|
PCPr
PCPr is an arylcyclohexylamine dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic and stimulant effects. It is around the same potency as phencyclidine, although slightly less potent than its ethyl homologue eticyclidine, and has reportedly been sold as a designer drug A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Des ... in Germany and other European countries since the late 1990s. Several other related derivatives have also been encountered, with the ''n''-propyl group of PCPr replaced by a 2-methoxyethyl, 2-ethoxyethyl or 3-methoxypropyl group to form PCMEA, PCEEA and PCMPA respectively. References Arylcyclohexylamines Dissociative drugs Designer drugs NMDA receptor antagonists {{hallucinogen-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamine
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arylcyclohexylamines
Arylcyclohexylamines, also known as arylcyclohexamines or arylcyclohexanamines, are a chemical class of pharmaceutical, designer, and experimental drugs. History Phencyclidine (PCP) is believed to be the first arylcyclohexylamine with recognized anesthetic properties, but several arylcyclohexylamines were described before PCP in the scientific literature, beginning with PCA (1-phenylcyclohexan-1-amine) the synthesis of which was first published in 1907. PCE was reported in 1953 and PCMo (4-(1-phenyl-cyclohexyl)-morpholine see chart below for figure) in 1954, with PCMo described as a potent sedative. Arylcyclohexylamine anesthetics were intensively investigated at Parke-Davis, beginning with the 1956 synthesis of phencyclidine and later the related compound ketamine. The 1970s saw the debut of these compounds, especially PCP and its analogues, as illicitly used recreational drugs due to their dissociative hallucinogenic and euphoriant effects. Since that time, the class has be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
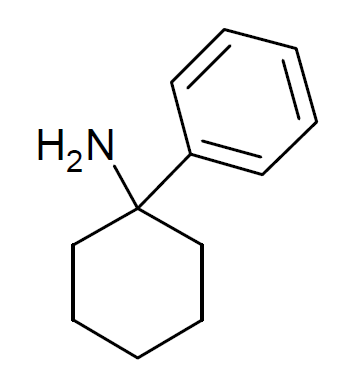
Eticyclidine
Eticyclidine (PCE, CI-400) is a dissociative anesthetic drug with hallucinogenic effects. It is similar in effects to phencyclidine but is slightly more potent. PCE was developed by Parke-Davis in the 1970s and evaluated for anesthetic potential under the code name CI-400, but research into PCE was not continued after the development of ketamine, a similar drug with more favourable properties. PCE is slightly more potent than PCP and has similar effects, but its unpleasant taste and tendency to cause nausea made it less accepted by users. Due to its similarity in effects to PCP, PCE was placed into the Schedule 1 list of illegal drugs in the 1970s, although it was only briefly abused in the 1970s and 1980s and is now little known. See also * Arylcyclohexylamine * 3-MeO-PCE * 3-MeO-PCP * 4-MeO-PCP * Phencyclidine * PCPr * Methoxetamine Methoxetamine, abbreviated as MXE, is a dissociative hallucinogen that has been sold as a designer drug. It differs from many dissociativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociative Drug
Dissociatives, colloquially dissos, are a subclass of hallucinogens which distort perception of sight and sound and produce feelings of detachment – dissociation – from the environment and/or self. Although many kinds of drugs are capable of such action, dissociatives are unique in that they do so in such a way that they produce hallucinogenic effects, which may include dissociation, a general decrease in sensory experience, hallucinations, dream-like states or anesthesia. Some of these substances, which are nonselective in action and affect the dopamine and/or opioid systems, may be capable of inducing euphoria or symptoms which are more akin to the effects of certain “hard drugs” or common drugs of abuse. This is likely why dissociatives are considered to be addictive with a fair to moderate potential for abuse, unlike psychedelics. Despite some dissociatives, such as phencyclidine (PCP) possessing stimulating properties, most dissociatives seem to have a general depre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), amnesia (loss of memory), and unconsciousness. An individual under the effects of anesthetic drugs is referred to as being anesthetized. Anesthesia enables the painless performance of procedures that would otherwise cause severe or intolerable pain in a non-anesthetized individual, or would otherwise be technically unfeasible. Three broad categories of anesthesia exist: * General anesthesia suppresses central nervous system activity and results in unconsciousness and total lack of sensation, using either injected or inhaled drugs. * Sedation suppresses the central nervous system to a lesser degree, inhibiting both anxiety and creation of long-term memories without resulting in unconsciousness. * Regional and local anesthesia, which blo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallucinogen
Hallucinogens are a large, diverse class of psychoactive drugs that can produce altered states of consciousness characterized by major alterations in thought, mood, and perception as well as other changes. Most hallucinogens can be categorized as either being psychedelics, dissociatives, or deliriants. However, certain hallucinogens such as Fly agaric as well as other gabaergic hallucinogenics are more often considered to technically be hypnotics, therefore indicating another separate subcategory of drugs which can substantially alter visual perception. Etymology The word ''hallucinogen'' is derived from the word ''hallucination''. The term ''hallucinate'' dates back to around 1595–1605, and is derived from the Latin ''hallūcinātus'', the past participle of ''(h)allūcināri'', meaning "to wander in the mind." Characteristics Leo Hollister gave five criteria for classifying a drug as hallucinogenic.Glennon RA. Classical drugs: an introductory overview. In Lin GC and Gle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulant
Stimulants (also often referred to as psychostimulants or colloquially as uppers) is an overarching term that covers many drugs including those that increase activity of the central nervous system and the body, drugs that are pleasurable and invigorating, or drugs that have Sympathomimetic drug, sympathomimetic effects. Stimulants are widely used throughout the world as prescription medicines as well as without a prescription (either legally or Prohibition (drugs), illicitly) as performance-enhancing substance, performance-enhancing or recreational drug use, recreational drugs. Among narcotics, stimulants produce a noticeable crash or ''Comedown (drugs), comedown'' at the end of their effects. The most frequently prescribed stimulants as of 2013 were lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Ritalin), and amphetamine (Adderall). It was estimated in 2015 that the percentage of the world population that had used cocaine during a year was 0.4%. For the category "amphetamines and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phencyclidine
Phencyclidine or phenylcyclohexyl piperidine (PCP), also known as angel dust among other names, is a dissociative anesthetic mainly used recreationally for its significant mind-altering effects. PCP may cause hallucinations, distorted perceptions of sounds, and violent behavior. As a recreational drug, it is typically smoked, but may be taken by mouth, snorted, or injected. It may also be mixed with cannabis or tobacco. Adverse effects may include seizures, coma, addiction, and an increased risk of suicide. Flashbacks may occur despite stopping usage. Chemically, PCP is a member of the arylcyclohexylamine class, and pharmacologically, it is a dissociative anesthetic. PCP works primarily as an NMDA receptor antagonist. PCP is most commonly used in the United States. While usage peaked in the US in the 1970s, between 2005 and 2011 an increase in visits to emergency departments as a result of the drug occurred. As of 2017 in the United States, about 1% of people in Twelfth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Designer Drug
A designer drug is a structural or functional analog of a controlled substance that has been designed to mimic the pharmacological effects of the original drug, while avoiding classification as illegal and/or detection in standard drug tests. Designer drugs include psychoactive substances that have been designated by the European Union as new psychoactive substances (NPS) as well as analogs of performance-enhancing drugs such as designer steroids. Some of these were originally synthesized by academic or industrial researchers in an effort to discover more potent derivatives with fewer side effects, and shorter duration (and possibly also because it is easier to apply for patents for new molecules) and were later co-opted for recreational use. Other designer drugs were prepared for the first time in clandestine laboratories. Because the efficacy and safety of these substances have not been thoroughly evaluated in animal and human trials, the use of some of these drugs may result i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propyl Group
In organic chemistry, propyl is a three-carbon alkyl substituent with chemical formula for the linear form. This substituent form is obtained by removing one hydrogen atom attached to the terminal carbon of propane. A propyl substituent is often represented in organic chemistry with the symbol Pr (not to be confused with the element praseodymium). An isomeric form of propyl is obtained by moving the point of attachment from a terminal carbon atom to the central carbon atom, named 1-methylethyl or isopropyl. To maintain four substituents on each carbon atom, one hydrogen atom has to be moved from the middle carbon atom to the carbon atom which served as attachment point in the ''n''-propyl variant, written as . Linear propyl is sometimes termed normal and hence written with a prefix ''n''- (i.e., ''n-''propyl), as the absence of the prefix ''n''- does not indicate which attachment point is chosen, i.e. absence of prefix does not automatically exclude the possibility of it being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biochemical Pharmacology (journal)
''Biochemical Pharmacology'' is a peer-reviewed medical journal published by Elsevier. It covers research on the pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of drugs and non-therapeutic xenobiotics. The editor-in-chief is S. J. Enna, University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City. , accessed on February 11th, 2013 Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: According to the '''', the journal received a 2019 |




.jpg)