|
Pacific–Antarctic Ridge
The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) is a divergent tectonic plate boundary located on the seafloor of the South Pacific Ocean, separating the Pacific Plate from the Antarctic Plate. It is regarded as the southern section of the East Pacific Rise in some usages, generally south of the Challenger Fracture Zone and stretching to the Macquarie Triple Junction south of New Zealand. The Louisville Ridge Stretching for 4,300 km north-west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge to the Osbourn Seamount at Tonga and Kermadec Junction is a long line of seamounts called the Louisville Ridge – the longest such chain in the Pacific – thought to have formed from the Pacific Plate sliding over a long-lived center of upwelling magma Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natura ... called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pacific Rise
The East Pacific Rise is a mid-ocean rise (termed an oceanic rise and not a mid-ocean ridge due to its higher rate of spreading that results in less elevation increase and more regular terrain), a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific Plate to the west from (north to south) the North American Plate, the Rivera Plate, the Cocos Plate, the Nazca Plate, and the Antarctic Plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near 55° S, 130° W, where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge trending west-southwest towards Antarctica, near New Zealand (though in some uses the PAR is regarded as the southern section of the EPR). Much of the rise lies about 3200 km (2000 mi) off the South American coast and rises about 1,800–2,700 m (6,000–9,000 ft) above the surrounding seafloor. Overview The oceanic crust is moving away ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisville Ridge
The Louisville Ridge, also known as the Louisville Seamount Chain, is an underwater chain of over 70 seamounts located in the Southwest portion of the Pacific Ocean. As one of the longest seamount chains on Earth it stretches some Vanderkluysen, L.; Mahoney, J. J.; Koppers, A. A.; and Lonsdale, P. F. (2007)Geochemical Evolution of the Louisville Seamount Chain American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2007, abstract #V42B-06. from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge northwest to the Tonga- Kermadec Trench, where it subducts under the Indo-Australian Plate as part of the Pacific Plate. The chain may have been formed by movement of the Pacific Plate over the Louisville hotspot or by leakage of magma from the shallow mantle up through the Eltanin fracture zone, which it follows closely. Depth-sounding data first revealed the existence of the seamount chain in 1972. Seamounts The Louisville Ridge includes the following: *Burton Seamount * Currituck Seamount * Danseur Seamount *Darvin G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
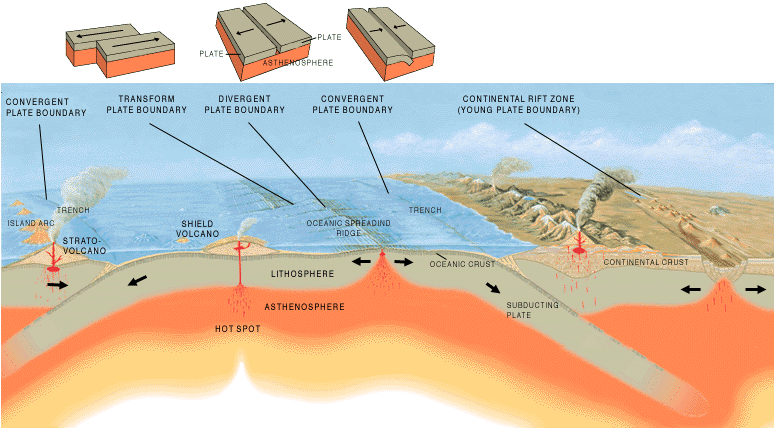
List Of Tectonic Plate Interactions
Tectonic plate interactions are classified into three basic types: * Divergent boundaries are areas where plates move away from each other, forming either mid-ocean ridges or rift valleys. These are also known as constructive boundaries. * Convergent boundaries are areas where plates move toward each other and collide. These are also known as compressional or destructive boundaries. ** Subduction zones occur where an ''oceanic'' plate meets a ''continental'' plate and is pushed underneath it. Subduction zones are marked by oceanic trenches. The descending end of the oceanic plate melts and creates pressure in the mantle, causing volcanoes to form. ** Obduction occurs when the ''continental'' plate is pushed under the ''oceanic'' plate, but this is unusual as the relative densities of the tectonic plates favours subduction of the ''oceanic'' plate. This causes the oceanic plate to buckle and usually results in a new mid-ocean ridge forming and turning the obduction into su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hollister Ridge
Hollister Ridge is a group of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean. They lie west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge and form three ridges that form a line; one of the ridges rises to a depth of and in the past formed an island. The seamounts are composed out of basaltic and other rocks and their ages range from about 2.5 million years ago to latest Pleistocene; an acoustic swarm recorded in the southern Pacific Ocean in 1991-1992 is considered to be the manifestation of a historical eruption of the Hollister Ridge. The origin of the Hollister Ridge is unclear, with various proposed mechanisms involving the neighbouring Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, crustal weaknesses and the Louisville hotspot. History The ridge was discovered either by gravimetry from satellites or by the research ship ''Eltanin'' in 1965 and first named "Hollister Ridge" in a 1995 publication. Rock samples were taken at the ridge in 1996. Geography and geomorphology The Hollister Ridge is an aseismic ridge in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisville Hotspot
The Louisville hotspot is a volcanic hotspot responsible for the volcanic activity that has formed the Louisville Ridge in the southern Pacific Ocean. Location The Louisville hotspot is believed to lie close to the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, although its exact location is uncertain. Geological history The Louisville hotspot has produced the Louisville Ridge, which is one of the longest seamount chains on Earth, stretching some Vanderkluysen, L.; Mahoney, J. J.; Koppers, A. A.; and Lonsdale, P. F. (2007)Geochemical Evolution of the Louisville Seamount Chain American Geophysical Union, Fall Meeting 2007, abstract #V42B-06. from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge to the Tonga Trench where it subducts under the Indo-Australian Plate as part of the Pacific Plate. The Louisville hotspot is believed to have been active since at least 78.8 ± 1.3 Ma based on age of the oldest seamount (Osbourn ). This duration is comparable to that of the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain, although the rate of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
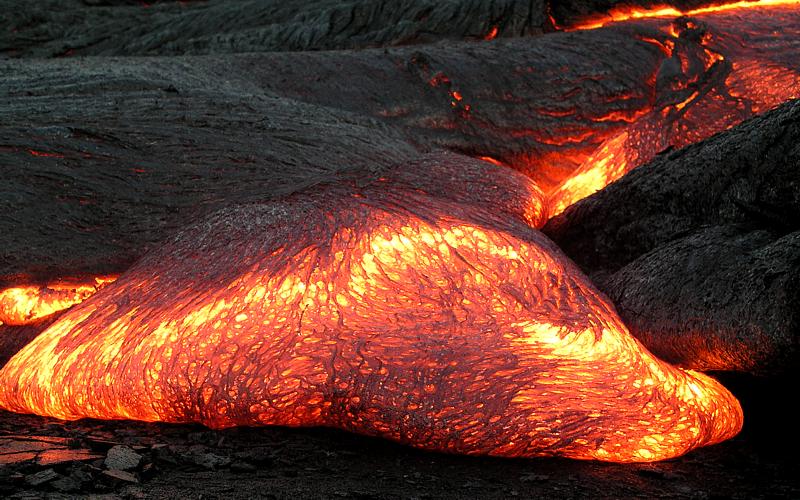
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle or the crust in various tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by fractional crystallization, contamination with crustal melts, magma mixing, and degassing. Following its ascent through the crust, magma may feed a volcano and be extruded as lava, or it may solidify underground to form an intrusion, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in the southern Pacific Ocean. As of 2021, according to Johnson's Tribune, Tonga has a population of 104,494, 70% of whom reside on the main island, Tongatapu. The country stretches approximately north-south. It is surrounded by Fiji and Wallis and Futuna (France) to the northwest; Samoa to the northeast; New Caledonia (France) and Vanuatu to the west; Niue (the nearest foreign territory) to the east; and Kermadec (New Zealand) to the southwest. Tonga is about from New Zealand's North Island. First inhabited roughly 2,500 years ago by the Lapita civilization, Tonga's Polynesian settlers gradually evolved a distinct and strong ethnic identity, language, and culture as the Tongan people. They were quick to establish a powerful footi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Divergent Boundary
In plate tectonics, a divergent boundary or divergent plate boundary (also known as a constructive boundary or an extensional boundary) is a linear feature that exists between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. Divergent boundaries within continents initially produce rifts, which eventually become rift valleys. Most active divergent plate boundaries occur between oceanic plates and exist as mid-oceanic ridges. Current research indicates that complex convection within the Earth's mantle allows material to rise to the base of the lithosphere beneath each divergent plate boundary. This supplies the area with huge amounts of heat and a reduction in pressure that melts rock from the asthenosphere (or upper mantle) beneath the rift area, forming large flood basalt or lava flows. Each eruption occurs in only a part of the plate boundary at any one time, but when it does occur, it fills in the opening gap as the two opposing plates move away from each ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louisville Seamount Chain - Bathymetry
Louisville ( , , ) is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky and the 28th most-populous city in the United States. Louisville is the historical seat and, since 2003, the nominal seat of Jefferson County, on the Indiana border. Named after King Louis XVI of France, Louisville was founded in 1778 by George Rogers Clark, making it one of the oldest cities west of the Appalachians. With nearby Falls of the Ohio as the only major obstruction to river traffic between the upper Ohio River and the Gulf of Mexico, the settlement first grew as a portage site. It was the founding city of the Louisville and Nashville Railroad, which grew into a system across 13 states. Today, the city is known as the home of boxer Muhammad Ali, the Kentucky Derby, Kentucky Fried Chicken, the University of Louisville and its Cardinals, Louisville Slugger baseball bats, and three of Kentucky's six ''Fortune'' 500 companies: Humana, Kindred Healthcare, and Yum! Brands. Muhammad Ali Intern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 List of islands of New Zealand, smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's Capital of New Zealand, capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |