|
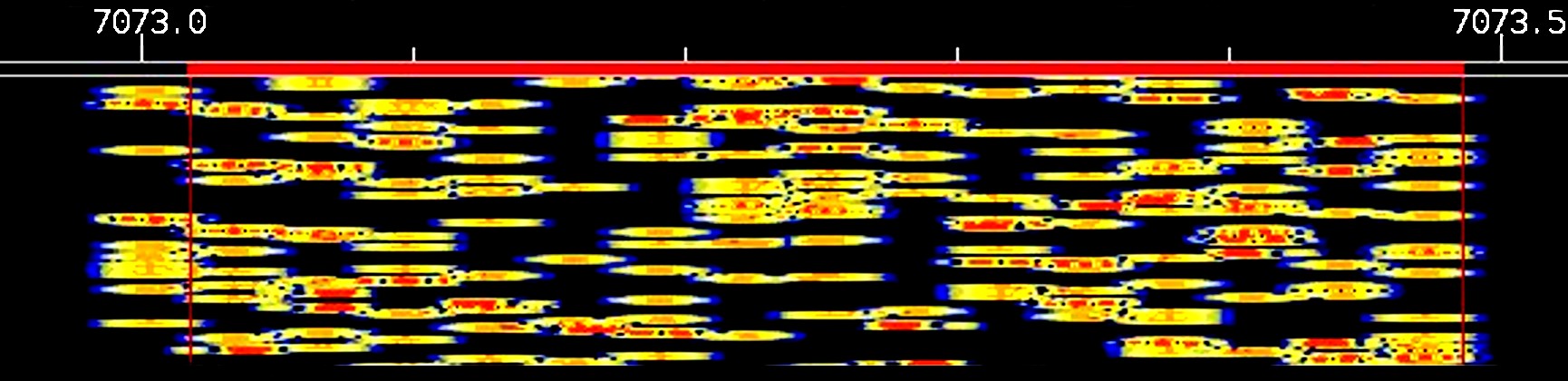
PSK-31
PSK31 or "Phase Shift Keying, 31 Baud", also BPSK31 and QPSK31, is a popular computer-sound card-generated radioteletype mode, used primarily by amateur radio operators to conduct real-time keyboard-to-keyboard chat, most often using frequencies in the high frequency amateur radio bands (near-shortwave). PSK31 is distinguished from other digital modes in that it is specifically tuned to have a data rate close to typing speed, and has an extremely narrow bandwidth, allowing many conversations in the same bandwidth as a single voice channel. This narrow bandwidth makes better use of the RF energy in a very narrow space thus allowing relatively low-power equipment (5 watts) to communicate globally using the same skywave propagation used by shortwave radio stations. History PSK31 was developed and named by English amateur radio operator Peter Martinez (call sign G3PLX) and introduced to the wider amateur radio community in December 1998. The 31 baud BPSK modulation system used in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSK Matrix
{{disambiguation ...
PSK may refer to: Organisations * Revolutionary Party of Kurdistan (PŞK), a Kurdish Separatist guerrilla group in Turkey * Kurdistan Socialist Party (PSK), a Kurdish party in Turkey * Phi Sigma Kappa, a fraternity * Österreichische Postsparkasse (P.S.K.), a postal savings bank in Austria * Post Südstadt Karlsruhe, a German sports club Science and technology * Phase-shift keying, a digital modulation technique * Pre-shared key, a method to set encryption keys * Polysaccharide-K, a protein-bound polysaccharide Other uses * " P.S.K. What Does It Mean?", a song by Schoolly D *''Pekerja Seks Komersial,'' Indonesian word for a prostitute Prostitution is the business or practice of engaging in sexual activity in exchange for payment. The definition of "sexual activity" varies, and is often defined as an activity requiring physical contact (e.g., sexual intercourse, non-penet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio
Amateur radio, also known as ham radio, is the use of the radio frequency spectrum for purposes of non-commercial exchange of messages, wireless experimentation, self-training, private recreation, radiosport, contesting, and emergency communications. The term "amateur" is used to specify "a duly authorised person interested in radioelectric practice with a purely personal aim and without pecuniary interest;" (either direct monetary or other similar reward) and to differentiate it from commercial broadcasting, public safety (such as police and fire), or professional two-way radio services (such as maritime, aviation, taxis, etc.). The amateur radio service (''amateur service'' and '' amateur-satellite service'') is established by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) through the Radio Regulations. National governments regulate technical and operational characteristics of transmissions and issue individual station licenses with a unique identifying call sign, which mus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amateur Radio Contest
Contesting (also known as ''radiosport'') is a competitive activity pursued by amateur radio operators. In a contest, an amateur radio station, which may be operated by an individual or a team, seeks to contact as many other amateur radio stations as possible in a given period of time and exchange information. Rules for each competition define the amateur radio bands, the mode of communication that may be used, and the kind of information that must be exchanged. The contacts made during the contest contribute to a score by which stations are ranked. Contest sponsors publish the results in magazines and on web sites. Contesting grew out of other amateur radio activities in the 1920s and 1930s. As intercontinental communications with amateur radio became more common, competitions were formed to challenge stations to make as many contacts as possible with amateur radio stations in other countries. Contests were also formed to provide opportunities for amateur radio operators to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSK63
PSK63 (meaning Phase Shift Keying at a rate of 63 baud) is a Digital data, digital :Radio modulation modes, radio modulation mode used primarily in the amateur radio field to conduct real-time keyboard-to-keyboard informal text Synchronous conferencing, chat between amateur radio operators. History In April 2003, Skip Teller, KH6TY, the creator of Digipan, requested an addition to Moe (AE4JY) Wheatley's PSKCore DLL to support the PSK63 mode. Subsequently, another mode - PSK125 - has been added to the PSKCore DLL. * Unlike PSK63F, PSK63 does not use forward error correction (FEC). * PSK 63 is twice as fast as PSK63F's but exactly the same speed as PSK125F. Mode Support PSK63 is now supported directly in KH6TY's own QuikPSK software, as well as in Digipan, AA6YQ's WinWarbler, F6CTE's MultiPSK, AE4JY's WinPSK, HB9DRV's DM780, PSK31 Deluxe, MMVARI, Fldigi, MIXW, and DL4RCK's RCKRtty. It is also supported in hardware by the Elecraft KX3. Others are likely to follow, now that ver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Throughput
Network throughput (or just throughput, when in context) refers to the rate of message delivery over a communication channel, such as Ethernet or packet radio, in a communication network. The data that these messages contain may be delivered over physical or logical links, or through network nodes. Throughput is usually measured in bits per second (bit/s or bps), and sometimes in data packets per second (p/s or pps) or data packets per time slot. The system throughput or aggregate throughput is the sum of the data rates that are delivered to all terminals in a network. Throughput is essentially synonymous to digital bandwidth consumption; it can be determined numerically by applying the queueing theory, where the load in packets per time unit is denoted as the arrival rate (), and the drop in packets per unit time is denoted as the departure rate (). The throughput of a communication system may be affected by various factors, including the limitations of the underlying analog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multipath Propagation
In radio communication, multipath is the propagation phenomenon that results in radio signals reaching the receiving antenna by two or more paths. Causes of multipath include atmospheric ducting, ionospheric reflection and refraction, and reflection from water bodies and terrestrial objects such as mountains and buildings. When the same signal is received over more than one path, it can create interference and phase shifting of the signal. Destructive interference causes fading; this may cause a radio signal to become too weak in certain areas to be received adequately. For this reason, this effect is also known as multipath interference or multipath distortion. Where the magnitudes of the signals arriving by the various paths have a distribution known as the Rayleigh distribution, this is known as Rayleigh fading. Where one component (often, but not necessarily, a line of sight component) dominates, a Rician distribution provides a more accurate model, and this is known as Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Q Code
The Q-code is a standardised collection of three-letter codes that each start with the letter "Q". It is an operating signal initially developed for commercial radiotelegraph communication and later adopted by other radio services, especially amateur radio. To distinguish the use of a Q-code transmitted as a question from the same Q-code transmitted as a statement, operators either prefixed it with the military network question marker "" (dit dit dah dit dah) or suffixed it with the standard Morse question mark (dit dit dah dah dit dit). Although Q-codes were created when radio used Morse code exclusively, they continued to be employed after the introduction of voice transmissions. To avoid confusion, transmitter call signs are restricted; no country is ever issued an ITU prefix starting with "Q". Codes in the range QAA–QNZ are reserved for aeronautical use; QOA–QQZ for maritime use and QRA–QUZ for all services. "Q" has no official meaning, but it is sometimes assign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Error Control
In information theory and coding theory with applications in computer science and telecommunication, error detection and correction (EDAC) or error control are techniques that enable reliable delivery of digital data over unreliable communication channels. Many communication channels are subject to channel noise, and thus errors may be introduced during transmission from the source to a receiver. Error detection techniques allow detecting such errors, while error correction enables reconstruction of the original data in many cases. Definitions ''Error detection'' is the detection of errors caused by noise or other impairments during transmission from the transmitter to the receiver. ''Error correction'' is the detection of errors and reconstruction of the original, error-free data. History In classical antiquity, copyists of the Hebrew Bible were paid for their work according to the number of stichs (lines of verse). As the prose books of the Bible were hardly ever writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Propagation
Radio propagation is the behavior of radio waves as they travel, or are propagated, from one point to another in vacuum, or into various parts of the atmosphere. As a form of electromagnetic radiation, like light waves, radio waves are affected by the phenomena of reflection, refraction, diffraction, absorption, polarization, and scattering. Understanding the effects of varying conditions on radio propagation has many practical applications, from choosing frequencies for amateur radio communications, international shortwave broadcasters, to designing reliable mobile telephone systems, to radio navigation, to operation of radar systems. Several different types of propagation are used in practical radio transmission systems. ''Line-of-sight propagation'' means radio waves which travel in a straight line from the transmitting antenna to the receiving antenna. Line of sight transmission is used for medium-distance radio transmission, such as cell phones, cordless phones, walkie- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Amateur Radio Modes
The following is a list of the modes of radio communication used in the amateur radio hobby. Modes of communication Amateurs use a variety of voice, text, image, and data communications modes over radio. Generally new modes can be tested in the amateur radio service, although national regulations may require disclosure of a new mode to permit radio licensing authorities to monitor the transmissions. Encryption, for example, is not generally permitted in the Amateur Radio service except for the special purpose of satellite vehicle control uplinks. The following is a partial list of the modes of communication used, where the mode includes both modulation types and operating protocols. Morse code Morse code is called the original digital mode. Radio telegraphy, designed for machine-to-machine communication is the direct on/off keying of a continuous wave carrier by Morse code symbols, often called amplitude-shift keying or ASK, may be considered to be an ''amplitude modulated'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Open Source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source code is openly shared so that people are encouraged to voluntarily improve the design of the software. This is in contrast to proprietary software, where the software is under restrictive copyright licensing and the source code is usually hidden from the users. FOSS maintains the software user's civil liberty rights (see the Four Essential Freedoms, below). Other benefits of using FOSS can include decreased software costs, increased security and stability (especially in regard to malware), protecting privacy, education, and giving users more control over their own hardware. Free and open-source operating systems such as Linux and descendants of BSD are widely utilized today, powering millions of servers, desktops, smartphones (e.g., A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivia MFSK
Olivia MFSK is an amateur radioteletype protocol, using multiple frequency-shift keying (MFSK) and designed to work in difficult (low signal-to-noise ratio plus multipath propagation) conditions on shortwave bands. The signal can be accurately received even if the surrounding noise is 10 dB stronger. It is commonly used by amateur radio operators to reliably transmit ASCII characters over noisy channels using the high frequency (3–30 MHz) spectrum. The effective data rate of the Olivia MFSK protocol is 150 characters/minute. Olivia modes are commonly referred to as Olivia ''X'' / ''Y'' (or, alternatively, Olivia ''Y'' / ''X'' ), where ''X'' refers to the number of different audio tones transmitted and ''Y'' refers to the bandwidth in hertz over which these signals are spread. Examples of common Olivia modes are 16/500, 32/1000 and 8/250. History The protocol was developed at the end of 2003 by Pawel Jalocha. The first on-the-air tests were performed by two radio amateur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |