|
PSB-10
PSB-10 is a drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the adenosine A3 receptor (ki value at human A3 receptor is 0.44 nM), with high selectivity over the other three adenosine receptor subtypes (ki values at human A1, A2A and A2B receptors are 4.1, 3.3 and 30 μM). Further pharmacological experiments in a 35S.html" ;"title="sup>35S">sup>35STPγS binding assay using hA3-CHO-cells indicated that PSB-10 acts as an inverse agonist (IC50 = 4 nM). It has been shown to produce antiinflammatory effects in animal studies. Simple xanthine derivatives such as caffeine and DPCPX 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX, PD-116,948) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the adenosine A1 receptor. It has high selectivity for A1 over other adenosine receptor subtypes, but as with other xanthine ... have generally low affinity for the A3 subtype and must be extended by expanding the ring system and adding an aromatic group to give high A3 affinity and sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine A3 Receptor
The adenosine A3 receptor, also known as ADORA3, is an adenosine receptor, but also denotes the human gene encoding it. Function Adenosine A3 receptors are G protein-coupled receptors that couple to Gi/Gq and are involved in a variety of intracellular signaling pathways and physiological functions. It mediates a sustained cardioprotective function during cardiac ischemia, it is involved in the inhibition of neutrophil degranulation in neutrophil-mediated tissue injury, it has been implicated in both neuroprotective and neurodegenerative effects, and it may also mediate both cell proliferation and cell death. Recent publications demonstrate that adenosine A3 receptor antagonists (SSR161421) could have therapeutic potential in bronchial asthma (17,18). Gene Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Therapeutic implications An adenosine A3 receptor agonist (CF-101) is in clinical trials for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine Receptor
The adenosine receptors (or P1 receptors) are a class of purinergic G protein-coupled receptors with adenosine as the endogenous ligand. There are four known types of adenosine receptors in humans: A1, A2A, A2B and A3; each is encoded by a different gene. The adenosine receptors are commonly known for their antagonists caffeine and theophylline, whose action on the receptors produces the stimulating effects of coffee, tea and chocolate. Pharmacology Each type of adenosine receptor has different functions, although with some overlap. For instance, both A1 receptors and A2A play roles in the heart, regulating myocardial oxygen consumption and coronary blood flow, while the A2A receptor also has broader anti-inflammatory effects throughout the body. These two receptors also have important roles in the brain, regulating the release of other neurotransmitters such as dopamine and glutamate, while the A2B and A3 receptors are located mainly peripherally and are involved in process ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist. Etymology The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, rival," which is derived from ''anti-'' ("against") and ''agonizesthai'' ("to contend for a prize"). Types Heroes and villains The antagonist is commonly positioned against the protagonist and their world order. While most narratives will often portray the protagonist as a hero and the antagonist as a villain, like Harry Potter and Lord Voldemort in '' Harry Potter'', the antagonist does not always appear as the villain. In some narratives, like Light Yagami and L in '' Death Note'', the protagonist is a villain and the antagonist is an opposing hero. Antagonists are conventionally presented as making moral choices less savory than those of protagonists. This condition is often used by an author to create conflict within a story. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adenosine
Adenosine ( symbol A) is an organic compound that occurs widely in nature in the form of diverse derivatives. The molecule consists of an adenine attached to a ribose via a β-N9-glycosidic bond. Adenosine is one of the four nucleoside building blocks of RNA (and its derivative deoxyadenosine is a building block of DNA), which are essential for all life. Its derivatives include the energy carriers adenosine mono-, di-, and triphosphate, also known as AMP/ADP/ATP. Cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) is pervasive in signal transduction. Adenosine is used as an intravenous medication for some cardiac arrhythmias. Adenosyl (abbreviated Ado or 5'-dAdo) is the chemical group formed by removal of the 5′-hydroxy (OH) group. It is found in adenosylcobalamin (an active form of vitamin B12) and as a radical in radical SAM enzymes. Medical uses Supraventricular tachycardia In individuals with supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), adenosine is used to help identify and convert the rhyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a ligand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiinflammatory
Anti-inflammatory is the property of a substance or treatment that reduces inflammation or swelling. Anti-inflammatory drugs, also called anti-inflammatories, make up about half of analgesics. These drugs remedy pain by reducing inflammation as opposed to opioids, which affect the central nervous system to block pain signaling to the brain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) alleviate pain by counteracting the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzyme. On its own, COX enzyme synthesizes prostaglandins, creating inflammation. In whole, the NSAIDs prevent the prostaglandins from ever being synthesized, reducing or eliminating the inflammation and resulting pain. Some common examples of NSAIDs are aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. The newer specific COX-inhibitors are not classified together with the traditional NSAIDs, even though they presumably share the same mode of action. On the other hand, there are analgesics that are commonly associat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthine
Xanthine ( or ; archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine base (genetics), base found in most human body tissues and fluids, as well as in other organisms. Several stimulants are derived from xanthine, including caffeine, theophylline, and theobromine. Xanthine is a product on the pathway of purine degradation. * It is created from guanine by guanine deaminase. * It is created from hypoxanthine by xanthine oxidoreductase. * It is also created from xanthosine by purine nucleoside phosphorylase. Xanthine is subsequently converted to uric acid by the action of the xanthine oxidase enzyme. Use and manufacturing Xanthine is used as a drug precursor (chemistry), precursor for human and animal medications, and is manufactured as a pesticide ingredient. Clinical significance Derivatives of xanthine (known collectively as xanthines) are a group of alkaloids commonly used for their effects as mild stimulants and as bronchodilators, notably in the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America, and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine
8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX, PD-116,948) is a drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the adenosine A1 receptor. It has high selectivity for A1 over other adenosine receptor subtypes, but as with other xanthine derivatives DPCPX also acts as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor, and is almost as potent as rolipram at inhibiting PDE4. It has been used to study the function of the adenosine A1 receptor in animals, which has been found to be involved in several important functions such as regulation of breathing and activity in various regions of the brain, and DPCPX has also been shown to produce behavioural effects such as increasing the hallucinogen-appropriate responding produced by the 5-HT2A agonist DOI, and the dopamine release induced by MDMA, as well as having interactions with a range of anticonvulsant drugs. See also * DMPX * CPX * Xanthine Xanthine ( or ; archaically xanthic acid; systematic name 3,7-dihydropurine-2,6-dione) is a purine ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorobenzenes
Chlorobenzene is an aromatic organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5Cl. This colorless, flammable liquid is a common solvent and a widely used intermediate in the manufacture of other chemicals. Uses Historical The major use of chlorobenzene is as an intermediate in the production of herbicides, dyestuffs, and rubber. Chlorobenzene is also used as a high-boiling solvent in industrial applications as well as in the laboratory. Chlorobenzene is nitrated on a large scale to give a mixture of 2-nitrochlorobenzene and 4-nitrochlorobenzene, which are separated. These mononitrochlorobenzenes are converted to related 2-nitrophenol, 2-nitroanisole, bis(2-nitrophenyl)disulfide, and 2-nitroaniline by nucleophilic displacement of the chloride, with respectively sodium hydroxide, sodium methoxide, sodium disulfide, and ammonia. The conversions of the 4-nitro derivative are similar. Chlorobenzene once was used in the manufacture of pesticides, most notably DDT, by reaction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
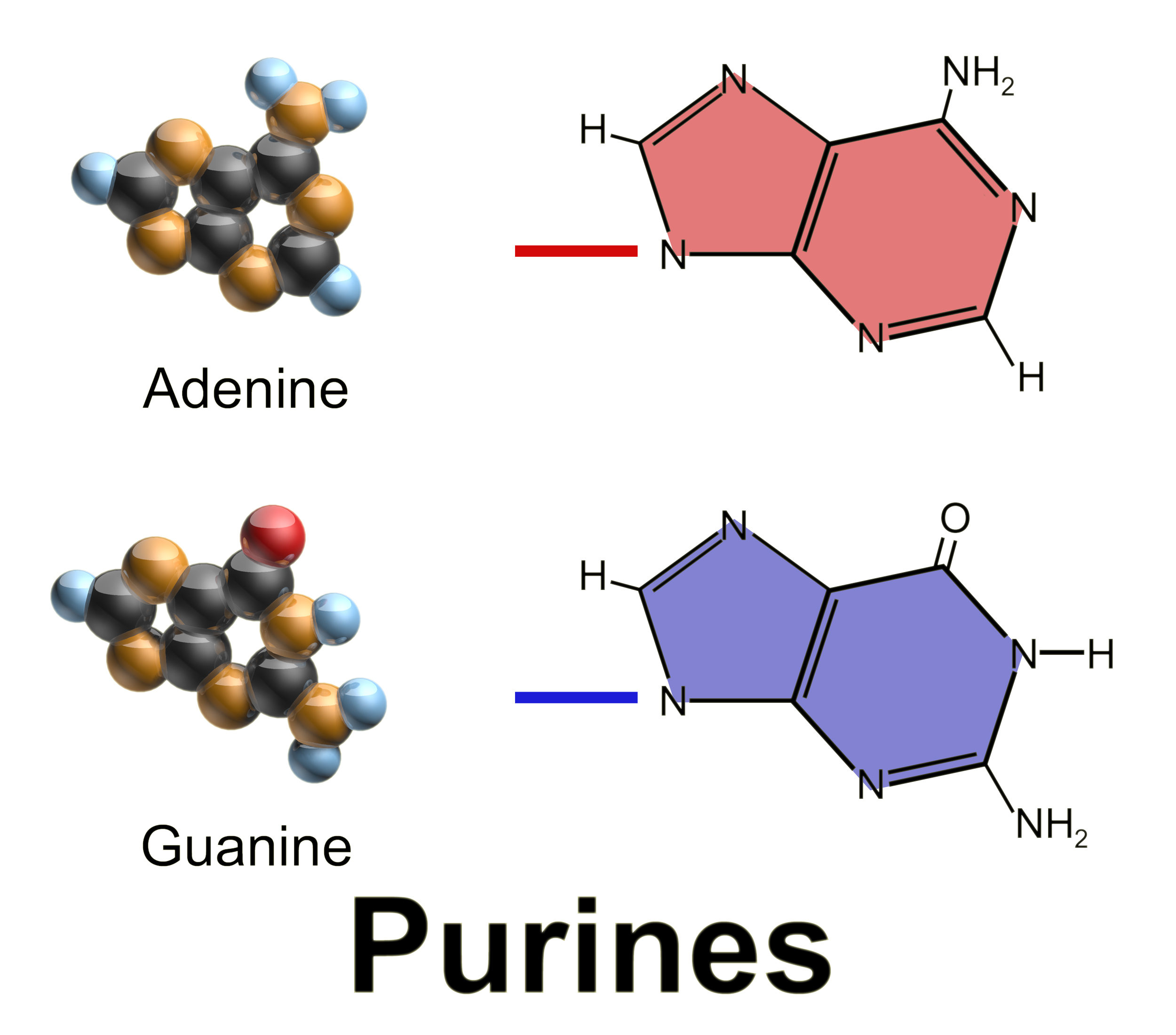
Purines
Purine is a heterocyclic aromatic organic compound that consists of two rings ( pyrimidine and imidazole) fused together. It is water-soluble. Purine also gives its name to the wider class of molecules, purines, which include substituted purines and their tautomers. They are the most widely occurring nitrogen-containing heterocycles in nature. Dietary sources Purines are found in high concentration in meat and meat products, especially internal organs such as liver and kidney. In general, plant-based diets are low in purines. High-purine plants and algae include some legumes (lentils and black eye peas) and spirulina. Examples of high-purine sources include: sweetbreads, anchovies, sardines, liver, beef kidneys, brains, meat extracts (e.g., Oxo, Bovril), herring, mackerel, scallops, game meats, yeast (beer, yeast extract, nutritional yeast) and gravy. A moderate amount of purine is also contained in red meat, beef, pork, poultry, fish and seafood, asparagus, cauliflower, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lactams
A lactam is a cyclic amide, formally derived from an amino alkanoic acid. The term is a portmanteau of the words ''lactone'' + ''amide''. Nomenclature Greek prefixes in alphabetical order indicate ring size: * α-Lactam (3-atom rings) * β-Lactam (4-atom rings) * γ-Lactam (5-atom rings) * δ-Lactam (6-atom rings) * ε-Lactam (7-atom rings) This ring-size nomenclature stems from the fact that a hydrolyzed α-Lactam leads to an α-amino acid and a β-Lactam to a β-amino acid, ''etc''. Synthesis General synthetic methods exist for the organic synthesis of lactams. Beckmann rearrangement Lactams form by the acid-catalyzed rearrangement of oximes in the Beckmann rearrangement. Schmidt reaction Lactams form from cyclic ketones and hydrazoic acid in the Schmidt reaction. Cyclization of amino acids Lactams can be formed from cyclisation of amino acids via the coupling between an amine and a carboxylic acid within the same molecule. Lactamization is most efficient in this wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |