|
Opatowiec
Opatowiec is a small town in Kazimierza County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Opatowiec. It lies in Lesser Poland, on the left bank of the River Vistula (opposite the confluence of the Dunajec), approximately east of Kazimierza Wielka and south of the regional capital Kielce. It regained its urban status on 1 January 2019, becoming the smallest town in Poland, with only 338 inhabitants. Opatowiec is situated on the National Road Nr. 79 (Warsaw–Bytom). Local points of interest include a 15th-century Dominican church and a central park. History The village of Opatowiec was first mentioned in 1085, when Judyta, the wife of Prince Władysław I Herman, presented it to the Benedictine monks from Tyniec. In 1271, Prince Boleslaw V the Chaste granted Opatowiec a town charter under Magdeburg rights, upon the request of abbot Modlibob. The town became a local trade center, due to its location ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Opatowiec
__NOTOC__ Gmina Opatowiec is a rural gmina (administrative district) in Kazimierza County, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, in south-central Poland. Its seat is the village of Opatowiec, which lies approximately east of Kazimierza Wielka and south of the regional capital Kielce. The gmina covers an area of , and as of 2006 its total population is 3,599. The gmina contains part of the protected area called Nida Landscape Park. Villages Gmina Opatowiec contains the villages and settlements of Charbinowice, Chrustowice, Chwalibogowice, Kamienna, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Kamienna, Kęsów, Kobiela, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Kobiela, Kocina, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Kocina, Kraśniów, Krzczonów, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Krzczonów, Ksany, Ławy, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Ławy, Mistrzowice, Opatowiec, Podskale, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Podskale, Rogów, Kazimierza County, Rogów, Rzemienowice, Senisławice, Trębaczów, Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, Trębac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kazimierza County
__NOTOC__ Kazimierza County ( pl, powiat kazimierski) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, south-central Poland. It came into being on January 1, 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat and largest town is Kazimierza Wielka, which lies south of the regional capital Kielce. The only other town in the county is Skalbmierz, lying north-west of Kazimierza Wielka. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 33,408, out of which the population of Kazimierza Wielka is 5,550, that of Skalbmierz is 1,285, and the rural population is 26,573. Neighbouring counties Kazimierza County is bordered by Pińczów County to the north, Busko County to the north-east, Dąbrowa County to the east, Tarnów County to the south-east, and Proszowice County __NOTOC__ Proszowice County ( pl, powiat proszowicki) is a unit of territorial administration and loca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship
The Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship, also known as the Świętokrzyskie Province, and the Holy Cross Voivodeship ( pl, województwo świętokrzyskie ) is a voivodeship (province) of Poland situated in southeastern part of the country, in the historical region of Lesser Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kielce. Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship is bounded by six other voivodeships: Masovian to the north, Lublin to the east, Subcarpathian to the southeast, Lesser Poland to the south, Silesian to the southwest and Łódź to the northwest. The province was created on 1 January 1999, out of the former Kielce Voivodeship, eastern part of Częstochowa Voivodeship and western part of Tarnobrzeg Voivodeship, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. It covers an area of , making it the second smallest of the voivodeships (after Opole). As at 2019, the total population of Świętokrzyskie Voivodeship is 1,237,369. Cities and towns The voivodeship contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
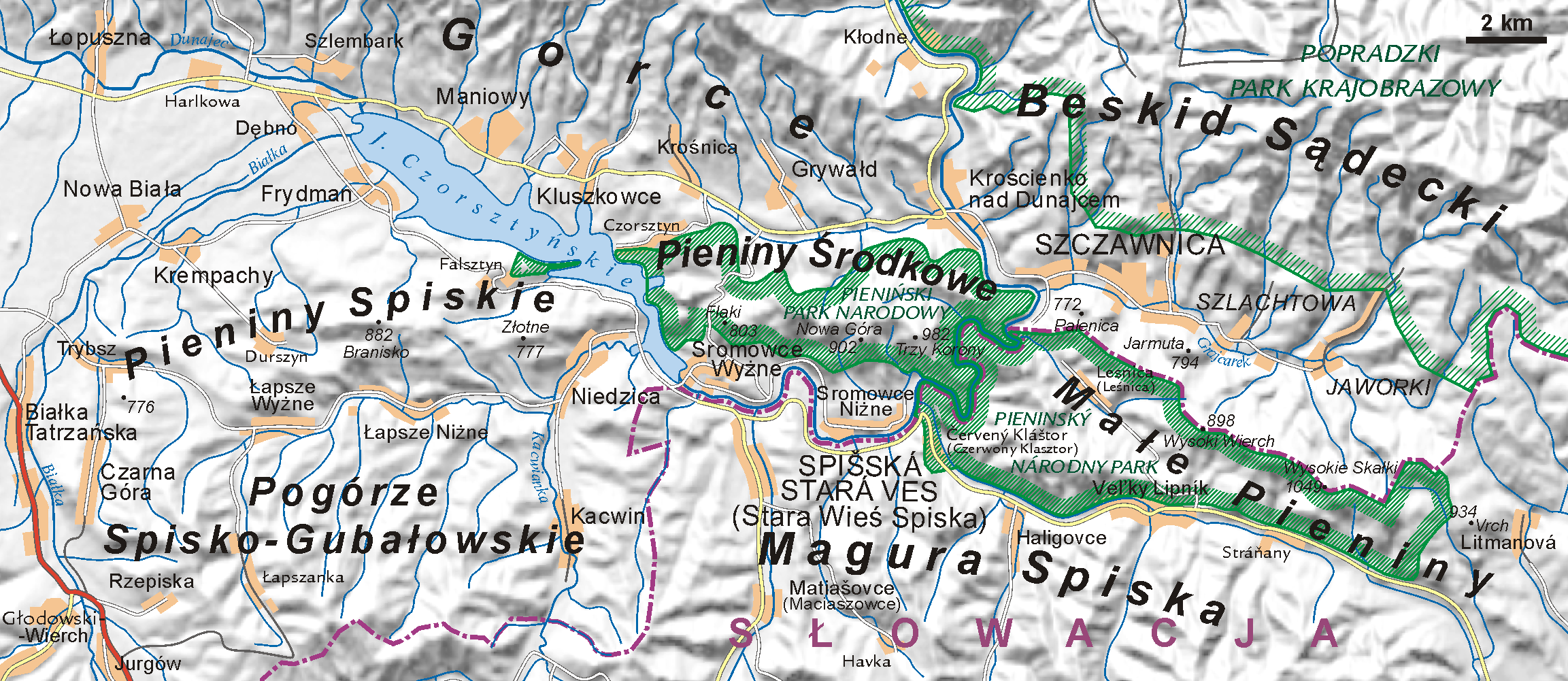
Dunajec
The Dunajec (); Goral dialects: ''Dónajec'') is a river running through northeastern Slovakia and southern Poland. It is also regarded as the main river of the Goral Lands. It is a right tributary of the Vistula River. It begins in Nowy Targ at the junction of two short mountain rivers, Czarny Dunajec and Biały Dunajec (Black and White Dunajec). Dunajec forms the border between Poland and Slovakia for in the Pieniny Środkowe (Slovak: Centrálne Pieniny) range, east of the Czorsztyn reservoir. Geography The Dunajec is long, including its source river Czarny Dunajec,Statistical Yearbook of the Republic of Poland 2017 |
Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland. The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in the south of Poland, above sea level in the Silesian Beskids (western part of Carpathian Mountains), where it begins with the Little White Vistula (''Biała Wisełka'') and the Black Little Vistula (''Czarna Wisełka''). It flows through Poland's largest cities, including Kraków, Sandomierz, Warsaw, Płock, Włocławek, Toruń, Bydgoszcz, Świecie, Grudziądz, Tczew and Gdańsk. It empties into the Vistula Lagoon (''Zalew Wiślany'') or directly into the Gdańsk Bay of the Baltic Sea with a delta of six main branches (Leniwka, Przekop, Śmiała Wisła, Martwa Wisła, Nogat and Szkarpawa). The river is often associated with Polish culture, history and national identity. It is the country's most important waterway and natural symbol, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the German city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Bohemia, Hungary, Poland and Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries, the Baltic states, and the interior (for example Braunschweig). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyniec
Tyniec is a historic village in Poland on the Vistula river, since 1973 a part of the city of Kraków (currently in the district of Dębniki). Tyniec is notable for its Benedictine abbey founded by King Casimir the Restorer in 1044. Etymology The name of the village comes from a Celtic language word "tyn", which means wall or fence, and which means that the history of Tyniec as a fortified settlement (see gord) dates back to pre- Slavic times. Geography Tyniec lies southwest of the centre of Kraków, on the right bank of the Vistula, among limestone Jurassic hills, called the Tyniec Hills, with the highest one being Wielogora (also called Guminek), above sea level. Furthermore, Tyniec has a Vistula canyon (called Tyniec Gate), a Skolczanka Nature Reserve (est. 1957), and a locally renowned water source, Zrodlo Swietojanskie, the only source of this kind in the city of Kraków. In ancient times the village was located along a merchant trade route from Kraków, via Oświęcim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The female equivalent is abbess. Origins The title had its origin in the monasteries of Egypt and Syria, spread through the eastern Mediterranean, and soon became accepted generally in all languages as the designation of the head of a monastery. The word is derived from the Aramaic ' meaning "father" or ', meaning "my father" (it still has this meaning in contemporary Hebrew: אבא and Aramaic: ܐܒܐ) In the Septuagint, it was written as "abbas". At first it was employed as a respectful title for any monk, but it was soon restricted by canon law to certain priestly superiors. At times it was applied to various priests, e.g. at the court of the Frankish monarchy the ' ("of the palace"') and ' ("of the camp") were chaplains to the Merovingian and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław I Herman
Władysław I Herman ( 1044 – 4 June 1102) was the duke of Poland from 1079 until his death. Accession Władysław was the second son of the Polish duke Casimir the Restorer and Maria Dobroniega of Kiev. As the second son, Władysław was not destined for the throne. However, due to the flight from Poland of his older brother Bolesław the Bold in 1079, he became duke of Poland. Opinions vary on whether Władysław played an active role in the plot to depose his brother or whether he was handed the authority simply because he was the best candidate to replace Bolesław. German relations In 1080, in order to improve the relations between Poland and Bohemia, Władysław married Judith, the daughter of Duke Vratislaus II of Bohemia, a vassal of the Holy Roman Empire. After this, Władysław's foreign policy gravitated strongly towards appeasing the Holy Roman Empire, and he accepted the overlordship of Emperor Henry IV. While Vratislaus was declared a king in 1085 by Emperor Hen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |