|
PDE4B
cAMP-specific 3',5'-cyclic phosphodiesterase 4B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PDE4B'' gene. This gene is a member of the type IV, cyclic AMP (cAMP)-specific, cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase (PDE) family. Cyclic nucleotides are important second messengers that regulate and mediate a number of cellular responses to extracellular signals, such as hormones, light, and neurotransmitters. The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDEs) regulate the cellular concentrations of cyclic nucleotides and thereby play a role in signal transduction. This gene encodes a protein that specifically hydrolyzes cAMP. Alternate transcriptional splice variants, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized. Clinical relevance Altered activity of this protein has been associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. PDE4B is believed to be the PDE4 subtype involved in the antipsychotic effects of PDE4 inhibitors such as rolipram. PDE4B is involved in dopamine-associated an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDE4 Inhibitor
A phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, commonly referred to as a PDE4 inhibitor, is a drug used to block the degradative action of phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) on cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP). It is a member of the larger family of PDE inhibitors. The PDE4 family of enzymes are the most prevalent PDE in immune cells. They are predominantly responsible for hydrolyzing cAMP within both immune cells and cells in the central nervous system. Therapeutic utility The prototypical PDE4 inhibitor is rolipram. PDE4 inhibitors are known to possess procognitive (including long term memory-improving), wakefulness-promoting, neuroprotective, and anti-inflammatory effects. Consequently, PDE4 inhibitors have been investigated as treatments for a diverse group of different diseases, including central nervous system disorders such as major depressive disorder (clinical depression), anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, multiple sclerosis, attention deficit-hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AN2728
Crisaborole, sold under the brand name Eucrisa among others, is a nonsteroidal topical medication used for the treatment of mild-to-moderate atopic dermatitis (eczema) in adults and children. The most common side effects are reactions at the application site (including burning or stinging). Crisaborole is a phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE-4) inhibitor, although its specific mechanism of action in atopic dermatitis is not known. Side effects At the site of application, crisaborole may cause burning or stinging. Rarely, there may be an allergic reaction. Medical uses In the US, crisaborole is indicated for topical treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in people three months of age and older. In the EU, crisaborole was authorized for treatment of mild to moderate atopic dermatitis in people two years of age and older with ≤ 40% body surface area (BSA) affected. Pharmacology Pharmacodynamics Crisaborole is a phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor, mainly acting on phosphodiestera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase
3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide phosphodiesterases (EC 3.1.4.17) are a family of phosphodiesterases. Generally, these enzymes hydrolyze a nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate to a nucleoside 5′-phosphate: :nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate + H2O = nucleoside 5′-phosphate They thus control the cellular levels of the cyclic second messengers and the rates of their degradation. Some examples of nucleoside 3′,5′-cyclic phosphate include: * 3′,5′-cyclic AMP *3′,5′-cyclic dAMP *3′,5′-cyclic IMP * 3′,5′-cyclic GMP *3′,5′-cyclic CMP There are 11 distinct phosphodiesterase families (PDE1–PDE11) with a variety in isoforms and splicing having unique three-dimensional structure, kinetic properties, modes of regulation, intracellular localization, cellular expression, and inhibitor sensitivities. Nomenclature The systematic name for this enzyme is 3′,5′-cyclic-nucleotide 5'-nucleotidohydrolase. Other names in use include cyclic 3′,5′-mononucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. Almost all metabolic processes in the cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts are catalytic RNA molecules, called ribozymes. Enzymes' specificity comes from their unique three-dimensional structures. Like all catalysts, enzymes increase the reaction ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
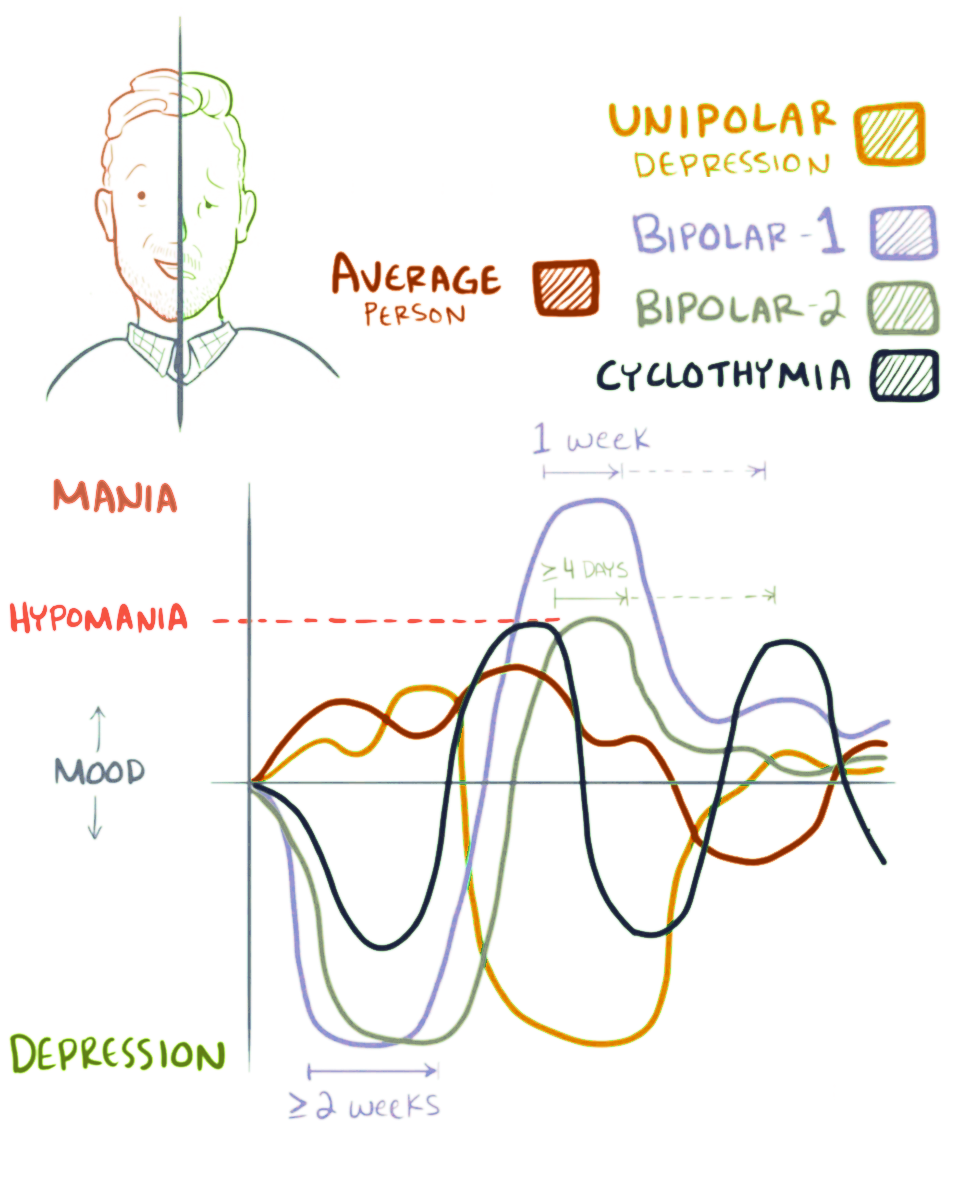
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mental disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally elevated mood that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder. While the causes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anacor
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer (1824–1906) and his cousin Charles F. Erhart (1821–1891). Pfizer develops and produces medicines and vaccines for immunology, oncology, cardiology, endocrinology, and neurology. The company has several blockbuster drugs or products that each generate more than billion in annual revenues. In 2020, 52% of the company's revenues came from the United States, 6% came from each of China and Japan, and 36% came from other countries. Pfizer was a component of the Dow Jones Industrial Average stock market index from 2004 to August 2020. The company ranks 64th on the Fortune 500 and 49th on the Forbes Global 2000. History 1849–1950: Early history Pfizer was founded in 1849 by Charles Pfizer and Charles F. Erhart, two cousins who had immi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boron
Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. In its crystalline form it is a brittle, dark, lustrous metalloid; in its amorphous form it is a brown powder. As the lightest element of the ''boron group'' it has three valence electrons for forming covalent bonds, resulting in many compounds such as boric acid, the mineral borax, sodium borate, and the ultra-hard crystals of boron carbide and boron nitride. Boron is synthesized entirely by cosmic ray spallation and supernovae and not by stellar nucleosynthesis, so it is a low-abundance element in the Solar System and in the Crust (geology), Earth's crust. It constitutes about 0.001 percent by weight of Earth's crust. It is concentrated on Earth by the water-solubility of its more common naturally occurring compounds, the borate minerals. These are mined industrially as evaporites, such as borax and kernite. The largest known deposits are in Turkey, the largest producer of boron minerals. Elemental b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolipram
Rolipram is a selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor discovered and developed by Schering AG as a potential antidepressant drug in the early 1990s. It served as a prototype molecule for several companies' drug discovery and development efforts.McKenna, JM and Muller, GW. Medicinal Chemistry of PDE4 Inhibitors. Chapter 33 in Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterases in Health and Disease, Eds Joseph A. Beavo et al. CRC Press, Dec 5, 2006 Rolipram was discontinued after clinical trials showed that its therapeutic window was too narrow; it could not be dosed at high enough levels to be effective without causing significant gastrointestinal side effects. Rolipram has several activities that make it a continuing focus for research. The etiology of many neurodegenerative diseases involves misfolded and clumped proteins which accumulate in the brain. Cells have a mechanism to dispose of such proteins called the proteasome. However, in Alzheimer's disease and some other conditions t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipsychotic
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of Psychiatric medication, psychotropic medication primarily used to manage psychosis (including delusions, hallucinations, paranoia or disordered thought), principally in schizophrenia but also in a range of other psychotic disorders. They are also the mainstay together with mood stabilizers in the treatment of bipolar disorder. Prior research has shown that use of any antipsychotic is associated with smaller brain tissue volumes, including white matter reduction and that this brain shrinkage is dose dependent and time dependent. A more recent controlled trial suggests that second generation antipsychotics combined with intensive psychosocial therapy may potentially prevent pallidal brain volume loss in first episode psychosis. The use of antipsychotics may result in many unwanted side effects such as Extrapyramidal symptoms, involuntary movement disorders, gynecomastia, impotence, weight gain and metabolic syndrome. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schizophrenia
Schizophrenia is a mental disorder characterized by continuous or relapsing episodes of psychosis. Major symptoms include hallucinations (typically hearing voices), delusions, and disorganized thinking. Other symptoms include social withdrawal, decreased emotional expression, and apathy. Symptoms typically develop gradually, begin during young adulthood, and in many cases never become resolved. There is no objective diagnostic test; diagnosis is based on observed behavior, a history that includes the person's reported experiences, and reports of others familiar with the person. To be diagnosed with schizophrenia, symptoms and functional impairment need to be present for six months (DSM-5) or one month (ICD-11). Many people with schizophrenia have other mental disorders, especially substance use disorders, depressive disorders, anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder. About 0.3% to 0.7% of people are diagnosed with schizophrenia during their lifetime. In 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |