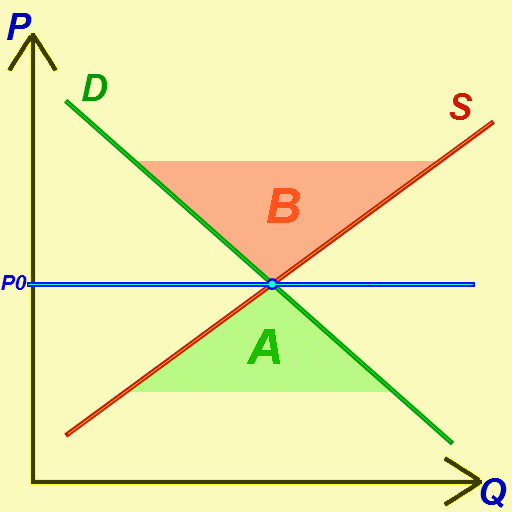
Economic Equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a situation in which economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external influences the ( equilibrium) values of economic variables will not change. For example, in the standard text perfect competition, equilibrium occurs at the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal. Market equilibrium in this case is a condition where a market price is established through competition such that the amount of goods or services sought by buyers is equal to the amount of goods or services produced by sellers. This price is often called the competitive price or market clearing price and will tend not to change unless demand or supply changes, and quantity is called the "competitive quantity" or market clearing quantity. But the concept of ''equilibrium'' in economics also applies to imperfectly competitive markets, where it takes the form of a Nash equilibrium. Understanding economic equilib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marginal Revenue
Marginal revenue (or marginal benefit) is a central concept in microeconomics that describes the additional total revenue generated by increasing product sales by 1 unit.Bradley R. chiller, "Essentials of Economics", New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1991.Edwin Mansfield, "Micro-Economics Theory and Applications, 3rd Edition", New York and London:W.W. Norton and Company, 1979.Roger LeRoy Miller, "Intermediate Microeconomics Theory Issues Applications, Third Edition", New York: McGraw-Hill, Inc, 1982.Tirole, Jean, "The Theory of Industrial Organization", Cambridge, Massachusetts: The MIT Press, 1988.John Black, "Oxford Dictionary of Economics", New York: Oxford University Press, 2003. To derive the value of marginal revenue, it is required to examine the difference between the aggregate benefits a firm received from the quantity of a good and service produced last period and the current period with one extra unit increase in the rate of production. Marginal revenue is a fundamental to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Market Power
In economics, market power refers to the ability of a firm to influence the price at which it sells a product or service by manipulating either the supply or demand of the product or service to increase economic profit. In other words, market power occurs if a firm does not face a perfectly elastic demand curve and can set its price (P) above marginal cost (MC) without losing revenue.Syverson, C. (2019). Macroeconomics and Market Power. The Journal of Economic Perspectives, 33(3), 23-43. https://doi.org/10.1257/jep.33.3.23 This indicates that the magnitude of market power is associated with the gap between P and MC at a firm's profit maximising level of output. Such propensities contradict perfectly competitive markets, where market participants have no market power, P = MC and firms earn zero economic profit. Market participants in perfectly competitive markets are consequently referred to as 'price takers', whereas market participants that exhibit market power are referred to as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopolist
A monopoly (from Greek el, μόνος, mónos, single, alone, label=none and el, πωλεῖν, pōleîn, to sell, label=none), as described by Irving Fisher, is a market with the "absence of competition", creating a situation where a specific person or enterprise is the only supplier of a particular thing. This contrasts with a monopsony which relates to a single entity's control of a market to purchase a good or service, and with oligopoly and duopoly which consists of a few sellers dominating a market. Monopolies are thus characterized by a lack of economic competition to produce the good or service, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a busin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demand Curve
In economics, a demand curve is a graph depicting the relationship between the price of a certain commodity (the ''y''-axis) and the quantity of that commodity that is demanded at that price (the ''x''-axis). Demand curves can be used either for the price-quantity relationship for an individual consumer (an individual demand curve), or for all consumers in a particular market (a market demand curve). It is generally assumed that demand curves slope down, as shown in the adjacent image. This is because of the law of demand: for most goods, the quantity demanded falls if the price rises. Certain unusual situations do not follow this law. These include Veblen goods, Giffen goods, and speculative bubbles where buyers are attracted to a commodity if its price rises. Demand curves are used to estimate behaviour in competitive markets and are often combined with supply curves to find the equilibrium price (the price at which sellers together are willing to sell the same amount as b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Price Discrimination
Price discrimination is a microeconomic pricing strategy where identical or largely similar goods or services are sold at different prices by the same provider in different markets. Price discrimination is distinguished from product differentiation by the more substantial difference in production cost for the differently priced products involved in the latter strategy. Price differentiation essentially relies on the variation in the customers' willingness to payApollo, M. (2014). Dual Pricing–Two Points of View (Citizen and Non-citizen) Case of Entrance Fees in Tourist Facilities in Nepal. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 120, 414-422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2014.02.119 and in the elasticity of their demand. For price discrimination to succeed, a firm must have market power, such as a dominant market share, product uniqueness, sole pricing power, etc. All prices under price discrimination are higher than the equilibrium price in a perfectly-competitive m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Journal Of Political Economy
The ''Journal of Political Economy'' is a monthly peer-reviewed academic journal published by the University of Chicago Press. Established by James Laurence Laughlin in 1892, it covers both theoretical and empirical economics. In the past, the journal published quarterly from its introduction through 1905, ten issues per volume from 1906 through 1921, and bimonthly from 1922 through 2019. The editor-in-chief is Magne Mogstad (University of Chicago). It is considered one of the top five journals in economics. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in EBSCO, ProQuest, EconLit , Research Papers in Economics, Current Contents/Social & Behavioral Sciences, and the Social Sciences Citation Index. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 9.103, ranking it 4/376 journals in the category "Economics". The journal is department-owned University of Chicago journal. Notable papers Among the most influential papers t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph E
Joseph is a common male given name, derived from the Hebrew Yosef (יוֹסֵף). "Joseph" is used, along with "Josef", mostly in English, French and partially German languages. This spelling is also found as a variant in the languages of the modern-day Nordic countries. In Portuguese and Spanish, the name is "José". In Arabic, including in the Quran, the name is spelled '' Yūsuf''. In Persian, the name is "Yousef". The name has enjoyed significant popularity in its many forms in numerous countries, and ''Joseph'' was one of the two names, along with ''Robert'', to have remained in the top 10 boys' names list in the US from 1925 to 1972. It is especially common in contemporary Israel, as either "Yossi" or "Yossef", and in Italy, where the name "Giuseppe" was the most common male name in the 20th century. In the first century CE, Joseph was the second most popular male name for Palestine Jews. In the Book of Genesis Joseph is Jacob's eleventh son and Rachel's first son, and k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |