|
Ovarian Stem Cell
Ovarian stem cells are oocytes formed in ovarian follicle before birth in female mammals. They do not form post-natally, and are depleted throughout reproductive life. In humans it is estimated that 500,000–1,000,000 primordial follicles are present at birth, decreasing rapidly with age until roughly age 51 when ovulation stops, resulting in menopause. The origin of these oocytes remains under discussion. The publication of a study in 2004 proposing germ cell renewal in adult mice sparked a debate on the possibility of stem cells in the postnatal ovary. An increasing number of studies suggest that stem cells exist within the mammalian ovary and can be manipulated in vitro to produce oocytes, but whether such ovarian stem cells have the potential to differentiate into oocytes remains uncertain. History 1870s Studies performed on humans, dogs, and cats revealed that oocyte production stops shortly after birth. If this is true, it would mean that females have a finite number of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Cat - An Introduction To The Study Of Backboned Animals, Especially Mammals (1881) (20593323261)
''The'' () is a grammatical Article (grammar), article in English language, English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the Most common words in English, most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology and its subdisciplines are traditionally done in labware such as test tubes, flasks, Petri dishes, and microtiter plates. Studies conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated from their usual biological surroundings permit a more detailed or more convenient analysis than can be done with whole organisms; however, results obtained from ''in vitro'' experiments may not fully or accurately predict the effects on a whole organism. In contrast to ''in vitro'' experiments, '' in vivo'' studies are those conducted in living organisms, including humans, and whole plants. Definition ''In vitro'' ( la, in glass; often not italicized in English usage) studies are conducted using components of an organism that have been isolated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine System
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is known as endocrinology. Glands that signal each other in sequence are often referred to as an axis, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems have secondary endocrine functions, including bone, kidneys, liver, heart and gonads. For example, the kidney secretes the endocrine hormone erythropoietin. Hormones can be amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins. The endocrine system can be contrasted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy (often abbreviated to chemo and sometimes CTX or CTx) is a type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs ( chemotherapeutic agents or alkylating agents) as part of a standardized chemotherapy regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent (which almost always involves combinations of drugs) or it may aim to prolong life or to reduce symptoms ( palliative chemotherapy). Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called ''medical oncology''. The term ''chemotherapy'' has come to connote non-specific usage of intracellular poisons to inhibit mitosis (cell division) or induce DNA damage, which is why inhibition of DNA repair can augment chemotherapy. The connotation of the word chemotherapy excludes more selective agents that block extracellular signals ( signal transduction). The development of therapies with specific molecular or genetic targ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
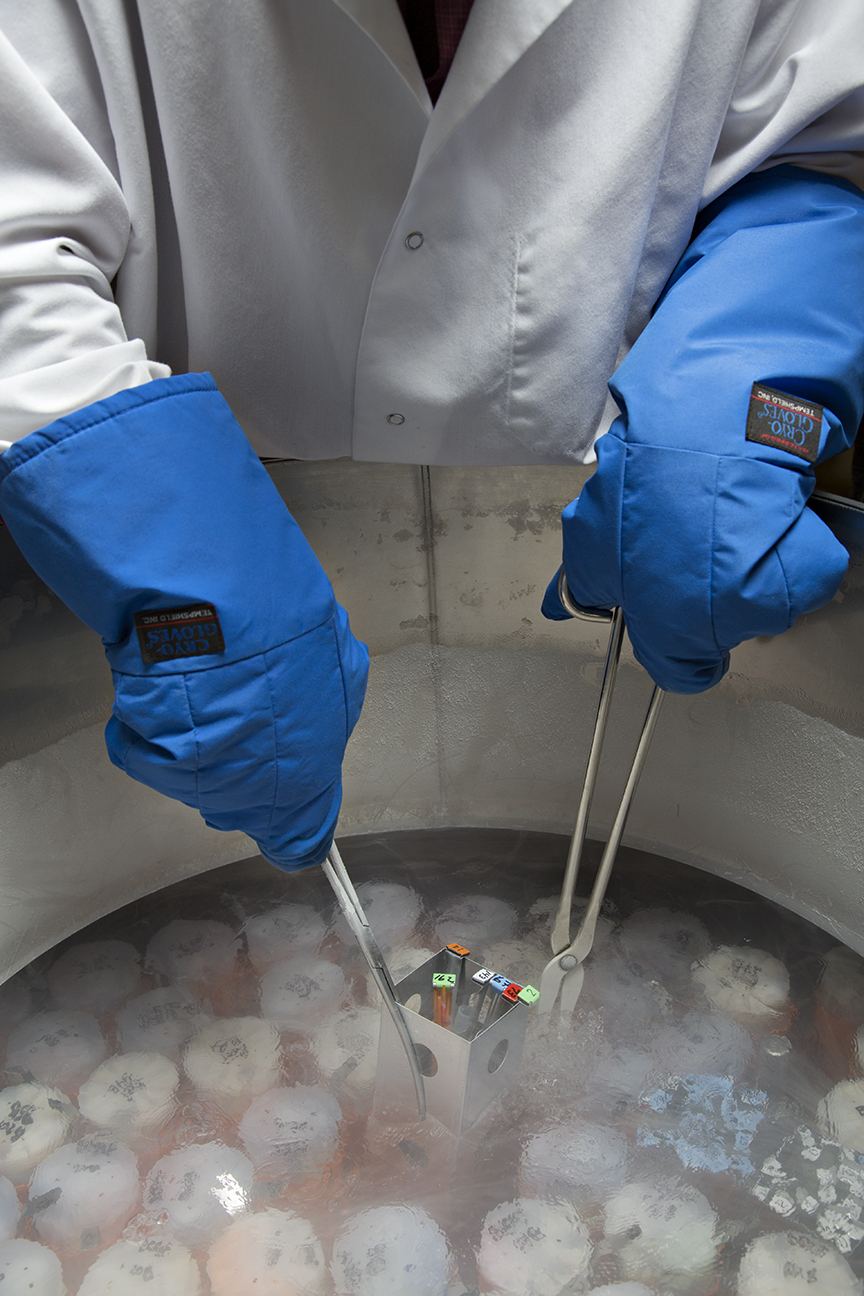
Cryopreservation
Cryo-preservation or cryo-conservation is a process where organisms, organelles, cells, tissues, extracellular matrix, organs, or any other biological constructs susceptible to damage caused by unregulated chemical kinetics are preserved by cooling to very low temperatures (typically using solid carbon dioxide or using liquid nitrogen). At low enough temperatures, any enzymatic or chemical activity which might cause damage to the biological material in question is effectively stopped. Cryopreservation methods seek to reach low temperatures without causing additional damage caused by the formation of ice crystals during freezing. Traditional cryopreservation has relied on coating the material to be frozen with a class of molecules termed cryoprotectants. New methods are being investigated due to the inherent toxicity of many cryoprotectants. Cryoconservation of animal genetic resources is done with the intention of conservation of the breed. Natural cryopreservation Tardig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female Infertility
Female infertility refers to infertility in women. It affects an estimated 48 million women, with the highest prevalence of infertility affecting women in South Asia, Sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa/Middle East, and Central/Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Infertility is caused by many sources, including nutrition, diseases, and other malformations of the uterus. Infertility affects women from around the world, and the cultural and social stigma surrounding it varies. Cause Causes or factors of female infertility can basically be classified regarding whether they are acquired or genetic, or strictly by location. Although factors of female infertility can be classified as either acquired or genetic, female infertility is usually more or less a combination of nature and nurture. Also, the presence of any single risk factor of female infertility (such as smoking, mentioned further below) does not necessarily cause infertility, and even if a woman is definitely infertile, the infer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Premature Ovarian Insufficiency
Primary ovarian insufficiency (POI) (also called premature ovarian insufficiency, premature menopause, and premature ovarian failure) is the partial or total loss of reproductive and hormonal function of the ovaries before age 40 because of folliclular (egg producing area) dysfunction or early loss of eggs. POI can be seen as part of a continuum of changes leading to menopause that differ from age-appropriate menopause in the age of onset, degree of symptoms, and sporadic return to normal ovarian function. POI affects approximately 1 in 10,000 women under age 20, 1 in 1,000 women under age 30, and 1 in 100 of those under age 40. A medical triad for the diagnosis is amenorrhea, hypergonadotropism, and hypoestrogenism. Physical and emotional symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, dry skin, vaginal dryness, irregular or absent menstruation, anxiety, depression, mental fog, irritability, nervousness, decreased libido, and increased autoimmune disruption. The sense of shock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Helicase
Helicases are a class of enzymes thought to be vital to all organisms. Their main function is to unpack an organism's genetic material. Helicases are motor proteins that move directionally along a nucleic acid phosphodiester backbone, separating two hybridized nucleic acid strands (hence '' helic- + -ase''), using energy from ATP hydrolysis. There are many helicases, representing the great variety of processes in which strand separation must be catalyzed. Approximately 1% of eukaryotic genes code for helicases. The human genome codes for 95 non-redundant helicases: 64 RNA helicases and 31 DNA helicases. Many cellular processes, such as DNA replication, transcription, translation, recombination, DNA repair, and ribosome biogenesis involve the separation of nucleic acid strands that necessitates the use of helicases. Some specialized helicases are also involved in sensing of viral nucleic acids during infection and fulfill a immunological function. Function Helicases ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stem Cell
In multicellular organisms, stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and proliferate indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell. They are the earliest type of cell in a cell lineage. They are found in both embryonic and adult organisms, but they have slightly different properties in each. They are usually distinguished from progenitor cells, which cannot divide indefinitely, and precursor or blast cells, which are usually committed to differentiating into one cell type. In mammals, roughly 50–150 cells make up the inner cell mass during the blastocyst stage of embryonic development, around days 5–14. These have stem-cell capability. ''In vivo'', they eventually differentiate into all of the body's cell types (making them pluripotent). This process starts with the differentiation into the three germ layers – the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm – at the gastrulation stage. How ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
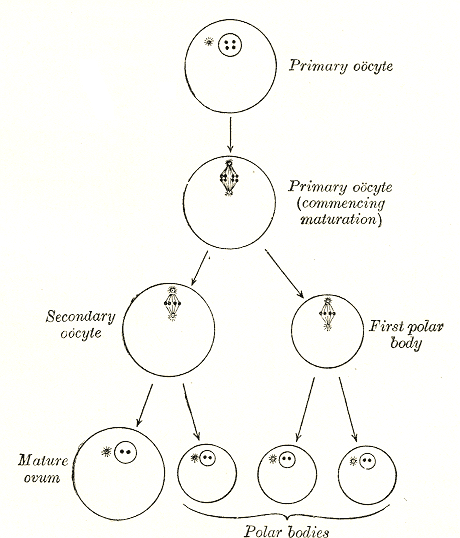
Oocyte
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female germ cells produce a primordial germ cell (PGC), which then undergoes mitosis, forming oogonia. During oogenesis, the oogonia become primary oocytes. An oocyte is a form of genetic material that can be collected for cryoconservation. Formation The formation of an oocyte is called oocytogenesis, which is a part of oogenesis. Oogenesis results in the formation of both primary oocytes during fetal period, and of secondary oocytes after it as part of ovulation. Characteristics Cytoplasm Oocytes are rich in cytoplasm, which contains yolk granules to nourish the cell early in development. Nucleus During the primary oocyte stage of oogenesis, the nucleus is called a germinal vesicle. The only normal human type of secondary oocyte ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germ Cell
Germ or germs may refer to: Science * Germ (microorganism), an informal word for a pathogen * Germ cell, cell that gives rise to the gametes of an organism that reproduces sexually * Germ layer, a primary layer of cells that forms during embryonic development * Cereal germ, the reproductive part of a cereal grain * Tooth germ, an aggregation of cells that eventually forms a tooth * Germ theory of disease, which states that some diseases are caused by microorganisms * Germ (mathematics), an object in a topological space that captures local properties Art and media Music * Germs (band), an American punk rock band * Germ (musician), a stage name of Tim Wright * Germ (rapper), an American rapper affiliated with Suicideboys and Pouya * "Germs" (song), by "Weird Al" Yankovic * ''The Germ'' (album), by Victim's Family Others * "Germs" (''Invader Zim''), an episode of ''Invader Zim'' * ''The Germ'' (periodical), a British art magazine published in 1850 * The Germs (com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menopause
Menopause, also known as the climacteric, is the time in women's lives when menstrual periods stop permanently, and they are no longer able to bear children. Menopause usually occurs between the age of 47 and 54. Medical professionals often define menopause as having occurred when a woman has not had any menstrual bleeding for a year. It may also be defined by a decrease in hormone production by the ovaries. In those who have had surgery to remove their uterus but still have functioning ovaries, menopause is not considered to have yet occurred. Following the removal of the uterus, symptoms typically occur earlier. In the years before menopause, a woman's periods typically become irregular, which means that periods may be longer or shorter in duration or be lighter or heavier in the amount of flow. During this time, women often experience hot flashes; these typically last from 30 seconds to ten minutes and may be associated with shivering, sweating, and reddening of the ski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.png)