|
Ovçular Tepesi
Ovçular Tepesi is an ancient settlement located at the northern end of Dizə, Sharur village in Sharur District of Azerbaijan, on the left bank of Arpa (river). It dates back to the fifth millennium BC, and continued to the third millenniums BC. Location This is a strategic point at the foot of the highlands; the site is at the crossroads of major trade routes linking the Iranian plateau to Anatolia (east to west), and the Caucasus to North Mesopotamia (north to south). The monument is located on a natural hill. The area of the monument is about 10 hectares. The characteristic feature of the site is that the Kura-Araxes layer is not covered by any cultural layers of later periods. Excavations First excavation campaigns at the site were conducted by Seyidov in 1980, and then later by Aliyev. Also Ashurov investigated the site in 2001.Ashurov, S.H., 2005: ―An introduction to Bronze Age sites in the Sarur plain‖. In Archäologische Mitteilungen aus Iran und Turan, Band 37 : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dizə, Sharur
Dizə (also, Diza and Dize) is a village and municipality in the Sharur District of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Azerbaijan. It is located on the left bank of the river Arpachay ( Arpa), on the Sharur plain. On the other side of the river is the village of Oğlanqala. Its population is busy with gardening, vegetable-growing, grain-growing and animal husbandry. There are secondary school, library, club, kindergarten and a medical center in the village. It has a population of 1,791. Etymology In the ancient Iranian languages the word of ''dizə'' means "wall, fence," "fortified town", "fortress wall", "fortress", "fortified". It passed in to several Turkic languages, including Azerbaijani language and is used in meaning as "village". Historical and archaeological monuments Ovcular Tepesi Ovçular Tepesi is located just to the north of Dize village, on the left bank of the Arpachay River. It is a settlement from the 5th-3rd millenniums BC. This is a strategic point at the foot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sharur District
Sharur District ( az, Şərur rayonu) is one of the 7 districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan. The district borders the districts of Kangarli, Sadarak, as well as the Vayots Dzor and Ararat provinces of Armenia and the West Azerbaijan Province of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Sharur. As of 2020, the district had a population of 117,600. Etymology The district was known as Norashen from 1930 to 1964, then Ilich or Ilichyovsk from 1964 to 1991 in honour of Vladimir Ilich Lenin. It was finally renamed to its original name Sharur upon the dissolution of the Soviet Union and the independence of Azerbaijan. History Following the disestablishment of the Nakhichevan Khanate upon the region's annexation into the Russian Empire in 1828, the Sharur area was included into the Nakhichevan Uyezd of the Armenian Oblast, and later, the Erivan Governorate. In 1870, the Sharur and Daralayaz ''mahals'' of the Nakhichevan district were detached into a separate di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
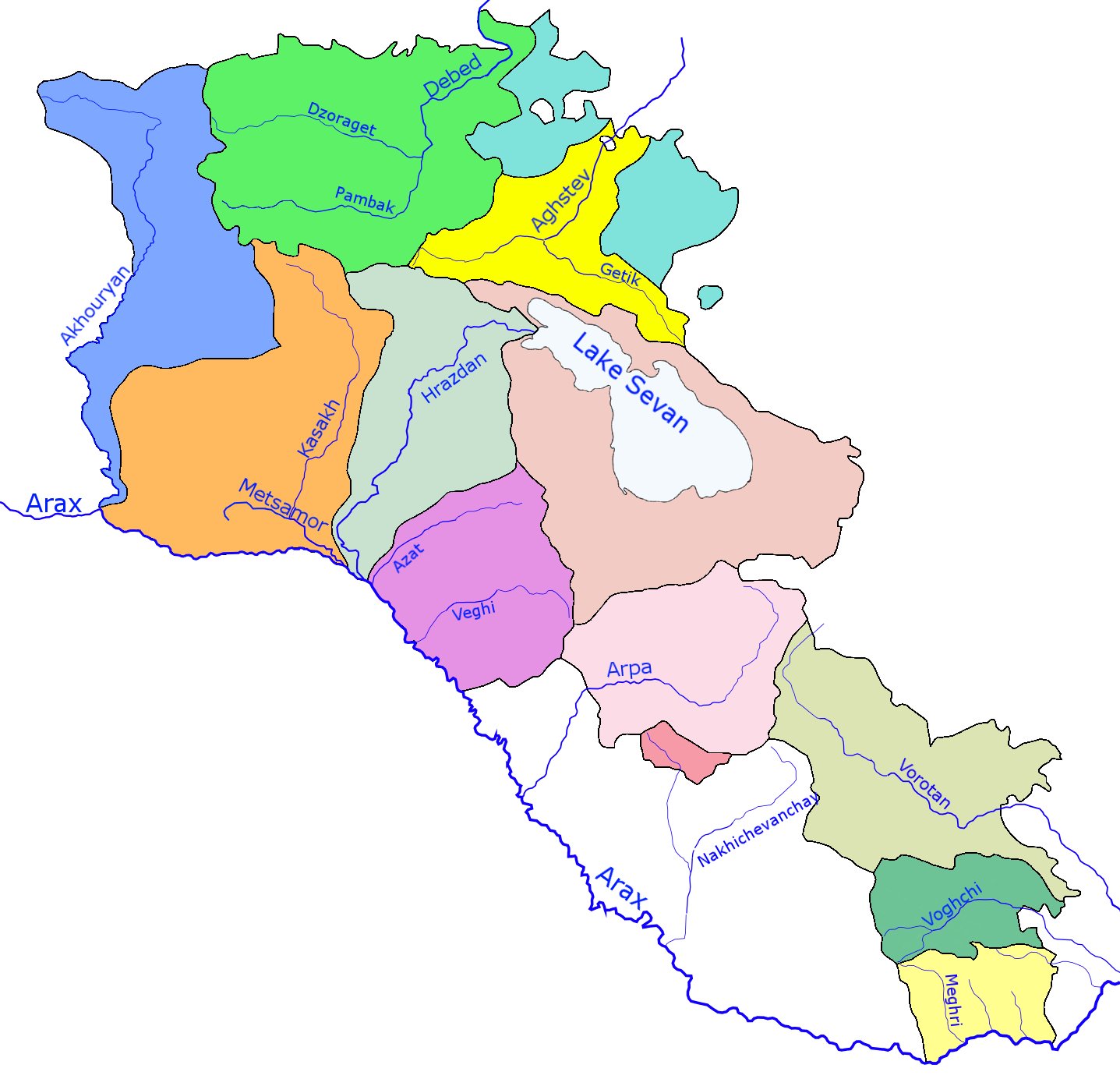
Arpa (river)
The Arpa ( hy, Արփա, az, Arpaçay) is a river that flows through Armenia and Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan exclave. It originates in the Vayots Dzor province (''marz'') of Armenia and is a left tributary of the Aras. It is long, and has a drainage basin of . It runs through many cities and towns, including , , Yeghegnadzor, |
Ubaid Period
The Ubaid period (c. 6500–3700 BC) is a prehistoric period of Mesopotamia. The name derives from Tell al-'Ubaid where the earliest large excavation of Ubaid period material was conducted initially in 1919 by Henry Hall and later by Leonard Woolley. In South Mesopotamia the period is the earliest known period on the alluvial plain although it is likely earlier periods exist obscured under the alluvium. In the south it has a very long duration between about 6500 and 3800 BC when it is replaced by the Uruk period.Carter, Robert A. and Philip, Graham. 2010. 'Deconstructing the Ubaid' in Carter, Robert A. and Philip, Graham (eds.) ''Beyond the Ubaid: Transformation and Integration in the Late Prehistoric Societies of the Middle East''. Chicago: The Oriental Institute of the University of Chicago. p. 2. In Northern Mesopotamia the period runs only between about 5300 and 4300 BC. It is preceded by the Halaf period and the Halaf-Ubaid Transitional period and succeeded by the Late Chalc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makhta Kultepe
Maxta (also, ''Makhta'', ''Makhta Kultepe'') is a village and municipality in the Sharur District of Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, Azerbaijan. It is located 7 km in the north-west from the district center, on the plain. Its population is busy with vine-growing, farming and animal husbandry. There are secondary school, library, cultural house and a hospital in the village. It has a population of 2,478. A monument was erected in honor of the compatriots killed in The Great Patriotic War (1941–45). In the north-east of the village, on the right side of the Nakhchivan-Sadarak highway is located the ''Qarabulaq'' necropolis of the Iron Age, and on the left side is located the ancient necropolis of ''Maxta''. The municipality consists of the villages of Maxta and Təzəkənd. Etymology According to some researchers, the name is a distorted form of the word of ''Mandeh''. They associated the name of the village with the words of ''mah'' (fortress, camp) and ''deh'' (village) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalcolithic
The Copper Age, also called the Chalcolithic (; from grc-gre, χαλκός ''khalkós'', "copper" and ''líthos'', "stone") or (A)eneolithic (from Latin '' aeneus'' "of copper"), is an archaeological period characterized by regular human manipulation of copper, but prior to the discovery of bronze alloys. Modern researchers consider the period as a subset of the broader Neolithic, but earlier scholars defined it as a transitional period between the Neolithic and the Bronze Age. The archaeological site of Belovode, on Rudnik mountain in Serbia, has the world's oldest securely dated evidence of copper smelting at high temperature, from (7000 BP). The transition from Copper Age to Bronze Age in Europe occurred between the late 5th and the late In the Ancient Near East the Copper Age covered about the same period, beginning in the late and lasting for about a millennium before it gave rise to the Early Bronze Age. Terminology The multiple names result from m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Azerbaijan
The history of Azerbaijan is understood as the history of the region now forming the Republic of Azerbaijan. Topographically, the land is contained by the southern slopes of the Caucasus Mountains in the north, the Caspian Sea in the east, and the Armenian Highlands in the west. In the south, its natural boundaries are less distinct, and here the country merges with the Iranian Plateau. The entity of Caucasian Albania was established on its soil in ancient times. The Caucasian Albanian language spoken by the founders of Caucasian Albania was most likely a predecessor of the now endangered Udi language spoken by the Udi people. From the time of the Medes and the Achaemenid Empire, until the coming of the Russians in the 19th century, the territories of the republic of Azerbaijan and Iran usually shared the same history. Azerbaijan retained its Iranian character even after the Arab conquest of Iran and the conversion of the area's inhabitants to Islam. Some four centuries later, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neolithic Asia
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several parts of the world. This "Neolithic package" included the introduction of farming, domestication of animals, and change from a hunter-gatherer lifestyle to one of settlement. It began about 12,000 years ago when farming appeared in the Epipalaeolithic Near East, and later in other parts of the world. The Neolithic lasted in the Near East until the transitional period of the Chalcolithic (Copper Age) from about 6,500 years ago (4500 BC), marked by the development of metallurgy, leading up to the Bronze Age and Iron Age. In other places the Neolithic followed the Mesolithic (Middle Stone Age) and then lasted until later. In Ancient Egypt, the Neolithic lasted until the Protodynastic period, 3150 BC.Karin Sowada and Peter Grave. Egypt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Azerbaijan
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes over 99% of the human past, from the Paleolithic until the advent of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Azerbaijan
The history of Azerbaijan is understood as the history of the region now forming the Republic of Azerbaijan. Topographically, the land is contained by the southern slopes of the Caucasus Mountains in the north, the Caspian Sea in the east, and the Armenian Highlands in the west. In the south, its natural boundaries are less distinct, and here the country merges with the Iranian Plateau. The entity of Caucasian Albania was established on its soil in ancient times. The Caucasian Albanian language spoken by the founders of Caucasian Albania was most likely a predecessor of the now endangered Udi language spoken by the Udi people. From the time of the Medes and the Achaemenid Empire, until the coming of the Russian Empire, Russians in the 19th century, the territories of the republic of Azerbaijan and Iran usually shared the same history. Azerbaijan retained its Iranian peoples, Iranian character even after the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab conquest of Iran and the conversion of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
