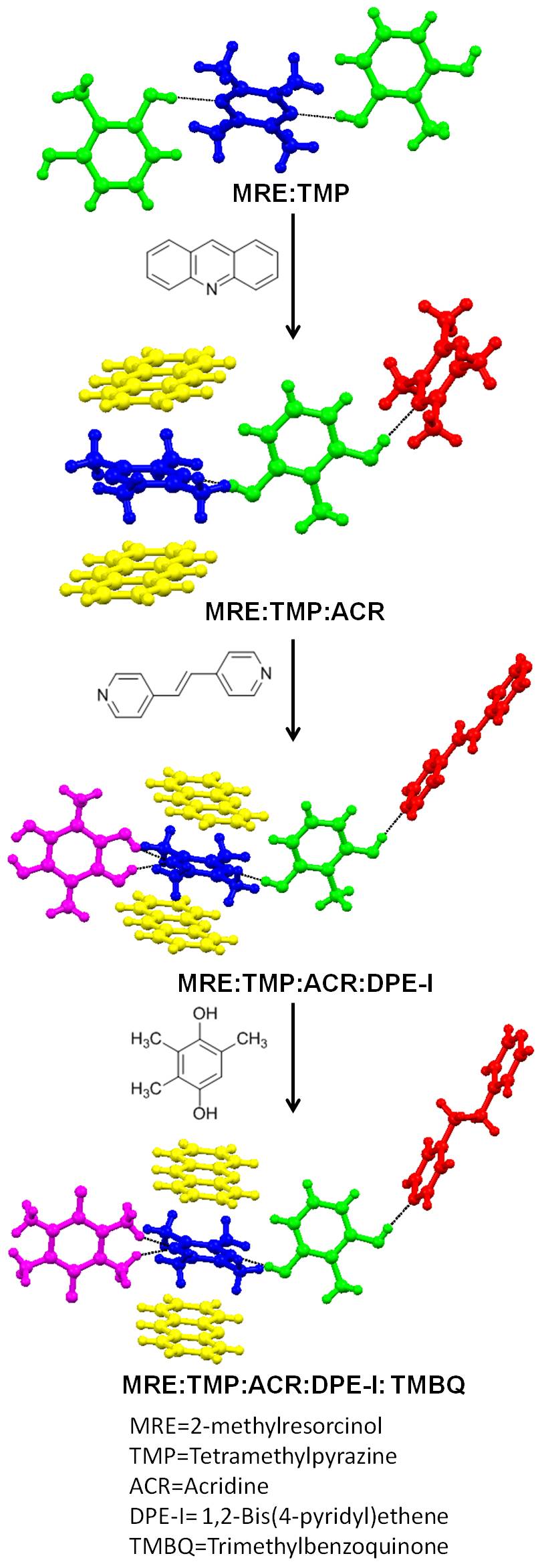
|
PIDA (polymer)
PIDA, or poly(diiododiacetylene), is an organic polymer that has a polydiacetylene backbone. It is one of the simplest polydiacetylenes that has been synthesized, having only iodine atoms as side chains. It is created by 1,4 topochemical polymerization of diiodobutadiyne. It has many implications in the field of polymer chemistry as it can be viewed as a precursor to other polydiacetylenes by replacing iodine atoms with other side chains using organic synthesis, or as an iodinated form of the carbon allotrope carbyne. Structure The backbone of PIDA is highly conjugated and allows for the formation of an extended pi system along the length of the polymer. This property of PIDA allows it to transport electricity and act as a molecular wire or an organic semiconductor. Considering PIDA's backbone and the fact that Iodine atoms can easily undergo elimination, it is conceivable that PIDA can be subjected to full reductive deiodination in the presence of a Lewis base, such as pyrrolidi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polydiacetylene
Polydiacetylenes (PDAs) are a family of conducting polymers closely related to polyacetylene. They are created by the 1,4 topochemical polymerization of diacetylenes. They have multiple applications from the development of organic films to immobilization of other molecules. History The first polydiacetylene to be discovered was Poly(1,6-bishydroxy hexa-2,4-diacetylene) by Gerhard Wegner in 1969. This was achieved by exposing crystals of 1,6-bishydroxy hexa-2,4-diyne to UV light. Polymerization was assumed to occur because of the spatial arrangement of diynes in the crystal, but this was not confirmed until 1972 when Raymond H. Baughman coined the term "topochemical polymerization" to describe polymerization due to spatial arrangement and put forth the spatial requirements needed for a polymerization of this sort. Synthesis Synthesis of polydiacetylenes occurs through topochemical polymerization of 1,3-diynes. Typically, this must occur in the solid state, because many diynes under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrrolidine
Pyrrolidine, also known as tetrahydropyrrole, is an organic compound with the molecular formula (CH2)4NH. It is a cyclic secondary amine, also classified as a saturated heterocycle. It is a colourless liquid that is miscible with water and most organic solvents. It has a characteristic odor that has been described as "ammoniacal, fishy, shellfish-like". In addition to pyrrolidine itself, many substituted pyrrolidines are known. Production and synthesis Industrial production Pyrrolidine is prepared industrially by the reaction of 1,4-butanediol and ammonia at a temperature of 165–200 °C and a pressure of 17–21 MPa in the presence of a cobalt- and nickel oxide catalyst, which is supported on alumina. : The reaction is carried out in the liquid phase in a continuous tube- or tube bundle reactor, which is operated in the cycle gas method. The catalyst is arranged as a fixed-bed and the conversion is carried out in the downflow mode. The product is obtained after mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + '' -mer'', "part") is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic and natural polymers play essential and ubiquitous roles in everyday life. Polymers range from familiar synthetic plastics such as polystyrene to natural biopolymers such as DNA and proteins that are fundamental to biological structure and function. Polymers, both natural and synthetic, are created via polymerization of many small molecules, known as monomers. Their consequently large molecular mass, relative to small molecule compounds, produces unique physical properties including toughness, high elasticity, viscoelasticity, and a tendency to form amorphous and semicrystalline structures rather than crystals. The term "polymer" derives from the Greek word πολύς (''polus'', meaning "many, much") and μέρος (''meros'', meaning "p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conductive Polymers
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that Electrical conductance, conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers is their processability, mainly by Dispersion (chemistry), dispersion. Conductive polymers are generally not thermoplastics, ''i.e.'', they are not thermoformable. But, like insulating polymers, they are organic materials. They can offer high electrical conductivity but do not show similar mechanical properties to other commercially available polymers. The electrical properties can be fine-tuned using the methods of organic synthesis and by advanced dispersion techniques. History Polyaniline was first described in the mid-19th century by Henry Letheby, who investigated the electrochemical and chemical oxidation products of aniline in acidic media. He noted that reduced form was colourless but the oxidized forms were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Engineering
Crystal engineering studies the design and synthesis of solid-state structures with desired properties through deliberate control of Intermolecular force, intermolecular interactions. It is an Interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary academic field, bridging solid-state and supramolecular chemistry. The main engineering strategies currently in use are hydrogen bond, hydrogen- and Halogen bond, halogen bonding and coordination bonding. These may be understood with key concepts such as the supramolecular synthon and the secondary building unit. History of term The term 'crystal engineering' was first used in 1955 by R. Pepinsky but the starting point is often credited to Gerhard Schmidt in connection with photodimerization reactions in crystalline cinnamic acids. Since this initial use, the meaning of the term has broadened considerably to include many aspects of solid state supramolecular chemistry. A useful modern definition is that provided by Gautam Radhakrishna Desiraju, Gaut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Structural Analog
A structural analog (analogue in modern traditional English; Commonwealth English), also known as a chemical analog or simply an analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another compound, but differing from it in respect to a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced with other atoms, groups, or substructures. A structural analog can be imagined to be formed, at least theoretically, from the other compound. Structural analogs are often isoelectronic. Despite a high chemical similarity, structural analogs are not necessarily functional analogs and can have very different physical, chemical, biochemical, or pharmacological properties. In drug discovery, either a large series of structural analogs of an initial lead compound are created and tested as part of a structure–activity relationship study or a database is screened for structural analogs of a lead compound. Chemical analogues of il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halogen Bond
A halogen bond occurs when there is evidence of a net attractive interaction between an electrophilic region associated with a halogen atom in a molecular entity and a nucleophilic region in another, or the same, molecular entity. Like a hydrogen bond, the result is not a formal chemical bond, but rather a strong electrostatic attraction. Mathematically, the interaction can be decomposed in two terms: one describing an electrostatic, orbital-mixing charge-transfer and another describing electron-cloud dispersion. Halogen bonds find application in supramolecular chemistry; drug design and biochemistry; crystal engineering and liquid crystals; and organic catalysis. Definition Halogen bonds occur when a halogen atom is electrostatically attracted to a partial negative charge. Necessarily, the atom must be covalently bonded in an antipodal σ-bond; the electron concentration associated with that bond leaves a positively charged "hole" on the other side. Although all halogens can t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugated System
In theoretical chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in a molecule, which in general lowers the overall energy of the molecule and increases stability. It is conventionally represented as having alternating single and multiple bonds. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the system, which may be cyclic, acyclic, linear or mixed. The term "conjugated" was coined in 1899 by the German chemist Johannes Thiele. Conjugation is the overlap of one p-orbital with another across an adjacent σ bond (in transition metals, d-orbitals can be involved). A conjugated system has a region of overlapping p-orbitals, bridging the interjacent locations that simple diagrams illustrate as not having a π bond. They allow a delocalization of π electrons across all the adjacent aligned p-orbitals. The π electrons do not belong to a single bond or atom, but rather to a group of atoms. Molecules containing conjugated syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diiodobutadiyne
Diiodobutadiyne (1,4-diiodobuta-1,3-diyne) is a small molecule related to diacetylene. It is used in the creation of the polymer poly(diiododiacetylene) PIDA, or poly(diiododiacetylene), is an organic polymer that has a polydiacetylene backbone. It is one of the simplest polydiacetylenes that has been synthesized, having only iodine atoms as side chains. It is created by 1,4 topochemical polymeriz ... (PIDA) by undergoing 1,4 polymerization. 1,4-Diiodobuta-1,3-diyne is light sensitive and explosive if stored out of solution as a dry solid. It will undergo random 1,2 and 1,4 polymerization, as well as decomposition in solution if kept over an extended period of time, having a half life of just about two weeks. References {{reflist Conjugated diynes Organoiodides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Acetylenic Carbon
Linear acetylenic carbon (LAC), also known as carbyne or Linear Carbon Chain (LCC), is an allotrope of carbon that has the chemical structure as a repeat unit, with alternating single and triple bonds. It would thus be the ultimate member of the polyyne family. This polymeric carbyne is of considerable interest to nanotechnology as its Young's modulus is – forty times that of diamond; this extraordinary number is, however, based on a novel definition of cross-sectional area that does not correspond to the space occupied by the structure. Carbyne has also been identified in interstellar space; however, its existence in condensed phases has been contested recently, as such chains would crosslink exothermically (and perhaps explosively) if they approached each other. History and controversy The first claims of detection of this allotrope were made in 1960Sladkov A.M, Kudryavtsev Y.P Diamond, graphite, carbyne 3/4 the allotropic forms of carbon, Priroda (Nature), 1969, 58:37 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the intentional construction of organic compounds. Organic molecules are often more complex than inorganic compounds, and their synthesis has developed into one of the most important branches of organic chemistry. There are several main areas of research within the general area of organic synthesis: ''total synthesis'', ''semisynthesis'', and ''methodology''. Total synthesis A total synthesis is the complete chemical synthesis of complex organic molecules from simple, commercially available petrochemical or natural precursors. Total synthesis may be accomplished either via a linear or convergent approach. In a ''linear'' synthesis—often adequate for simple structures—several steps are performed one after another until the molecule is complete; the chemical compounds made in each step are called synthetic intermediates. Most often, each step in a synthesis refers to a separate rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |