|
Org 27569
Org 27569 is a drug which acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. Studies ''in vitro'' suggest that it binds to a regulatory site on the CB1 receptor target, causing a conformational change that increases the binding affinity of CB1 agonists such as CP 55,940, while decreasing the binding affinity of CB1 antagonists or inverse agonists such as rimonabant. However while Org 27569 increases the ability of CB1 agonists to bind to the receptor, it decreases their efficacy at stimulating second messenger signalling once bound, and so in practice behaves as an insurmountable antagonist of CB1 receptor function. See also * GAT100 * PSNCBAM-1 * ZCZ-011 ZCZ-011 is a positive allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic c ... References Cannabinoids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allosteric Modulator
In pharmacology and biochemistry, allosteric modulators are a group of substances that bind to a receptor to change that receptor's response to stimulus. Some of them, like benzodiazepines, are drugs. The site that an allosteric modulator binds to (i.e., an ''allosteric site'') is not the same one to which an endogenous agonist of the receptor would bind (i.e., an ''orthosteric site''). Modulators and agonists can both be called receptor ligands. Allosteric modulators can be 1 of 3 types either: positive, negative or neutral. Positive types increase the response of the receptor by increasing the probability that an agonist will bind to a receptor (i.e. affinity), increasing its ability to activate the receptor (i.e. efficacy), or both. Negative types decrease the agonist affinity and/or efficacy. Neutral types don't affect agonist activity but can stop other modulators from binding to an allosteric site. Some modulators also work as allosteric agonists. The term "allosteric" de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid
Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic compounds. The most notable cannabinoid is the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) (delta-9-THC), the primary intoxicating compound in cannabis. Cannabidiol (CBD) is a major constituent of temperate Cannabis plants and a minor constituent in tropical varieties. At least 113 distinct phytocannabinoids have been isolated from cannabis, although only four (i.e., THCA, CBDA, CBCA and their common precursor CBGA) have been demonstrated to have a biogenetic origin. It was reported in 2020 that phytocannabinoids can be found in other plants such as rhododendron, licorice and liverwort, and earlier in Echinacea. Phytocannabinoids are multi-ring phenolic compounds structurally related to THC, but endocannabinoids are fatty acid derivatives. Nonclassical synthetic cannabinoids (cannabimimetics) include amin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cannabinoid Receptor 1
Cannabinoid receptor type 1 (CB1), also known as cannabinoid receptor 1, is a G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor that in humans is encoded by the ''CNR1'' gene. The human CB1 receptor is expressed in the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system. It is activated by: endocannabinoids, a group of retrograde neurotransmitters that include anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG); plant phytocannabinoids, such as the compound THC which is an active ingredient of the psychoactive drug cannabis; and, synthetic analogs of THC. CB1 is antagonized by the phytocannabinoid tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV). The primary endogenous agonist of the human CB1 receptor is anandamide. Structure The CB1 receptor shares the structure characteristic of all G-protein-coupled receptors, possessing seven transmembrane domains connected by three extracellular and three intracellular loops, an extracellular N-terminal tail, and an intracellular C-terminal tail. The receptor ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor (biochemistry)
In biochemistry and pharmacology, receptors are chemical structures, composed of protein, that receive and transduce signals that may be integrated into biological systems. These signals are typically chemical messengers which bind to a receptor and cause some form of cellular/tissue response, e.g. a change in the electrical activity of a cell. There are three main ways the action of the receptor can be classified: relay of signal, amplification, or integration. Relaying sends the signal onward, amplification increases the effect of a single ligand, and integration allows the signal to be incorporated into another biochemical pathway. Receptor proteins can be classified by their location. Transmembrane receptors include ligand-gated ion channels, G protein-coupled receptors, and enzyme-linked hormone receptors. Intracellular receptors are those found inside the cell, and include cytoplasmic receptors and nuclear receptors. A molecule that binds to a receptor is called a li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dissociation Constant
In chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmacology, a dissociation constant (K_D) is a specific type of equilibrium constant that measures the propensity of a larger object to separate (dissociate) reversibly into smaller components, as when a complex falls apart into its component molecules, or when a salt splits up into its component ions. The dissociation constant is the inverse of the association constant. In the special case of salts, the dissociation constant can also be called an ionization constant. For a general reaction: : A_\mathit B_\mathit \mathit A + \mathit B in which a complex \ce_x \ce_y breaks down into ''x'' A subunits and ''y'' B subunits, the dissociation constant is defined as : K_D = \frac where and ''x'' B''y''are the equilibrium concentrations of A, B, and the complex A''x'' B''y'', respectively. One reason for the popularity of the dissociation constant in biochemistry and pharmacology is that in the frequently en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP 55,940
55,940 is a synthetic cannabinoid which mimics the effects of naturally occurring THC (one of the psychoactive compounds found in cannabis). CP 55,940 was created by Pfizer in 1974 but was never marketed. It is currently used to study the endocannabinoid system. A study found that CP 55,940 can upregulate 5-HT2A receptors in mice. CP 55,940 is 45 times more potent than Δ9-THC, and fully antagonized by rimonabant (SR141716A). CP 55,940 is considered a full agonist at both CB1 and CB2 receptors and has Ki values of 0.58 nM and 0.68 nM respectively, but is an antagonist at GPR55, the putative "CB3" receptor. CP 55,940 showed protective effects on rat brain mitochondria upon paraquat exposure. It also showed neuroprotective effects by reducing intracellular calcium release and reducing hippocampal cell death in cultured neurons subjected to high levels of NMDA ''N''-methyl--aspartic acid or ''N''-methyl--aspartate (NMDA) is an amino acid derivative that acts as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimonabant
Rimonabant (also known as SR141716; trade names Acomplia, Zimulti) is an anorectic antiobesity drug that was first approved in Europe in 2006 but was withdrawn worldwide in 2008 due to serious psychiatric side effects; it was never approved in the United States. Rimonabant is an inverse agonist for the cannabinoid receptor CB1 and was the first drug approved in that class. History Rimonabant is a selective CB1 receptor blocker and was discovered and developed by Sanofi-Aventis; On 21 June 2006, the European Commission approved the sale of rimonabant in the then-25-member European Union as a prescription drug for use in conjunction with diet and exercise for patients with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 30 kg/m2, or patients with a BMI greater than 27 kg/m2 with associated risk factors, such as type 2 diabetes or dyslipidaemia. FroEMA index page/ref> It was first in its class to be approved anywhere in the world. Rimonabant was submitted to the Food and D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
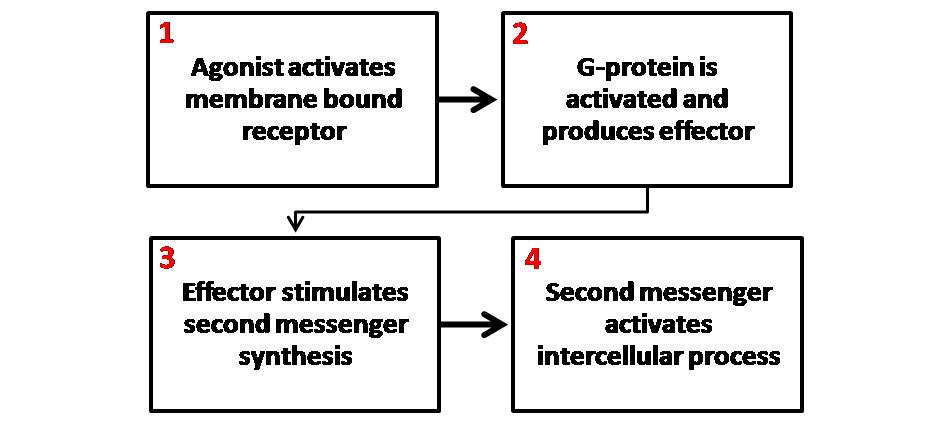
Second Messenger
Second messengers are intracellular signaling molecules released by the cell in response to exposure to extracellular signaling molecules—the first messengers. (Intercellular signals, a non-local form or cell signaling, encompassing both first messengers and second messengers, are classified as autocrine, juxtacrine, paracrine, and endocrine depending on the range of the signal.) Second messengers trigger physiological changes at cellular level such as proliferation, differentiation, migration, survival, apoptosis and depolarization. They are one of the triggers of intracellular signal transduction cascades. Examples of second messenger molecules include cyclic AMP, cyclic GMP, inositol triphosphate, diacylglycerol, and calcium. First messengers are extracellular factors, often hormones or neurotransmitters, such as epinephrine, growth hormone, and serotonin. Because peptide hormones and neurotransmitters typically are biochemically hydrophilic molecules, these first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Receptor Antagonist
A receptor antagonist is a type of receptor ligand or drug that blocks or dampens a biological response by binding to and blocking a receptor rather than activating it like an agonist. Antagonist drugs interfere in the natural operation of receptor proteins.Pharmacology Guide: In vitro pharmacology: concentration-response curves " '' GlaxoWellcome.'' Retrieved on December 6, 2007. They are sometimes called blockers; examples include alpha blockers, |
GAT100
GAT100 is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. See also * Org 27569 * PSNCBAM-1 * ZCZ-011 ZCZ-011 is a positive allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic c ... References Cannabinoids CB1 receptor antagonists Isothiocyanates {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSNCBAM-1
PSNCBAM-1 is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. See also * GAT100 * Org 27569 * ZCZ-011 ZCZ-011 is a positive allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compounds found in the cannabis plant primarily and most animal organisms (although insects lack such receptors) or as synthetic c ... References Cannabinoids CB1 receptor antagonists Aminopyridines {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZCZ-011
ZCZ-011 is a positive allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. See also * GAT100 * Org 27569 * PSNCBAM-1 PSNCBAM-1 is a negative allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor. See also * GAT100 * Org 27569 * ZCZ-011 ZCZ-011 is a positive allosteric modulator of the cannabinoid Cannabinoids () are several structural classes of compound ... References Cannabinoids Tryptamines {{cannabinoid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |