|
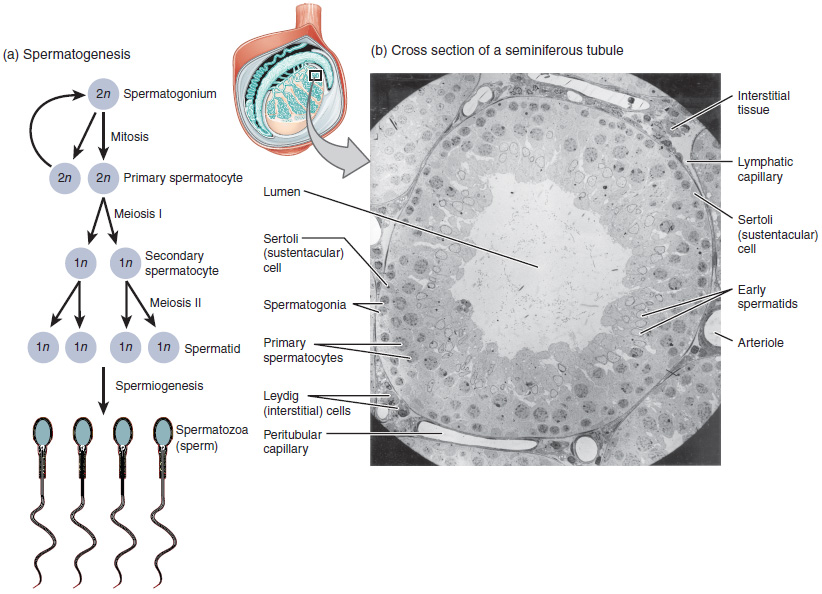
Spermatocyte
Spermatocytes are a type of male gametocyte in animals. They derive from immature germ cells called spermatogonia. They are found in the testis, in a structure known as the seminiferous tubules. There are two types of spermatocytes, primary and secondary spermatocytes. Primary and secondary spermatocytes are formed through the process of spermatocytogenesis. Primary spermatocytes are diploid (2N) cells. After meiosis I, two secondary spermatocytes are formed. Secondary spermatocytes are haploid (N) cells that contain half the number of chromosomes. In all animals, Male, males produce spermatocytes, even hermaphrodites such as Caenorhabditis elegans, ''C. elegans'', which exist as a male or hermaphrodite. In hermaphrodite ''C. elegans'', sperm production occurs first and is then stored in the spermatheca. Once the egg cell, eggs are formed, they are able to self-fertilize and produce up to 350 offspring, progeny. Development At puberty, spermatogonia located along the walls of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogonia
A spermatogonium (plural: ''spermatogonia'') is an undifferentiated male germ cell. Spermatogonia undergo spermatogenesis to form mature spermatozoa in the seminiferous tubules of the testicles. There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans: Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonial stem cells which do not usually undergo active mitosis. Type A (pale) cells, with pale nuclei. These are the spermatogonial stem cells that undergo active mitosis. These cells divide to produce Type B cells. Type B cells, which undergo growth and become primary spermatocytes. Types of spermatogonia Spermatogonia are often classified into different types depending on their stage in the differentiation process. In humans and most mammals, spermatogonia are divided into two types, A and B, but this can differ for other organisms. There are three subtypes of spermatogonia in humans: *Type A (dark) cells, with dark nuclei. These cells are reserve spermatogonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatogonial Stem Cells
A spermatogonial stem cell (SSC), also known as a type A spermatogonium, is a spermatogonium that does not differentiate into a spermatocyte, a precursor of sperm cells. Instead, they continue dividing into other spermatogonia or remain dormant to maintain a reserve of spermatogonia. Type B spermatogonia, on the other hand, differentiate into spermatocytes, which in turn undergo meiosis to eventually form mature sperm cells. Spermatogonial stem cells in the testis During fetal development, gonocytes develop from primordial germ cells, and following this SSCs develop from gonocytes in the testis. SSCs are the early precursor for spermatozoa and are responsible for the continuation of spermatogenesis in adult mammals. The stem cells are capable of dividing into more SSCs which is vital for maintaining the stem cell pool. Alternatively, they go on to differentiate into spermatocytes, spermatids, and finally spermatozoa. One SSC is the precursor for multiple spermatozoa and ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cells
A germ cell is any cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually. In many animals, the germ cells originate in the primitive streak and migrate via the gut of an embryo to the developing gonads. There, they undergo meiosis, followed by cellular differentiation into mature gametes, either eggs or sperm. Unlike animals, plants do not have germ cells designated in early development. Instead, germ cells can arise from somatic cells in the adult, such as the floral meristem of flowering plants. Introduction Multicellular eukaryotes are made of two fundamental cell types: germ and somatic cells. Germ cells produce gametes and are the only cells that can undergo meiosis as well as mitosis. Somatic cells are all the other cells that form the building blocks of the body and they only divide by mitosis. The lineage of germ cells is called the germline. Germ cell specification begins during cleavage in many animals or in the epiblast during gastrulation in bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatids
The spermatid is the haploid male gametid that results from division of secondary spermatocytes. As a result of meiosis, each spermatid contains only half of the genetic material present in the original primary spermatocyte. Spermatids are connected by cytoplasmic material and have superfluous cytoplasmic material around their nuclei. When formed, ''early round spermatids'' must undergo further maturational events to develop into spermatozoa, a process termed spermiogenesis (also termed ''spermeteliosis''). The spermatids begin to grow a living thread, develop a thickened mid-piece where the mitochondria become localised, and form an acrosome. Spermatid DNA also undergoes packaging, becoming highly condensed. The DNA is packaged firstly with specific nuclear basic proteins, which are subsequently replaced with protamines during spermatid elongation. The resultant tightly packed chromatin is transcriptionally inactive. In 2016 scientists at Nanjing Medical University claim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testis
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is Homology (biology), homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of Androgen, androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and compari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis I
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meiosis II
Meiosis () is a special type of cell division of germ cells in sexually-reproducing organisms that produces the gametes, the sperm or egg cells. It involves two rounds of division that ultimately result in four cells, each with only one copy of each chromosome (haploid). Additionally, prior to the division, genetic material from the paternal and maternal copies of each chromosome is crossed over, creating new combinations of code on each chromosome. Later on, during fertilisation, the haploid cells produced by meiosis from a male and a female will fuse to create a zygote, a cell with two copies of each chromosome. Errors in meiosis resulting in aneuploidy (an abnormal number of chromosomes) are the leading known cause of miscarriage and the most frequent genetic cause of developmental disabilities. In meiosis, DNA replication is followed by two rounds of cell division to produce four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the original parent cell. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gametocyte
A gametocyte is a eukaryotic germ cell that divides by mitosis into other gametocytes or by meiosis into gametids during gametogenesis. Male gametocytes are called ''spermatocytes'', and female gametocytes are called ''oocytes''. Development The development of gametogonia to primary gametocytes is called gametocytogenesis. The further development of primary gametocytes to secondary gametocytes is a part of gametidogenesis. Gametogenesis is the formation or production of gametes (taking place during meiosis). The development and maturation of sex cells also takes place during meiosis. Gametogenesis is also the process of formation in male and female gametes that occur in the gonads (ovary and testis). Both male and female produce gametes. Male gametocytes are called spermatocytes and female gametocytes are called oocytes. The term gametocyte is also used, for example, when talking about gametocytes of species like ''Plasmodium falciparum'' or ''Plasmodium vivax'', which transmit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spermatocytogenesis
Spermatocytogenesis is the male form of gametocytogenesis and involves stem cells dividing to replace themselves and to produce a population of cells destined to become mature sperm. The stem cells involved are called spermatogonia and are a specific type of stem cell known as gametogonia. Three functionally separate spermatogonia cell types are recognized on the basis of the appearance of the nuclei: ''type A dark spermatogonia'' (Ad), ''type A pale spermatogonia'' (Ap), and ''type B spermatogonia'' (B). Type Ad spermatogonia ("dark") The population of spermatogonia is maintained by ''type Ad spermatogonia''. These cells do not directly participate in producing sperm, instead serving to maintain the supply of stem cells for spermatogenesis. Each type Ad spermatogonium divides to produce another type Ad spermatogonium, which can further carry on spermatogenesis, and one ''type Ap spermatogonium'', which differentiates further. Type Ap spermatogonia ("pale") ''Type Ap sperm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mitotically
Mitosis () is a part of the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells in which replicated chromosomes are separated into two new nuclei. Cell division by mitosis is an equational division which gives rise to genetically identical cells in which the total number of chromosomes is maintained. Mitosis is preceded by the S phase of interphase (during which DNA replication occurs) and is followed by telophase and cytokinesis, which divide the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane of one cell into two new cells containing roughly equal shares of these cellular components. The different stages of mitosis altogether define the mitotic phase (M phase) of a cell cycle—the division of the mother cell into two daughter cells genetically identical to each other. The process of mitosis is divided into stages corresponding to the completion of one set of activities and the start of the next. These stages are preprophase (specific to plant cells), prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |