|
Organophosphorus
Organophosphorus compounds are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents. Organophosphorus chemistry is the corresponding science of the properties and reactivity of organophosphorus compounds. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. It has a concentration in the Earth's crust of about one gram per kilogram (compare copper at about 0.06 grams). In minerals, phosphorus generally occurs as phosphate. Elemental phosphorus was first isolated as white phosphorus in 1669. White phosphorus emits a faint glow when exposed to oxygen – hence the name, taken from Greek mythology, meaning 'light-bearer' (Latin ), referring to the " Morning Star", the planet Venus. The term '' phosphorescence'', meaning glow after illumination, derives from this property of phosphorus, although the word has since been used for a different physical process that produces a glow. The glow of phosphorus is caused by oxidation of the white (but not red) phosphorus — a process now called chem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
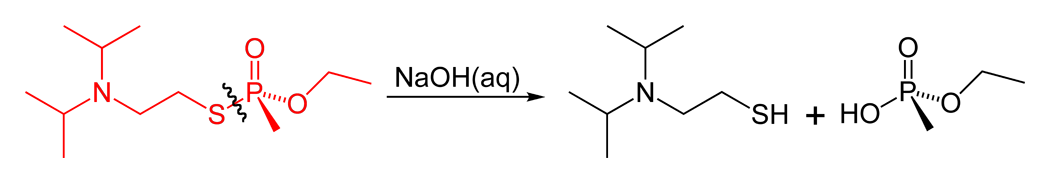
VX (nerve Agent)
VX is an extremely toxic synthetic chemical compound in the organophosphorus class, specifically, a thiophosphonate. In the class of nerve agents, it was developed for military use in chemical warfare after translation of earlier discoveries of organophosphate toxicity in pesticide research. In recent years, VX was found to be the agent used in the assassination of Kim Jong-nam. In its pure form, VX is an oily, relatively non-volatile liquid that is amber-like in colour. Because of its low volatility, VX persists in environments where it is dispersed. VX, short for "venomous agent X", is one of the best known of the V nerve agents and was first discovered at Porton Down by Ranajit Ghosh in England during the early 1950s based on research first done by Gerhard Schrader, a chemist working for IG Farben in Germany during the 1930s. It is now one of a broader V-series of agents which are classified as nerve agents and have been used as a chemical weapon in various recorded dead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB G-series, "B"">Nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for Nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic synthetic organophosphorus compound.Sarin (GB) Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed April 20, 2009. A colourless, odourless , it is used as a due to its extreme potency as a . Exposure is lethal even at very low concen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flame Retardant
The term flame retardants subsumes a diverse group of chemicals that are added to manufactured materials, such as plastics and textiles, and surface finishes and coatings. Flame retardants are activated by the presence of an ignition source and are intended to prevent or slow the further development of ignition by a variety of different physical and chemical methods. They may be added as a copolymer during the polymerisation process, or later added to the polymer at a moulding or extrusion process or (particularly for textiles) applied as a topical finish. Mineral flame retardants are typically additive while organohalogen and organophosphorus compounds can be either reactive or additive. Classes Both Reactive and Additive Flame retardants types, can be further separated into four distinct classes: * Minerals such as aluminium hydroxide (ATH), magnesium hydroxide (MDH), huntite and hydromagnesite, various hydrates, red phosphorus, and boron compounds, mostly borates. * Organ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. The study of the properties, reactions, and syntheses of organic compounds comprise the discipline known as organic chemistry. For historical reasons, a few classes of carbon-containing compounds (e.g., carbonate salts and cyanide salts), along with a few other exceptions (e.g., carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide), are not classified as organic compounds and are considered inorganic. Other than those just named, little consensus exists among chemists on precisely which carbon-containing compounds are excluded, making any rigorous definition of an organic compound elusive. Although organic compounds make up only a small percentage of Earth's crust, they are of central importance because all known life is based on organic compounds. Living t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glyphosate
Glyphosate (IUPAC name: ''N''-(phosphonomethyl)glycine) is a broad-spectrum Herbicide, systemic herbicide and Crop desiccation, crop desiccant. It is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphonate, which acts by inhibiting the plant enzyme 5-enolpyruvylshikimate-3-phosphate synthase. It is used to kill weeds, especially annual Forbs, broadleaf weeds and grasses that compete with crops. Its herbicidal effectiveness was discovered by Monsanto chemist John E. Franz in 1970. Monsanto brought it to market for agricultural use in 1974 under the trade name Roundup (herbicide), Roundup. Monsanto's last commercially relevant United States patent expired in 2000. Farmers quickly adopted glyphosate for agricultural weed control, especially after Monsanto introduced glyphosate-resistant Roundup Ready crops, enabling farmers to kill weeds without killing their crops. In 2007, glyphosate was the most used herbicide in the United States' agricultural sector and the second-most use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphonate
In organic chemistry, phosphonates or phosphonic acids are organophosphorus compounds containing groups (where R = alkyl, aryl, or just hydrogen). Phosphonic acids, typically handled as salts, are generally nonvolatile solids that are poorly soluble in organic solvents, but soluble in water and common alcohols. Many commercially important compounds are phosphonates, including glyphosate (the active molecule of the herbicide Roundup), and ethephon, a widely used plant growth regulator. Bisphosphonates are popular drugs for treatment of osteoporosis.Svara, J.; Weferling, N.; Hofmann, T. "Phosphorus Compounds, Organic," in ''Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry'', Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2008. . In biochemistry and medicinal chemistry, phosphonate groups are used as stable bioisoteres for phosphate, such as in the antiviral nucleotide analog, Tenofovir, one of the cornerstones of anti-HIV therapy. And there is an indication that phosphonate derivatives are "promising ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid . The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosphoric acid by the removal of three protons . Removal of one or two protons gives the dihydrogen phosphate ion and the hydrogen phosphate ion ion, respectively. These names are also used for salts of those anions, such as ammonium dihydrogen phosphate and trisodium phosphate. File:3-phosphoric-acid-3D-balls.png, Phosphoricacid File:2-dihydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Dihydrogenphosphate File:1-hydrogenphosphate-3D-balls.png, Hydrogenphosphate File:0-phosphate-3D-balls.png, Phosphate In organic chemistry, phosphate or orthophosphate is an organophosphate, an ester of orthophosphoric acid of the form where one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by organic groups. An example is trimethyl phosphate, . The term also refers to the triv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phosphate Ester
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or Aryl, aromatic substituents. They can be considered as esters of phosphoric acid. Like most functional groups, organophosphates occur in a diverse range of forms, with important examples including key biomolecules such as DNA, RNA and adenosine triphosphate, ATP, as well as many insecticides, herbicides, nerve agents and flame retardants. OPEs have been widely used in various products as flame retardants, plasticizers, and performance additives to engine oil. The popularity of OPEs as flame retardants came as a substitution for the highly regulated brominated flame retardants. The low cost of production and compatibility to diverse polymers made OPEs to be widely used in industry including textile, furniture, electronics as plasticizers and flame retardants. These compounds are added t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pnictogen
A pnictogen ( or ; from grc, πνῑ́γω "to choke" and -gen, "generator") is any of the chemical elements in group 15 of the periodic table. Group 15 is also known as the nitrogen group or nitrogen family. Group 15 consists of the elements nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), arsenic (As), antimony (Sb), bismuth (Bi), and moscovium (Mc). Since 1988, IUPAC calls it Group 15. Before that, in America it was called Group VA, owing to a text by H. C. Deming and the Sargent-Welch Scientific Company, while in Europe it was called Group VB and IUPAC recommended that in 1970. (Pronounced "group five A" and "group five B"; "V" is the Roman numeral 5). In semiconductor physics, it is still usually called Group V. The "five" ("V") in the historical names comes from the " pentavalency" of nitrogen, reflected by the stoichiometry of compounds such as N2O5. They have also been called the pentels. Characteristics Chemical Like other groups, the members of this family show similar patterns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituent
A substituent is one or a group of atoms that replaces (one or more) atoms, thereby becoming a moiety in the resultant (new) molecule. (In organic chemistry and biochemistry, the terms ''substituent'' and ''functional group'', as well as ''side chain'' and '' pendant group'', are used almost interchangeably to describe those branches from the parent structure, though certain distinctions are made in polymer chemistry. In polymers, side chains extend from the backbone structure. In proteins, side chains are attached to the alpha carbon atoms of the amino acid backbone.) The suffix ''-yl'' is used when naming organic compounds that contain a single bond replacing one hydrogen; ''-ylidene'' and ''-ylidyne'' are used with double bonds and triple bonds, respectively. In addition, when naming hydrocarbons that contain a substituent, positional numbers are used to indicate which carbon atom the substituent attaches to when such information is needed to distinguish between isomers. Su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Dithiophosphate
Zinc dialkyldithiophosphates (often referred to as ZDDP) are a family of coordination compounds developed in the 1940s that feature zinc bound to the anion of a dialkyldithiophosphoric salt (e.g., ammonium diethyl dithiophosphate). These uncharged compounds are not salts. They are soluble in nonpolar solvents, and the longer-chain derivatives easily dissolve in mineral and synthetic oils used as lubricants. They come under CAS number . In aftermarket oil additives, the percentage of ZDDP ranges approximately between 2 and 15%. Zinc dithiophosphates have many names, including ZDDP, ZnDTP, and ZDP. Applications The main application of ZDDPs are as anti-wear additives in lubricants including greases, hydraulic oils, and motor oils. ZDDPs also act as corrosion inhibitors and antioxidants. They are almost ubiquitous in lubricants, and treatment rates are usually between 600 ppm for modern, energy-conserving low-viscosity oils to 2000 ppm of this additive in some racing oils. It ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

