|
Outline Of Slavic History And Culture
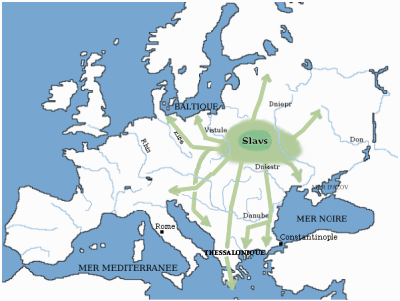
Topical outline of articles about Slavic history and culture. This outline is an overview of Slavic topics; for outlines related to specific Slavic groups and topics, see the links in the Other Slavic outlines section below. Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, mainly inhabiting Central and Eastern Europe, the Balkans, and Siberia. A large Slavic minority is also scattered across the Baltic states and Central Asia, and from the late 19th century, a substantial Slavic diaspora is found throughout the Americas. Human geography * Slavs * East Slavs, West Slavs, South Slavs * Antes people, Braničevci, Buzhans, Carantanians, Guduscani, Melingoi, Merehani, Slavs in Lower Pannonia, Praedenecenti, Sclaveni, Sebbirozi, Seven Slavic tribes, Severians, Zeriuani, Znetalici * Belarusians, B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Other Slavic Outlines
Other often refers to: * Other (philosophy), a concept in psychology and philosophy Other or The Other may also refer to: Film and television * ''The Other'' (1913 film), a German silent film directed by Max Mack * ''The Other'' (1930 film), a German film directed by Robert Wiene * ''The Other'' (1972 film), an American film directed by Robert Mulligan * ''The Other'' (1999 film), a French-Egyptian film directed by Youssef Chahine * ''The Other'' (2007 film), an Argentine-French-German film by Ariel Rotter * The Other (''Doctor Who''), a fictional character in ''Doctor Who'' * The Other (Marvel Cinematic Universe), a fictional character in the Marvel Cinematic Universe Literature * '' Other: British and Irish Poetry since 1970'', a 1999 poetry anthology * ''The Other'' (Applegate novel), a 2000 ''Animorphs'' novel by K.A. Applegate * ''The Other'' (Tryon novel), a 1971 horror novel by Tom Tryon * "The Other" (short story), a 1972 short story by Jorge Luis Borges * ''The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hungary, Romania, and the Black Sea, the South Slavs today include Bosniaks, Bulgarians, Croats, Macedonians, Montenegrins, Serbs, and Slovenes, respectively the main populations of Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, Croatia, North Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Slovenia. In the 20th century, the country of Yugoslavia (from Serbo-Croatian, literally meaning "South Slavia" or "South Slavdom") united majority of South Slavic peoples and lands—with the exception of Bulgarians and Bulgaria—into a single state. The Pan-Slavic concept of ''Yugoslavia'' emerged in the late 17th century Croatia, at the time party of Habsburg Monarchy, and gained prominence through the 19th-century Illyrian movement. The Kingdom of Serbs, Cro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Severians
The Severians or Severyans or Siverians ( be, Севяране; bg, Севери; russian: Северяне; uk, Сiверяни, translit=Siveriany) were a tribe or tribal confederation of early East Slavs occupying areas to the east of the middle Dnieper River and southeast of the Danube River. They are mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer (9th century), Emperor Constantine VII (956–959), the Khazar ruler Joseph (c. 955), and in the Primary Chronicle (1113). Ethnonym The etymology of the name "Severian" is uncertain. The name of the Severia region originated from the Slavic tribes. One theory proposes derivation from the Slavic word for "north" (''sěver''; men of the north), but the Severians never were the northernmost tribe of Slavs. Another theory proposes an Iranic derivation, from the name of the Sarmatian ''Seuer'' tribe (''seu'' meaning "black"). Some scholars have argued that Jews called this tribe the ''Sawarta,'' based on the '' Kievan Letter'' (c. 930), writ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seven Slavic Tribes
The Seven Slavic tribes ( bg, Седемте славянски племена, Sedemte slavyanski plemena), or the Seven clans ( bg, Седемте рода, Sedemte roda, links=no) were a union of Slavic tribes in the Danubian Plain, that was established around the middle of the 7th century and took part in the formation of the First Bulgarian Empire together with the Bulgars in 680−681. Since its establishment it faced attacks of the Byzantine Empire. The Bulgars crossed the Danube and in the 670's they concluded an alliance with the Slavic Union. Theophanes writes that the Bulgars became masters of the Slavs. The Slavic Union recognized the sovereignty of Khan Asparukh and together, in the spring of 681, they won a major victory over the Byzantines. In the late 7th century the Seven tribes were assigned the defence of the newly established Bulgar Khanate's western and northwestern border (the Iskar River up to its mouth in the Danube) against Avar raids, as well as som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sebbirozi
The Sebbirozi was a tribe mentioned by the 9th-century Bavarian Geographer (). It states that the Sebbirozi inhabit 90 settlements (Sebbirozi habent civitates XC). Linguist Aleksander Brückner related ''Sebbirozi'' with another tribe from the source, ''Zabrozi'', deriving from Proto-Polish ''*sebr'' (Old Polish ''siebr'' and ''siabr'', or ''szabr''), transcribing to what he believed as true names ''*sebracy'' and ''*siabracy''. Historian Henryk Łowmiański and linguist Stanisław Rospond connected the ethnonym to the Severians, while the others to the Sabirs The Sabirs (Savirs, Suars, Sawar, Sawirk among others; el, Σάβιροι) were nomadic people who lived in the north of the Caucasus beginning in the late-5th -7th century, on the eastern shores of the Black Sea, in the Kuban area, and possibly .... More recently, Krzysztof Tomasz Witczak also treats the Sebbirozi as one of the five Turkic tribes from the source, precisely the Sabirs. Already in 1958 Łowmiański conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclaveni
The ' (in Latin) or ' (various forms in Greek, see below) were early Slavic tribes that raided, invaded and settled the Balkans in the Early Middle Ages and eventually became the progenitors of modern South Slavs. They were mentioned by early Byzantine chroniclers as barbarians having appeared at the Byzantine borders along with the Antes ( East Slavs), another Slavic group. The Sclaveni were differentiated from the Antes and Wends (West Slavs); however, they were described as kin. Eventually, most South Slavic tribes accepted Byzantine or Frankish suzerainty, and came under their cultural influences and Chalcedonian Christianity. The term was widely used as general catch-all term until the emergence of separate tribal names by the 10th century. Customs The Sclaveni had similar if not identical customs and culture as the Antes. They were carefully described by chroniclers such as Procopius and Maurice, whose works contribute greatly to our understanding of these two Earl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praedenecenti
Praedenecenti was an early medieval Slavic tribe, mentioned only in the '' Royal Frankish Annals'' in 822 and 824. They lived in the buffer zone between the Carolingian and Bulgarian empires. The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' associated them with the Abodriti, while modern scholars have also connected them to other Slavic tribes, especially the Braničevci or Merehani. The Praedenecenti sought assistance from the Franks against the Bulgars, but they obviously lost their independence because they were not mentioned after 824. Sources The Praedenecenti was an "enigmatic" tribe living near the Middle Danube frontier of the Carolingian Empire in the 820s. The '' Royal Frankish Annals'' mentioned them twice (under the years 822 and 824), but no other written primary source referred to them. Since the ''Royal Frankish Annals'' apparently associated them with the Abodriti (a Slavic tribe near the Baltic Sea), Vasil Gyuzelev equates them with the "Ostabtrezi" (or Eastern Abodriti), whom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavs In Lower Pannonia
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spodnja Panonija) was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into ''Upper'' and ''Lower'' inherited from the Roman terminology. From the middle of the 6th to the end of the 8th century, the region was under the domination of the Avars, while the Slavic inhabitants lived under Avar rule. By the beginning of the 9th century, that state was destroyed and replaced by the supreme rule of the Frankish Empire, which lasted until the Magyar conquest (c. 900). During the Frankish period, the region of Lower Pannonia was governed by local Slavic rulers, who were under the suzerainty of Frankish kings. Within the Frankish administrative system, the March of Pannoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merehani
The ''Merehani'' was a Slavic tribe mentioned by the Bavarian Geographer. They are often connected to the Moravians (''Marhari''), although some scholars believe that the tribe was separate. The 9th-century ''Catalogue of Fortresses and Regions to the North of the Danube''which lists the peoples along the borders of East Francia in a north-to-south ordermentions that the Moravians or ''Marharii'' had 11 fortresses or ''civitates''. The document locates the ''Marhari'' between the Bohemians and the Bulgars The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomad ..., and also makes mention of the ''Merehani'' and their 30 fortresses. According to Havlík, who writes that ''Conversion'' is a consolidated version of notes made by several authors in different years, the Moravians are twice me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melingoi
The Melingoi or Milingoi ( el, Μηλιγγοί) were a Slavic tribe that settled in the Peloponnese in southern Greece during the Middle Ages. In the early decades of the 7th century, Slavic tribes (Sclaveni) settled throughout the Balkans following the collapse of the Byzantine Empire's defense of the Danube frontier with some groups reaching as far south as the Peloponnese. The Sclaveni often settled in small groups (i.e., families and clans) and their demographic impact in mainland Greece was both weak and diffuse. Of these, two groups are known by name from later sources, the Melingoi and the Ezeritai, of whom the Melingoi settled on the western slopes of Mount Taygetos. The origin and etymology of the name ''Melingoi'' is unknown. History Like the Ezeritai, the Melingoi are first mentioned in the ''De administrando imperio'', a manual on statecraft written by the Byzantine emperor Constantine VII Porphyrogennetos (r. 945–959). The emperor records that in his time they pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guduscani (905–959) menti ...
The Guduscani or Goduscani ( hr, Guduščani, Gačani) were a tribe whose location and origin on the territory of early medieval Croatia remains a matter of dispute. According to one hypothesis they were located around present-day Gacka (Lika), between upper Kupa river and the Dalmatian coast, or that were inhabitants around the river Guduča near the Bribir region. Etymology They are mentioned three times in the ''Frankish Annals'' (''Guduscani'', ''Guduscanorum'', ''Guduscanis'') and twice in '' Vita Hludovici'' (''Goduscanorum''). Petar Skok and Radoslav Katičić derived their ethnonym from Proto-Slavic ''*gъd-'', similar to Proto-Prussian ''gude'' in the meaning of "forest". Skok, and Petar Šimunović, also derived it from Proto-Slavic ''*gadъ'' ('' [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carantanians
Carantanians ( la, Quarantani, sl, Karantanci) were a Slavic people of the Early Middle Ages (Latin: , or "Slavs called Caranthanians"), living in the principality of Carantania, later known as Carinthia, which covered present-day southern Austria and parts of Slovenia. They are considered ancestors of modern Slovenes, particularly Carinthian Slovenes. In the high Middle Ages, the term Carantanians and Carinthians were used interchangibly and denoted both the inhabitants of the bilingual Slavic-German Duchy of Carinthia, as well as South Slavs living within the borders of the Holy Roman Empire (that is, the ancestors of present-day Slovenes and Istrian Croats). Historical background After the disintegration of Samo's realm, Alpine Slavs established the Principality of Carantania in the Eastern Alps, which was independent from around 660 to around 745, when it fell under the Bavarian zone of influence and was later incorporated in the Frankish Empire. The formation of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |