|
Oögonia
An oogonium (plural oogonia) is a small diploid cell which, upon maturation, forms a primordial follicle in a female fetus or the female (haploid or diploid) gametangium of certain thallophytes. In the mammalian fetus Oogonia are formed in large numbers by mitosis early in fetal development from primordial germ cells. In humans they start to develop between weeks 4 and 8 and are present in the fetus between weeks 5 and 30. Structure Normal oogonia in human ovaries are spherical or ovoid in shape and are found amongst neighboring somatic cells and oocytes at different phases of development. Oogonia can be distinguished from neighboring somatic cells, under an electron microscope, by observing their nuclei. Oogonial nuclei contain randomly dispersed fibrillar and granular material whereas the somatic cells have a more condensed nucleus that creates a darker outline under the microscope. Oogonial nuclei also contain dense prominent nucleoli. The chromosomal material in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diploid
Ploidy () is the number of complete sets of chromosomes in a cell, and hence the number of possible alleles for autosomal and pseudoautosomal genes. Sets of chromosomes refer to the number of maternal and paternal chromosome copies, respectively, in each homologous chromosome pair, which chromosomes naturally exist as. Somatic cells, tissues, and individual organisms can be described according to the number of sets of chromosomes present (the "ploidy level"): monoploid (1 set), diploid (2 sets), triploid (3 sets), tetraploid (4 sets), pentaploid (5 sets), hexaploid (6 sets), heptaploid or septaploid (7 sets), etc. The generic term polyploid is often used to describe cells with three or more chromosome sets. Virtually all sexually reproducing organisms are made up of somatic cells that are diploid or greater, but ploidy level may vary widely between different organisms, between different tissues within the same organism, and at different stages in an organism's life cycle. Half ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
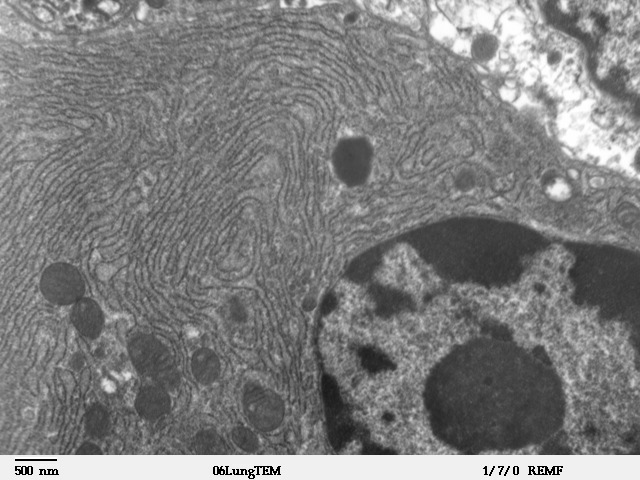
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is, in essence, the transportation system of the eukaryotic cell, and has many other important functions such as protein folding. It is a type of organelle made up of two subunits – rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER). The endoplasmic reticulum is found in most eukaryotic cells and forms an interconnected network of flattened, membrane-enclosed sacs known as cisternae (in the RER), and tubular structures in the SER. The membranes of the ER are continuous with the outer nuclear membrane. The endoplasmic reticulum is not found in red blood cells, or spermatozoa. The two types of ER share many of the same proteins and engage in certain common activities such as the synthesis of certain lipids and cholesterol. Different types of cells contain different ratios of the two types of ER depending on the activities of the cell. RER is found mainly toward the nucleus of cell and SER towards the cell membrane or plasma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametocyte
A gametocyte is a eukaryotic germ cell that divides by mitosis into other gametocytes or by meiosis into gametids during gametogenesis. Male gametocytes are called ''spermatocytes'', and female gametocytes are called ''oocytes''. Development The development of gametogonia to primary gametocytes is called gametocytogenesis. The further development of primary gametocytes to secondary gametocytes is a part of gametidogenesis. Gametogenesis is the formation or production of gametes (taking place during meiosis). The development and maturation of sex cells also takes place during meiosis. Gametogenesis is also the process of formation in male and female gametes that occur in the gonads (ovary and testis). Both male and female produce gametes. Male gametocytes are called spermatocytes and female gametocytes are called oocytes. The term gametocyte is also used, for example, when talking about gametocytes of species like ''Plasmodium falciparum'' or ''Plasmodium vivax'', which transmi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
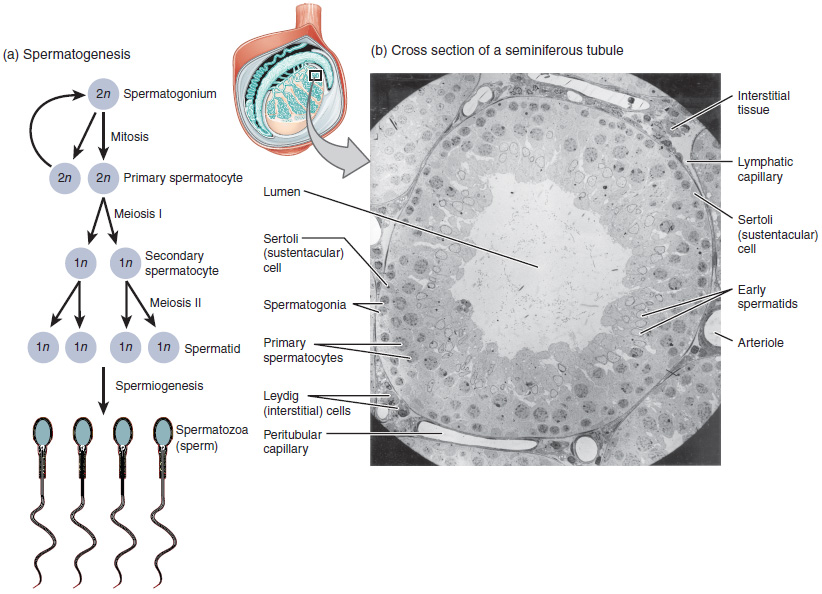
Spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and secondary spermatocytes. Primary and secondary spermatocytes are formed through the process of spermatocytogenesis. Primary spermatocytes are diploid (2N) cells. After meiosis I, two secondary spermatocytes are formed. Secondary spermatocytes are haploid (N) cells that contain half the number of chromosomes. In all animals, males produce spermatocytes, even hermaphrodites such as ''C. elegans'', which exist as a male or hermaphrodite. In hermaphrodite ''C. elegans'', sperm production occurs first and is then stored in the spermatheca. Once the eggs are formed, they are able to self-fertilize and produce up to 350 progeny. Development At puberty, spermatogonia located along the walls of the seminiferous tubules within the testis will be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubules. These cells are called spermatogonial stem cells. The mitotic division of these produces two types of cells. Type A cells replenish the stem cells, and type B cells differentiate into primary spermatocytes. The primary spermatocyte divides meiotically (Meiosis I) into two secondary spermatocytes; each secondary spermatocyte divides into two equal haploid spermatids by Meiosis II. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm) by the process of spermiogenesis. These develop into mature spermatozoa, also known as sperm cells. Thus, the primary spermatocyte gives rise to two cells, the secondary spermatocytes, and the two secondary spermatocytes by their subdivision produce four spermatozoa and four haploid cells. Spermatozoa are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis
Meiosis (; , since it is a reductional division) is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, such as sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells with only one copy of each chromosome ( haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and female will fuse to create a cell with two copies of each chromosome again, the zygote. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oogenesis
Oogenesis, ovogenesis, or oögenesis is the differentiation of the ovum (egg cell) into a cell competent to further develop when fertilized. It is developed from the primary oocyte by maturation. Oogenesis is initiated in the embryonic stage. Oogenesis in non-human mammals In mammals, the first part of oogenesis starts in the germinal epithelium, which gives rise to the development of ovarian follicles, the functional unit of the ovary. Oogenesis consists of several sub-processes: oocytogenesis, ootidogenesis, and finally maturation to form an ovum (oogenesis proper). Folliculogenesis is a separate sub-process that accompanies and supports all three oogenetic sub-processes. Oogonium —(Oocytogenesis)—> Primary Oocyte —(Meiosis I)—> First Polar body (Discarded afterward) + Secondary oocyte —(Meiosis II)—> Second Polar Body (Discarded afterward) + Ovum Oocyte meiosis, important to all animal life cycles yet unlike all other instances of animal cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gonad
A gonad, sex gland, or reproductive gland is a mixed gland that produces the gametes and sex hormones of an organism. Female reproductive cells are egg cells, and male reproductive cells are sperm. The male gonad, the testicle, produces sperm in the form of spermatozoa. The female gonad, the ovary, produces egg cells. Both of these gametes are haploid cells. Some hermaphroditic animals have a type of gonad called an ovotestis. Evolution It is hard to find a common origin for gonads, but gonads most likely evolved independently several times. Regulation The gonads are controlled by luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone, produced and secreted by gonadotropes or gonadotrophins in the anterior pituitary gland. This secretion is regulated by gonadotropin-releasing hormone produced in the hypothalamus. Development Gonads start developing as a common primordium (an organ in the earliest stage of development), in the form of genital ridges, which are only l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genital Ridge
The genital ridge (or gonadal ridge) is the precursor to the gonads. The genital ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic cells. Development proceeds and the oogonia become fully surrounded by a layer of cells (pre-granulosa cells). The genital ridge appears at approximately five weeks, and gives rise to the sex cords. Associated genes Genes associated with the developing gonad can be categorized into those that form the sexually indifferent gonad, those that determine whether the indifferent gonad will differentiate as male or female, and those that promote differentiation into male or female parts. Genes that form the sexually indifferent gonad are ''SF1 (gene), SF1'' and ''WT1''. Genes that determine sex are ''Testis-determining factor, SRY'', ''SOX9'', and ''DAX1''. Genes driving the differentiation into male or female structures are ''SF1'', ''WT1'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryo
An embryo is an initial stage of development of a multicellular organism. In organisms that reproduce sexually, embryonic development is the part of the life cycle that begins just after fertilization of the female egg cell by the male sperm cell. The resulting fusion of these two cells produces a single-celled zygote that undergoes many cell divisions that produce cells known as blastomeres. The blastomeres are arranged as a solid ball that when reaching a certain size, called a morula, takes in fluid to create a cavity called a blastocoel. The structure is then termed a blastula, or a blastocyst in mammals. The mammalian blastocyst hatches before implantating into the endometrial lining of the womb. Once implanted the embryo will continue its development through the next stages of gastrulation, neurulation, and organogenesis. Gastrulation is the formation of the three germ layers that will form all of the different parts of the body. Neurulation forms the nervous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastocyst
The blastocyst is a structure formed in the early embryonic development of mammals. It possesses an inner cell mass (ICM) also known as the ''embryoblast'' which subsequently forms the embryo, and an outer layer of trophoblast cells called the trophectoderm. This layer surrounds the inner cell mass and a fluid-filled cavity known as the blastocoel. In the late blastocyst the trophectoderm is known as the trophoblast. The trophoblast gives rise to the chorion and amnion, the two fetal membranes that surround the embryo. The placenta derives from the embryonic chorion (the portion of the chorion that develops villi) and the underlying uterine tissue of the mother. The name "blastocyst" arises from the Greek ' ("a sprout") and ' ("bladder, capsule"). In other animals this is a structure consisting of an undifferentiated ball of cells and is called a blastula. In humans, blastocyst formation begins about five days after fertilization when a fluid-filled cavity opens up in the mor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is called a phagocyte. In a multicellular organism's immune system, phagocytosis is a major mechanism used to remove pathogens and cell debris. The ingested material is then digested in the phagosome. Bacteria, dead tissue cells, and small mineral particles are all examples of objects that may be phagocytized. Some protozoa use phagocytosis as means to obtain nutrients. History Phagocytosis was first noted by Canadian physician William Osler (1876), and later studied and named by Élie Metchnikoff (1880, 1883). In immune system Phagocytosis is one main mechanisms of the innate immune defense. It is one of the first processes responding to infection, and is also one of the initiating branches of an adaptive immune response. Although mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)