|
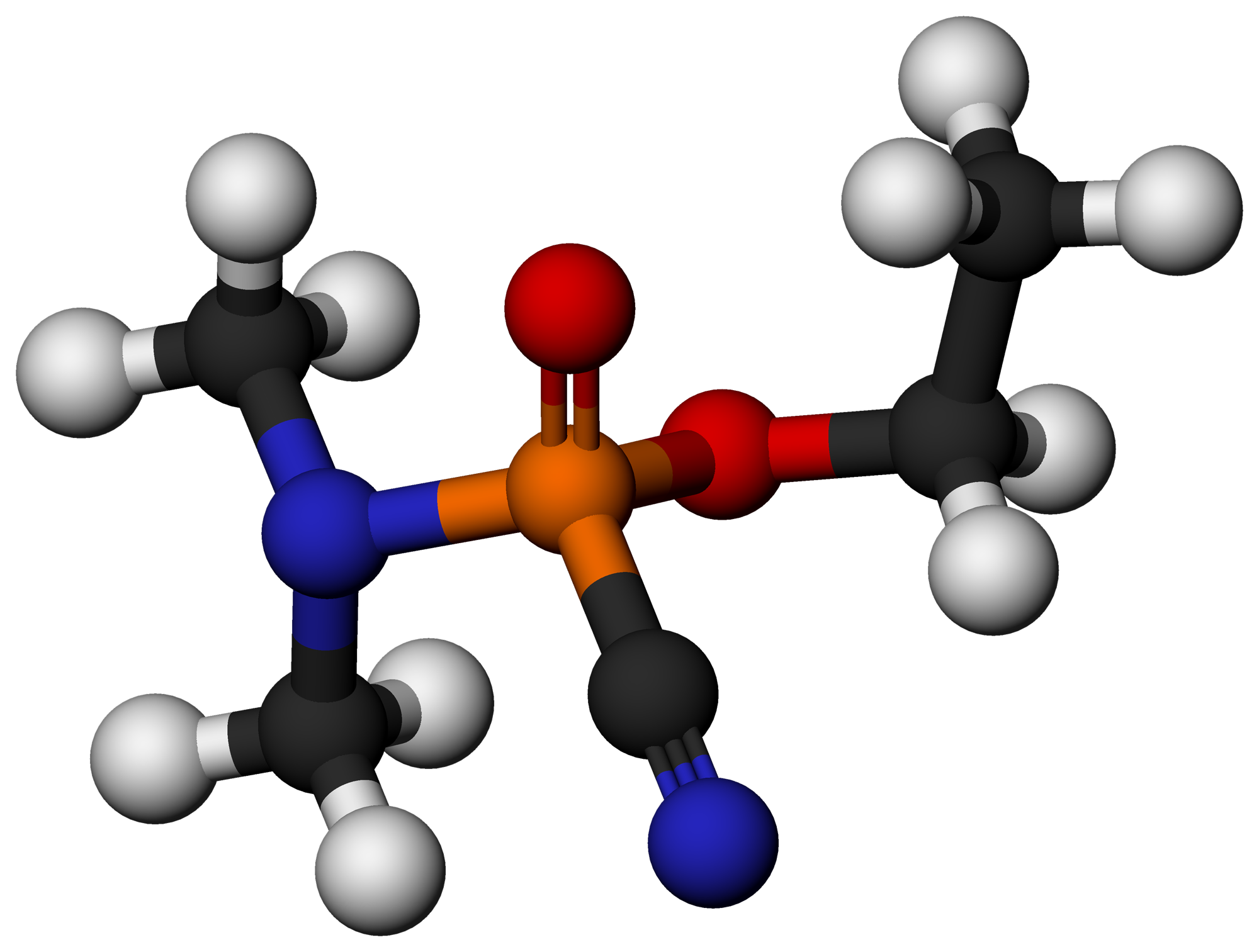
Sarin
Sarin (NATO designation GB nerve_agent#G-series.html" ;"title="hort for nerve agent#G-series">G-series, "B" is an extremely toxic organophosphorus compound.Sarin (GB) Emergency Response Safety and Health Database. National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health. Accessed April 20, 2009. that has been often used as a due to its extreme potency as a . Sarin is a volatile, colorless and odorless liquid. Exposure can be lethal even at very low concentrations, and death can occur within one to ten minutes after direct inhalation of a leth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Weapon
A chemical weapon (CW) is a specialized munition that uses chemicals formulated to inflict death or harm on humans. According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), this can be any chemical compound intended as a weapon "or its precursor that can cause death, injury, temporary incapacitation or sensory irritation through its chemical action. Munitions or other delivery devices designed to deliver chemical weapons, whether filled or unfilled, are also considered weapons themselves." Chemical weapons are classified as weapons of mass destruction (WMD), though they are distinct from nuclear weapons, biological weapons, and radiological weapons. All may be used in warfare and are known by the military acronym NBC (for nuclear, biological, and chemical warfare). Weapons of mass destruction are distinct from conventional weapons, which are primarily effective due to their explosive, kinetic, or incendiary potential. Chemical weapons can be widely ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
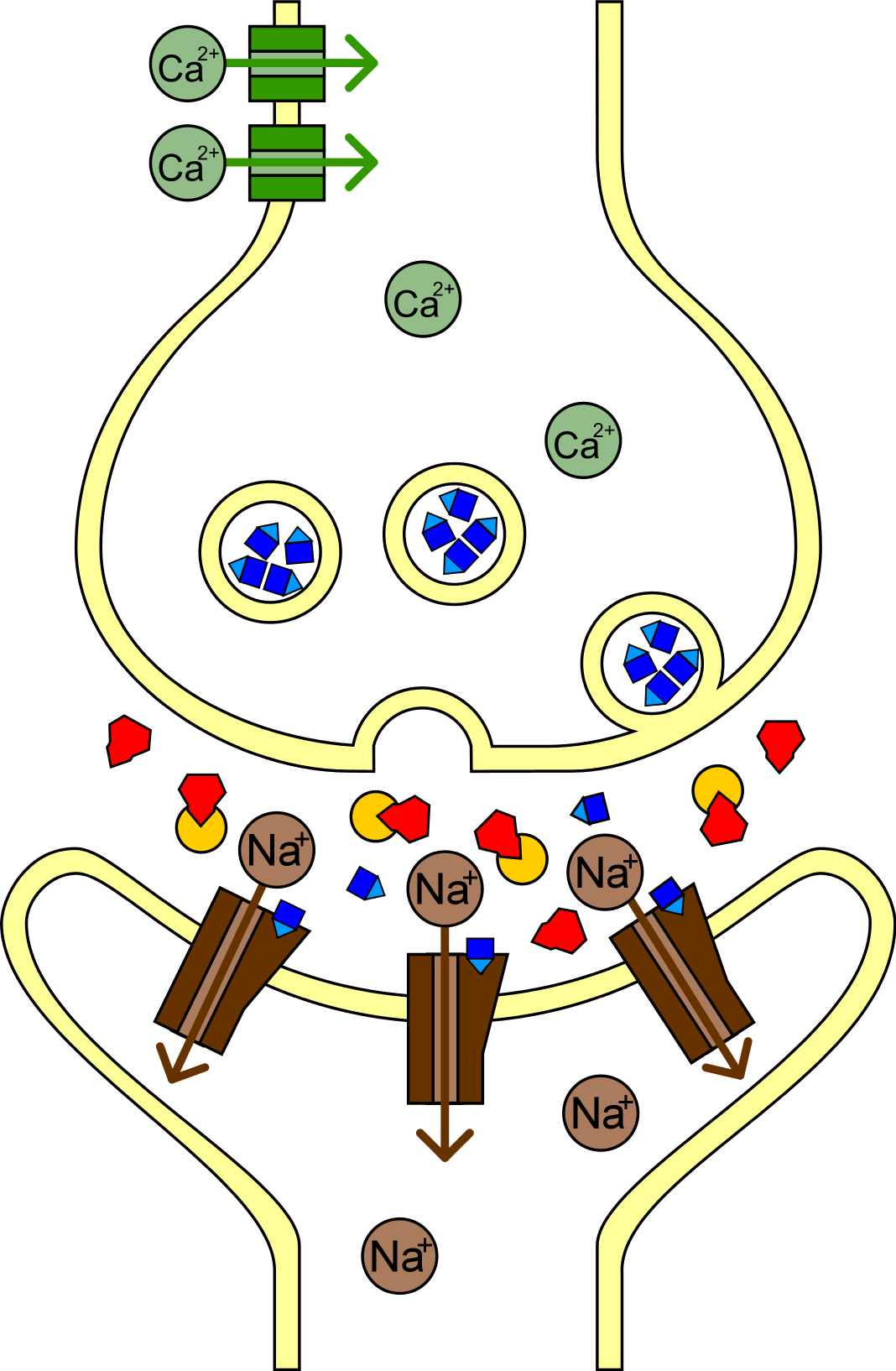
Nerve Agent
Nerve agents, sometimes also called nerve gases, are a class of organic chemistry, organic chemicals that disrupt the mechanisms by which nerves transfer messages to organs. The disruption is caused by the blocking of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), an enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter. Nerve agents are irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors used as poison. Poisoning by a nerve agent leads to constriction of pupils, profuse salivation, convulsions, and involuntary urination and defecation, with the first symptoms appearing in seconds after exposure. Death by asphyxiation or cardiac arrest may follow in minutes due to the loss of the body's control over Respiration (physiology), respiratory and other muscles. Some nerve agents are readily vaporized or aerosolized, and the primary portal of entry into the body is the respiratory system. Nervous agents can also be absorbed through the skin, requiring that those likely to be subjected to su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weapon Of Mass Destruction
A weapon of mass destruction (WMD) is a biological, chemical, radiological, nuclear, or any other weapon that can kill or significantly harm many people or cause great damage to artificial structures (e.g., buildings), natural structures (e.g., mountains), or the biosphere. The scope and usage of the term has evolved and been disputed, often signifying more politically than technically. Originally coined in reference to aerial bombing with chemical explosives during World War II, it has later come to refer to large-scale weaponry of warfare-related technologies, such as biological, chemical, radiological, or nuclear warfare. Early usage The first use of the term "weapon of mass destruction" on record is by Cosmo Gordon Lang, Archbishop of Canterbury, in 1937 in reference to the bombing of Guernica, Spain: At the time, nuclear weapons had not been developed fully. Japan conducted research on biological weapons, and chemical weapons had seen wide battlefield use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organophosphorus Compound
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX (nerve agent), VX nerve agents. Phosphorus, like nitrogen, is in pnictogen, group 15 of the periodic table, and thus phosphorus compounds and nitrogen compounds have many similar properties. The definition of organophosphorus compounds is variable, which can lead to confusion. In industrial and environmental chemistry, an organophosphorus compound need contain only an organic substituent, but need not have a direct phosphorus-carbon (P-C) bond. Thus a large proportion of pesticides (e.g., malathion), are often included in this class of compounds. Phosphorus can adopt a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pralidoxime
Pralidoxime (2-pyridine aldoxime methyl chloride) or 2-PAM, usually as the chloride or iodide salts, belongs to a family of compounds called oximes that bind to organophosphate-inactivated acetylcholinesterase. It is used to treat organophosphate poisoning in conjunction with atropine and either diazepam or midazolam. It is a white solid. Chemical synthesis Pralidoxime, 2-pyridinaldoxime methylchloride, is prepared by treating pyridine-2-carboxaldehyde with hydroxylamine. The resulting pyridine-2-aldoxime is alkylated with methyl iodide giving pralidoxime as the iodide salt. Mechanism of action Pralidoxime is typically used in cases of organophosphate poisoning. Organophosphates such as sarin bind to the hydroxy component (the site) of the active site of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, thereby blocking its activity. Pralidoxime binds to the other half (the unblocked, anionic site) of the active site and then displaces the phosphate from the serine residue. The conjoine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Schedule 1 Substances (CWC)
Schedule 1 substances, in the sense of the Chemical Weapons Convention, are chemicals which are feasible either to be used directly as chemical weapons or in the manufacture of chemical weapons, and which have very limited to no use outside of chemical warfare. These may be produced or used for research, medical, pharmaceutical or chemical weapon defence testing (called "protective testing" in the treaty) purposes but production above 100 grams per year must be declared to the OPCW in accordance with Part VI of the "Verification Annex". A country is limited to possessing a maximum of one tonne of these materials. Schedule 1 is divided into Part A substances, which are chemicals that can be used directly as weapons, and Part B which are precursors useful in the manufacture of chemical weapons. Examples are mustard and nerve agents, and substances which are solely used as precursor chemicals in their manufacture. A few of these chemicals have very small-scale non-military applicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SLUDGE Syndrome
A cholinergic crisis is an over-stimulation at a neuromuscular junction due to an excess of acetylcholine, as a result of the inactivity of the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, which normally breaks down acetylcholine. Signs and symptoms As a result of cholinergic crisis, the muscles stop responding to the high synaptic levels of acetylcholine, leading to flaccid paralysis, respiratory failure, and other signs and symptoms reminiscent of organophosphate poisoning. Other symptoms include increased sweating, salivation, bronchial secretions along with miosis (constricted pupils). Some of the symptoms of increased cholinergic stimulation include: * Salivation: stimulation of the salivary glands * Lacrimation: stimulation of the lacrimal glands (tearing) * Urination: relaxation of the internal sphincter muscle of urethra, and contraction of the detrusor muscles * Defecation * Gastrointestinal distress: Smooth muscle tone changes causing gastrointestinal problems, including cramp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic compound that functions in the brain and body of many types of animals (including humans) as a neurotransmitter. Its name is derived from its chemical structure: it is an ester of acetic acid and choline. Parts in the body that use or are affected by acetylcholine are referred to as cholinergic. Acetylcholine is the neurotransmitter used at the neuromuscular junction. In other words, it is the chemical that motor neurons of the nervous system release in order to activate muscles. This property means that drugs that affect cholinergic systems can have very dangerous effects ranging from paralysis to convulsions. Acetylcholine is also a neurotransmitter in the autonomic nervous system, both as an internal transmitter for both the sympathetic nervous system, sympathetic and the parasympathetic nervous system, and as the final product released by the parasympathetic nervous system. Acetylcholine is the primary neurotransmitter of the parasympathet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Weapons Convention
The Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), officially the Convention on the Prohibition of the Development, Production, Stockpiling and Use of Chemical Weapons and on their Destruction, is an arms control treaty administered by the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW), an intergovernmental organization based in The Hague, Netherlands. The treaty entered into force on 29 April 1997. It prohibits the use of chemical weapons, and the large-scale development, production, stockpiling, or transfer of chemical weapons or their precursors, except for very limited purposes (research, medical, pharmaceutical or protective). The main obligation of member states under the convention is to effect this prohibition, as well as the destruction of all current chemical weapons. All destruction activities must take place under OPCW verification. 193 states have become parties to the CWC and accept its obligations. Israel has signed but not ratified the agreement, while three o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given intravenously or by injection into a muscle. Eye drops are also available which are used to treat uveitis and early amblyopia. The intravenous solution usually begins working within a minute and lasts half an hour to an hour. Large doses may be required to treat some poisonings. Common side effects include dry mouth, abnormally large pupils, urinary retention, constipation, and a fast heart rate. It should generally not be used in people with closed-angle glaucoma. While there is no evidence that its use during pregnancy causes birth defects, this has not been well studied so sound clinical judgment should be used. It is likely safe during breastfeeding. It is an antimuscarinic (a type of anticholinergic) that works by inhibit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spasm
A spasm is a sudden involuntary contraction of a muscle, a group of muscles, or a hollow organ, such as the bladder. A spasmodic muscle contraction may be caused by many medical conditions, including dystonia. Most commonly, it is a muscle cramp which is accompanied by a sudden burst of pain. A muscle cramp is usually harmless and ceases after a few minutes. It is typically caused by ion imbalance or muscle fatigue. There are other causes of involuntary muscle contractions, and some of these may cause a health problem. A series of spasms, or permanent spasms, is referred to as a "spasmism". Description and causes Spasms occur when the part of the brain that controls movement malfunctions, causing involuntary muscle activity. A spasm may be a muscle contraction caused by abnormal nerve stimulation or by abnormal activity of the muscle itself. Causes The cause of spasms is often unknown, but it can be due to an inherited genetic problem, a side effect of medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |