|
OS-CON
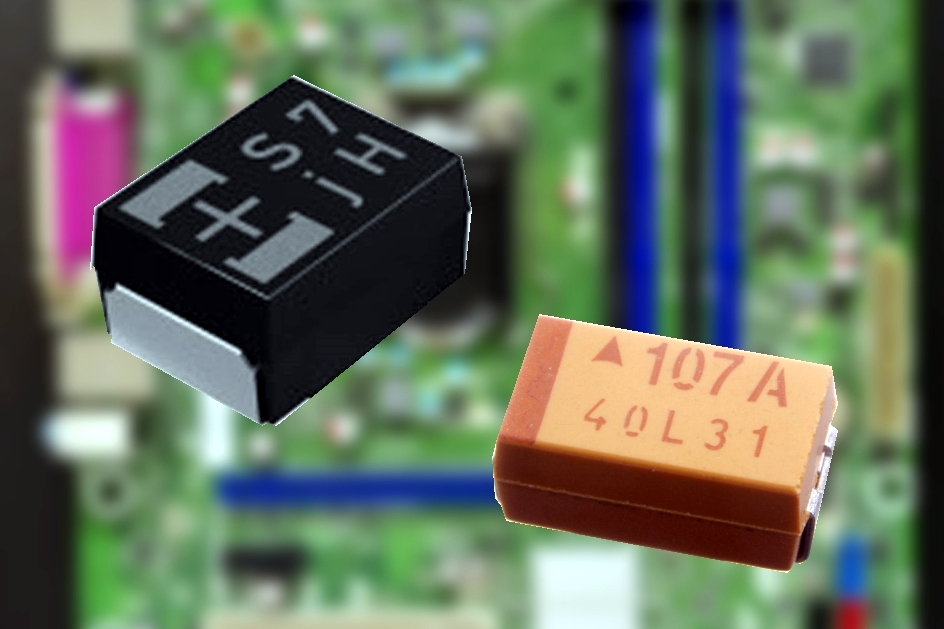
A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid conductive polymer electrolyte. There are four different types: * Polymer tantalum electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Ta-e-cap) * Polymer aluminium electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Al-e-cap) * Hybrid polymer capacitor (Hybrid polymer Al-e-cap) * Polymer niobium electrolytic capacitors Polymer Ta-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device ( SMD) chip style. Polymer Al-e-caps and hybrid polymer Al-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (SMD) chip style, in cylindrical SMDs (V-chips) style or as radial leaded versions (single-ended). Polymer electrolytic capacitors are characterized by particularly low internal equivalent series resistances (ESR) and high ripple current ratings. Their electrical parameters have similar temperature dependence, reliability and service life compared to solid tantalum capacitors, but have a much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymer Capacitor
A polymer capacitor, or more accurately a polymer electrolytic capacitor, is an electrolytic capacitor (e-cap) with a solid conductive polymer electrolyte. There are four different types: * Polymer tantalum capacitor, tantalum electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Ta-e-cap) * Polymer aluminum electrolytic capacitor, aluminium electrolytic capacitor (Polymer Al-e-cap) * Hybrid polymer capacitor (Hybrid polymer Al-e-cap) * Polymer Niobium capacitor, niobium electrolytic capacitors Polymer Ta-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (Surface-mount technology, SMD) chip style. Polymer Al-e-caps and hybrid polymer Al-e-caps are available in rectangular surface-mounted device (SMD) chip style, in cylindrical SMDs (V-chips) style or as radial leaded versions (single-ended). Polymer electrolytic capacitors are characterized by particularly low internal equivalent series resistances (ESR) and high ripple current ratings. Their electrical parameters have similar temperature de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolytic Capacitor
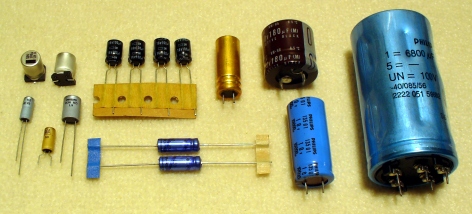
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Due to their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The large capacitance of electrolytic capacitors makes them particularly suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and for storing large amounts of energy. They are widely used for decoupling or noise filtering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Series Resistance
Practical capacitors and inductors as used in electric circuits are not ideal components with only capacitance or inductance. However, they can be treated, to a very good degree of approximation, as being ideal capacitors and inductors in series with a resistance; this resistance is defined as the equivalent series resistance (ESR). If not otherwise specified, the ESR is always an AC resistance, which means it is measured at specified frequencies, 100 kHz for switched-mode power supply components, 120 Hz for linear power-supply components, and at its self-resonant frequency for general-application components. Additionally, audio components may report a " Q factor", incorporating ESR among other things, at 1000 Hz. Overview Electrical circuit theory deals with ideal resistors, capacitors and inductors, each assumed to contribute only resistance, capacitance or inductance to the circuit. However, all components have a non-zero value of each of these parameters. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
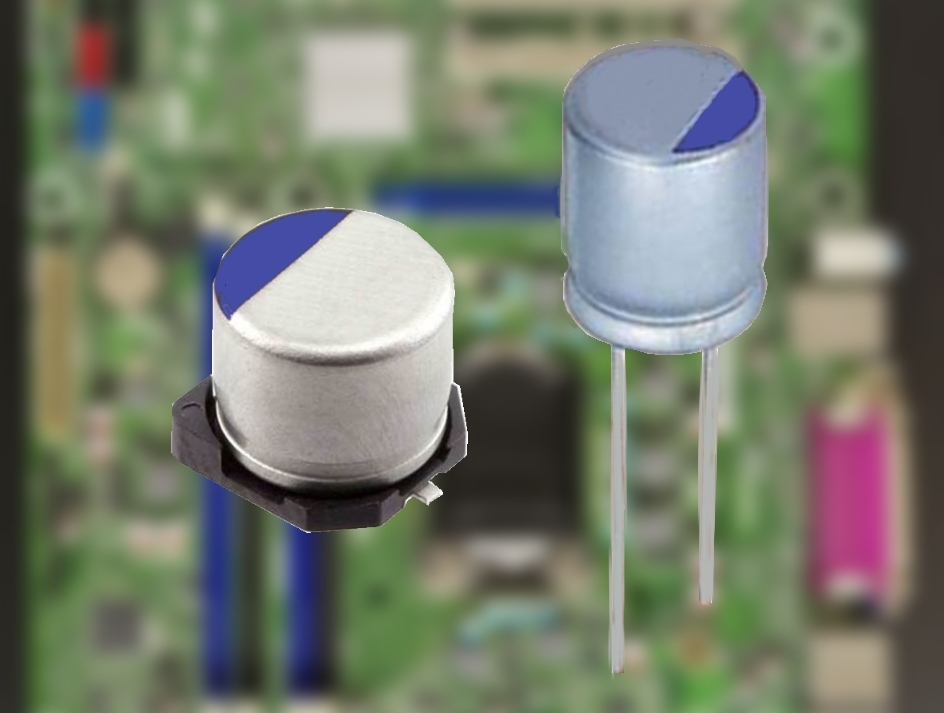
Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitor
Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are polarized electrolytic capacitors whose anode electrode (+) is made of a pure aluminum foil with an etched surface. The aluminum forms a very thin insulating layer of aluminum oxide by anodization that acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A non-solid electrolyte covers the rough surface of the oxide layer, serving in principle as the second electrode (cathode) (-) of the capacitor. A second aluminum foil called “cathode foil” contacts the electrolyte and serves as the electrical connection to the negative terminal of the capacitor. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors are divided into three subfamilies by electrolyte type: *non-solid (liquid, wet) aluminum electrolytic capacitors, * solid manganese dioxide aluminum electrolytic capacitors, and * solid polymer aluminum electrolytic capacitors. Aluminum electrolytic capacitors with non-solid electrolyte are the most inexpensive type and also those with widest range of sizes, capacitance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equivalent Series Inductance
Equivalent series inductance (ESL) is an effective inductance that is used to describe the inductive part of the impedance of certain electrical components. Overview The theoretical treatment of devices such as capacitors and resistors tends to assume they are ''ideal'' or "perfect" devices, contributing only capacitance or resistance to the circuit. However, all physical devices are connected to a circuit through conductive leads and paths, which contain inherent, usually unwanted, inductance. This means that physical components contain some inductance in addition to their other properties.{{Cite book, last=Maniktala, first=Sanjaya, url=https://books.google.com/books?id=zMVTv6py7woC&dq=%22Equivalent+series+inductance%22&pg=PA631, title=Switching Power Supplies A - Z, date=2012-04-18, publisher=Elsevier, isbn=978-0-12-386533-5, pages=631, language=en An easy way to deal with these inherent inductances in circuit analysis is by using a lumped element model to express each physic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7,7,8,8-tetracyanoquinodimethane
Tetracyanoquinodimethane (TCNQ) is the organic compound with the formula . This cyanocarbon, a relative of para-quinone, is an electron acceptor that is used to prepare charge transfer salts, which are of interest in molecular electronics. Preparation and structure TCNQ is prepared by the condensation of 1,4-cyclohexanedione with malononitrile, followed by dehydrogenation of the resulting diene with bromine: : : The molecule is planar, with D2h symmetry. Reactions Like tetracyanoethylene (TCNE), TCNQ is easily reduced to give a blue-coloured radical anion. The reduction potential is about −0.3 V relative to the ferrocene/ferrocenium couple. This property is exploited in the development of charge transfer salts. TCNQ also forms complexes with electron-rich metal complexes. Charge transfer salts TCNQ achieved great attention because it forms charge-transfer salts with high electrical conductivity. These discoveries were influential in the development of organic electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrathiafulvalene
Tetrathiafulvalene is an organosulfur compound with the formula (. Studies on this heterocyclic compound contributed to the development of molecular electronics. TTF is related to the hydrocarbon fulvalene, , by replacement of four CH groups with sulfur atoms. Over 10,000 scientific publications discuss TTF and its derivatives. Preparation The high level of interest in TTFs has spawned the development of many syntheses of TTF and its analogues. Most preparations entail the coupling of cyclic building blocks such as 1,3-dithiole-2-thion or the related 1,3-dithiole-2-ones. For TTF itself, the synthesis begins with the trithiocarbonate , which is S-methylated and then reduced to give , which is treated as follows: :H2C2S2CH(SCH3) + HBF4 -> 2C2S2CH+F4- + HSCH3 :2 2C2S2CH+F4- + 2 Et3N -> (H2C2S2C)2 + 2 Et3NHBF4 Redox properties Bulk TTF itself has unremarkable electrical properties. Distinctive properties are, however, associated with salts of its oxidized derivatives, suc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sanyo
, stylized as SANYO, is a Japanese electronics company and formerly a member of the Fortune Global 500, ''Fortune'' Global 500 whose headquarters was located in Moriguchi, Osaka, Moriguchi, Osaka prefecture, Japan. Sanyo had over 230 subsidiaries and affiliates, and was founded by Toshio Iue in 1947. On December 21, 2009, Panasonic completed a 400 billion yen ($4.5 billion) acquisition of a 50.2% stake in Sanyo, making Sanyo a subsidiary of Panasonic. In April 2011, Sanyo became a wholly owned subsidiary of Panasonic, with its assets integrated into the latter's portfolio. History Beginnings Sanyo was founded when Toshio Iue the brother-in-law of Konosuke Matsushita and also a former Panasonic Corporation, Matsushita employee, was lent an unused Matsushita plant in 1947 and used it to make bicycle generator lamps. Sanyo was incorporated in 1949; in 1952 it made Japan's first plastic radio and in 1954 Japan's first pulsator-type washing machine. The company's name means ''thre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink). A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch electrical signals and electrical power, power. The transistor is one of the basic building blocks of modern electronics. It is composed of semiconductor material, usually with at least three terminals for connection to an electronic circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor's terminals controls the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be higher than the controlling (input) power, a transistor can amplify a signal. Some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits. Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld proposed the concept of a field-effect transistor in 1926, but it was not possible to actually constru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)