|
Hollister Ridge
Hollister Ridge is a group of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean. They lie west from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge and form three ridges that form a line; one of the ridges rises to a depth of and in the past formed an island. The seamounts are composed out of basaltic and other rocks and their ages range from about 2.5 million years ago to latest Pleistocene; an acoustic swarm recorded in the southern Pacific Ocean in 1991-1992 is considered to be the manifestation of a historical eruption of the Hollister Ridge. The origin of the Hollister Ridge is unclear, with various proposed mechanisms involving the neighbouring Pacific-Antarctic Ridge, crustal weaknesses and the Louisville hotspot. History The ridge was discovered either by gravimetry from satellites or by the research ship '' Eltanin'' in 1965 and first named "Hollister Ridge" in a 1995 publication. Rock samples were taken at the ridge in 1996. Geography and geomorphology The Hollister Ridge is an aseismic ridge in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliocene
The Pliocene ( ; also Pleiocene) is the epoch in the geologic time scale that extends from 5.333 million to 2.58See the 2014 version of the ICS geologic time scale million years ago. It is the second and most recent epoch of the Neogene Period in the . The Pliocene follows the Epoch and is followed by the Epoch. Prior to the 2009 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations. The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''escarpment''. Some sources differentiate the two terms, with ''escarpment'' referring to the margin between two landforms, and ''scarp'' referring to a cliff or a steep slope. In this usage an escarpment is a ridge which has a gentle slope on one side and a steep scarp on the other side. More loosely, the term ''scarp'' also describes a zone between a coastal lowland and a continental plateau which shows a marked, abrupt change in elevation caused by coastal erosion at the base of the plateau. Formation and description Scarps are generally formed by one of two processes: either by differential erosion of sedimentary rocks, or by movement of the Earth's crust at a geologic fault. The first process is the more common type: the escarpment is a t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenocryst
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter 2.3 cm) for scale. A phenocryst is an early forming, relatively large and usually conspicuous crystal distinctly larger than the grains of the rock groundmass of an igneous rock. Such rocks that have a distinct difference in the size of the crystals are called porphyries, and the adjective porphyritic is used to describe them. Phenocrysts often have euhedral forms, either due to early growth within a magma, or by post-emplacement recrystallization. Normally the term ''phenocryst'' is not used unless the crystals are directly observable, which is sometimes stated as greater than .5 millimeter in diameter. Phenocrysts below this level, but still larger than the groundmass crystals, are termed ''microphenocrysts''. Very large phenocrysts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porphyric
Porphyry ( ) is a textural term for an igneous rock consisting of coarse-grained crystals such as feldspar or quartz dispersed in a fine-grained silicate-rich, generally aphanitic matrix or groundmass. The larger crystals are called phenocrysts. In its non-geologic, traditional use, the term ''porphyry'' refers to the purple-red form of this stone, valued for its appearance. The term ''porphyry'' is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "purple". Purple was the color of royalty, and the "imperial porphyry" was a deep purple igneous rock with large crystals of plagioclase. Some authors claimed the rock was the hardest known in antiquity. Thus, "imperial"-grade porphyry was prized for monuments and building projects in Imperial Rome and thereafter. Subsequently, the name was given to any igneous rocks with large crystals. The adjective '' porphyritic'' now refers to a certain texture of igneous rock regardless of its chemical and mineralogical composition. Its chief character ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". The sinking of the ''Titanic'' in 1912 led to the formation of the International Ice Patrol in 1914. Much of an iceberg is below the surface, which led to the expression "tip of the iceberg" to illustrate a small part of a larger unseen issue. Icebergs are considered a serious maritime hazard. Icebergs vary considerably in size and shape. Icebergs that calve from glaciers in Greenland are often irregularly shaped while Antarctic ice shelves often produce large tabular (table top) icebergs. The largest iceberg in recent history (2000), named B-15, measured nearly 300 km × 40 km. The largest iceberg on record was an Antarctic tabular iceberg of over [] sighted west of Scott Island, in the South Pacific Ocean, by the USS Glacier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dropstone
Dropstones are isolated fragments of rock found within finer-grained water-deposited sedimentary rocks or pyroclastic beds. They range in size from small pebbles to boulders. The critical distinguishing feature is that there is evidence that they were not transported by normal water currents, but rather dropped in vertically through the air or water column. Such deposition can occur i.e. during a volcanic eruption. Background When deposited into fine layered mud, such evidence includes an impact depression beneath the dropstone, and indication that the mud has been squeezed up around the edges of the falling rock. Subsequent deposits of mud drape over the dropstone and its crater. Glacial dropstones, involving rocks falling out of icebergs, are one of the most common types of dropstone preserved in the geological record, particularly when deposited in low-energy deep sea or lake environments. Dropstones differ from erratics found in glacial till in that they are deposited in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tholeiite
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma into a more evolved, silica rich end member. Rock types of the tholeiitic magma series include tholeiitic basalt, ferro-basalt, tholeiitic basaltic andesite, tholeiitic andesite, dacite and rhyolite. The variety of basalt in the series was originally called ''tholeiite'' but the International Union of Geological Sciences recommends that ''tholeiitic basalt'' be used in preference to that term.Le Maitre ''et al.'' 2002 Tholeiitic rock types tend to be more enriched in iron and less enriched in aluminium than calc-alkaline rock types. They are thought to form in a less oxidized environment than calc-alkaline rocks. Tholeiitic basalt is formed at mid-ocean ridges and makes up much of the oceanic crust. Almost all the basalt found on the Moon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picrite
Picrite basalt or picrobasalt is a variety of high-magnesium olivine basalt that is very rich in the mineral olivine. It is dark with yellow-green olivine phenocrysts (20-50%) and black to dark brown pyroxene, mostly augite. The olivine-rich picrite basalts that occur with the more common tholeiitic basalts of Kīlauea and other volcanoes of the Hawaiian Islands are the result of accumulation of olivine crystals either in a portion of the magma chamber or in a caldera lava lake. The compositions of these rocks are well represented by mixes of olivine and more typical tholeiitic basalt. The name "picrite" can also be applied to an olivine-rich alkali basalt: such picrite consists largely of phenocrysts of olivine and titanium-rich augite pyroxene with minor plagioclase set in a groundmass of augite and more sodic plagioclase and perhaps analcite and biotite. Picrites and komatiites are somewhat similar chemically (defined as >18% MgO), but differ in having 1 to 2% total alkalis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
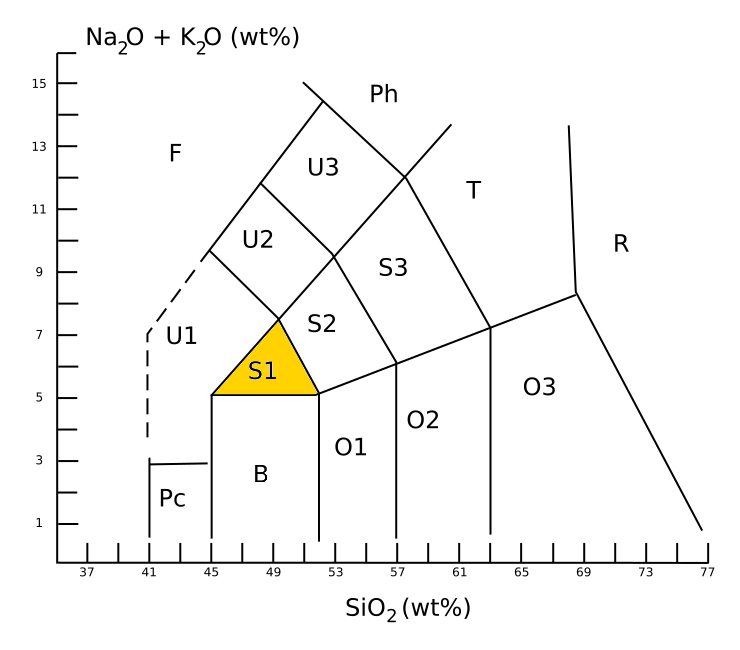
Hawaiite
Hawaiite is an olivine basalt with a composition between alkali basalt and mugearite. It was first used as a name for some lavas found on the island of Hawaii. It occurs during the later stages of volcanic activity on oceanic islands such as Hawaii, which happens to be when the alkaline metals are most present. In gemology, hawaiite is a colloquial term for Hawaii-originated peridot, which is a gem-quality form of the mineral olivine. Description Hawaiite is an aphanitic (fine-grained) volcanic rock produced by rapid cooling of lava moderately poor in silica and enriched in alkali metal oxides (potassium oxide plus sodium oxide). It is often impractical to determine the mineral composition of such a fine-grained rock, and so hawaiite is defined chemically. Under the TAS classification, hawaiite is sodic trachybasalt, with a silica content close to 49 wt%, a total alkali metal oxide content close to 6%, and wt% > wt% + 2. This places hawaiite in the S1 field of the TAS dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkali Basalt
Alkali basalt or alkali olivine basalt is a dark-colored, porphyritic volcanic rock usually found in oceanic and continental areas associated with volcanic activity, such as oceanic islands, continental rifts and volcanic fields. Alkali basalt is characterized by relatively high alkali (Na2O and K2O) content relative to other basalts and by the presence of olivine and titanium-rich augite in its groundmass and phenocrysts, and nepheline in its CIPW norm. Geochemical characterization Alkali basalt is chemically classified as a rock in region B (basalt) of the total alkali versus silica (TAS) diagram that contains nepheline in its CIPW norm. Basalts that do not contain normative nepheline are characterized as sub-alkali basalts, which include tholeiitic basalts and calc-alkaline basalts. Petrography The groundmass of alkali basalt is mainly composed of olivine, titanium-rich augite and plagioclase feldspar and may have alkali feldspar or feldspathoid interstitially, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |