|
Oud
, image=File:oud2.jpg , image_capt=Syrian oud made by Abdo Nahat in 1921 , background= , classification= *String instruments * Necked bowl lutes , hornbostel_sachs=321.321-6 , hornbostel_sachs_desc=Composite chordophone sounded with a plectrum , developed= Islamic Golden Age , range= , related= * Angélique * Archlute * Barbat (lute) * Baglamadaki *Bağlama *Biwa * Bouzouki * Cobza * Cümbüş *Daguangxian * Đàn tỳ bà * Dombra * Domra *Dutar * Kobza * Lavta * Liuqin *Lute * Mandocello * Mandola *Mandolin * Mandolute * Pandura *Pipa * Qanbus *Rud *Setar * Tanbur * Tanbur (Turkish) * Tar (Azerbaijani instrument) * Tembûr * Theorbo * Torban The oud ( ar, عود, translit=ʿūd, ; so, kaban or so, cuud, label=none) is a short-neck lute-type, pear-shaped, fretless stringed instrument (a chordophone in the Hornbostel–Sachs classification of instruments), usually with 11 strings grouped in six courses, but some models have five or seven courses, with 10 or 13 strings re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lute
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted. More specifically, the term "lute" can refer to an instrument from the family of European lutes. The term also refers generally to any string instrument having the strings running in a plane parallel to the sound table (in the Hornbostel–Sachs system). The strings are attached to pegs or posts at the end of the neck, which have some type of turning mechanism to enable the player to tighten the tension on the string or loosen the tension before playing (which respectively raise or lower the pitch of a string), so that each string is tuned to a specific pitch (or note). The lute is plucked or strummed with one hand while the other hand "frets" (presses down) the strings on the neck's fingerboard. By pressing the strings on different places of the fingerboard, the player can sho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
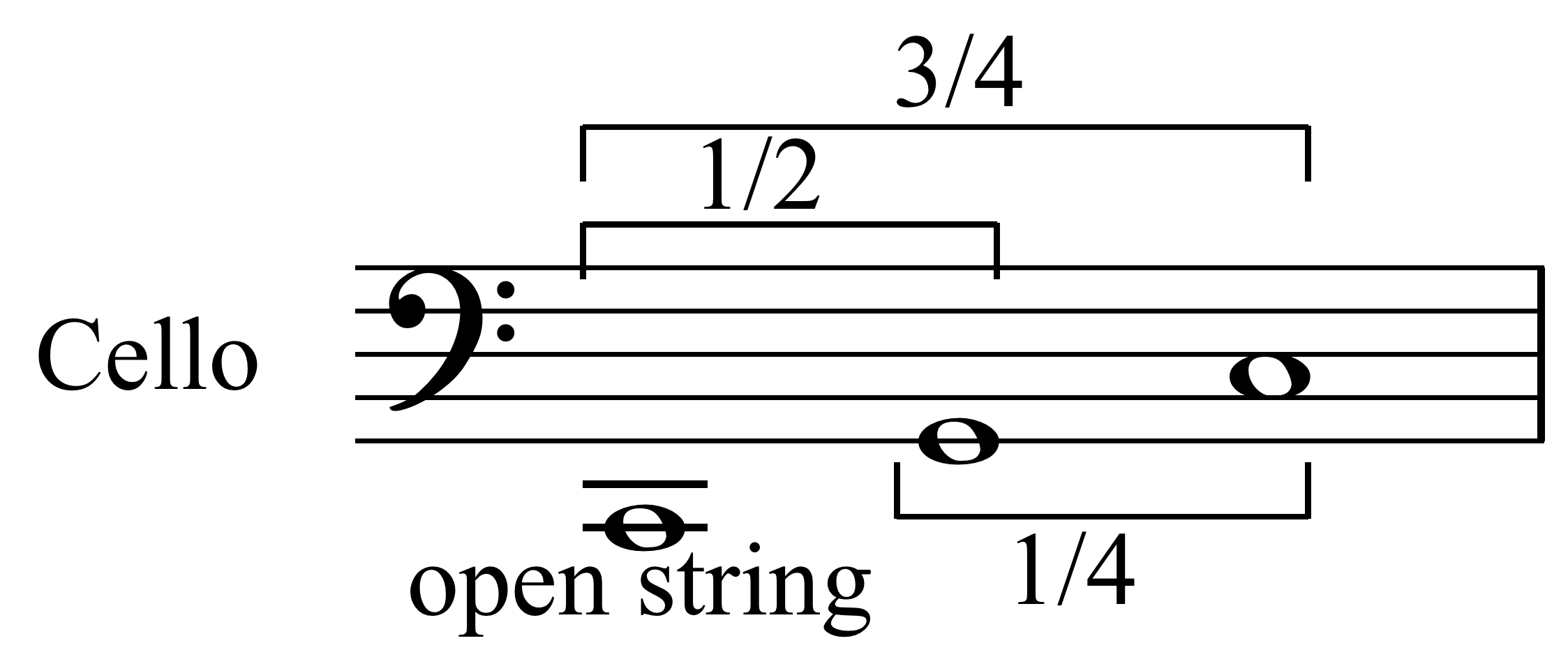
String Instruments
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the Baroq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chordophone
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner. Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the strings with their fingers or a plectrum—and others by hitting the strings with a light wooden hammer or by rubbing the strings with a bow. In some keyboard instruments, such as the harpsichord, the musician presses a key that plucks the string. Other musical instruments generate sound by striking the string. With bowed instruments, the player pulls a rosined horsehair bow across the strings, causing them to vibrate. With a hurdy-gurdy, the musician cranks a wheel whose rosined edge touches the strings. Bowed instruments include the string section instruments of the orchestra in Western classical music (violin, viola, cello and double bass) and a number of other instruments (e.g., viols and gambas used in early music from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbat (lute)
The ''barbat'' ( fa, بربت) or ''barbud'' was a lute of Central Asian or Greater Iranian or Persian origin. Barbat is characterized as carved from a single piece of wood, including the neck and a wooden sound board. Possibly a skin-topped instrument for part of its history, it is ancestral to the wood-topped oud and biwa and the skin-topped Yemeni qanbus. Although the original barbat disappeared, modern Iranian luthiers have re-created the instrument, looking at historical images for details. The modern re-created instrument (Iranian Barbat) resembles the oud, although differences include a smaller body, longer neck, a slightly raised fingerboard, and a sound that is distinct from that of the oud. History The ''barbat'' probably originated in Central Asia. The earliest image of the ''barbat'' dates back to the 1st century BC from ancient northern Bactria. While in his book (''Les instruments de musique de l’Inde ancienne'') musicologist Claudie Marcel-Dubois pointed out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandolin
A mandolin ( it, mandolino ; literally "small mandola") is a stringed musical instrument in the lute family and is generally plucked with a pick. It most commonly has four courses of doubled strings tuned in unison, thus giving a total of 8 strings, although five (10 strings) and six (12 strings) course versions also exist. There are of course different types of strings that can be used, metal strings are the main ones since they are the cheapest and easiest to make. The courses are typically tuned in an interval of perfect fifths, with the same tuning as a violin (G3, D4, A4, E5). Also, like the violin, it is the soprano member of a family that includes the mandola, octave mandolin, mandocello and mandobass. There are many styles of mandolin, but the three most common types are the ''Neapolitan'' or ''round-backed'' mandolin, the ''archtop'' mandolin and the ''flat-backed'' mandolin. The round-backed version has a deep bottom, constructed of strips of wood, glued toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lavta
The lavta is a plucked string music instrument from Istanbul. Description The Lavta has a small body made of many ribs made using carvel bending technique. Its appearance is somewhat like a small (Turkish) oud - the strings are made from gut like an oud but it has only 7 strings in 4 courses and is tuned E AA dd gg (like the oud), or sometimes A dd aa d'd' (in intervals of 5ths like laouto - as well as 4ths); it is also sometimes tuned to Turkish Bolahenk tuning C G D A, which is the same as G D A E in concert pitch. The adjustable frets are made from tied bits of gut on the fingerboard, at the microtonal intervals of the makam system. This is more closely related to instruments like tanbur than to the fretless oud and the 12-frets of the octave laouto. The bridge usually has mustache-shaped ends. The fingerboard is flush with the soundboard, is often unvarnished, and has a carved and inlaid rosette. Some lavta have a pegbox like the oud (angling down), others more lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cümbüş
The ''cümbüş'' (; ) is a Turkish stringed instrument of relatively modern origin. It was developed in 1930 by Zeynel Abidin Cümbüş (1881–1947) as an oud-like instrument that could be heard as part of a larger ensemble. The cümbüş is shaped like an American banjo, with a spun-aluminum resonator bowl and skin soundboard. Although originally configured as an oud, the instrument has been converted to other instruments by attaching a different set of neck and strings. The standard cümbüş is fretless, but guitar, mandolin and ukulele versions have fretboards. The neck is adjustable, allowing the musician to change the angle of the neck to its strings by turning a screw. One model is made with a wooden resonator bowl, with the effect of a less tinny, softer sound.Zeynel Abidin Cümbüş manufacturers, ''Cumb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Golden Age
The Islamic Golden Age was a period of cultural, economic, and scientific flourishing in the history of Islam, traditionally dated from the 8th century to the 14th century. This period is traditionally understood to have begun during the reign of the Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid caliph Harun al-Rashid (786 to 809) with the inauguration of the House of Wisdom in Baghdad, the world's largest city by then, where Muslim Ulama, scholars and polymaths from various parts of the world with different cultural backgrounds were mandated to gather and translate all of the known world's classical knowledge into Aramaic and Arabic. The period is traditionally said to have ended with the collapse of the Abbasid caliphate due to Mongol invasions and conquests, Mongol invasions and the Siege of Baghdad (1258), Siege of Baghdad in 1258. A few scholars date the end of the golden age around 1350 linking with the Timurid Renaissance, while several modern historians and scholars place the end of the Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plectrum
A plectrum is a small flat tool used for plucking or strumming of a stringed instrument. For hand-held instruments such as guitars and mandolins, the plectrum is often called a pick and is held as a separate tool in the player's hand. In harpsichords, the plectra are attached to the jack mechanism. Plectra wielded by hand Guitars and similar instruments A plectrum for electric guitars, acoustic guitars, bass guitars and mandolins is typically a thin piece of plastic or other material most commonly shaped like a pointed teardrop or triangle, though the size, gauge, shape and width may vary considerably. Banjo and guitar players may wear a metal or plastic thumb pick mounted on a ring, and bluegrass banjo players often wear metal or plastic fingerpicks on their fingertips. Many guitarists use fingerpicks as well. Guitar picks are made of a variety of materials, including celluloid, metal, and rarely other exotic materials such as turtle shell, but today delrin (a synthetic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobza
The ''cobza'' (also ''cobsa'', ''cobuz'', ''koboz'') is a multi- stringed instrument of the lute family of folk origin popular in the Romanian folklore from both Romania and Republic of Moldova (it is considered the oldest accompaniment instrument in the region). It is also used in the Hungarian Táncház movement (end of the 20th Century). It is distinct from the Ukrainian Kobza, an instrument of different construction and origin. Overview The Romanian Cobza is metal-strung (although modern nylon-strung models exist, mostly in Hungary), and has a very short neck without frets (although a newer fretted cobza can be found in the Republic of Moldova), with a bent-back pegbox. The back is ribbed. It is usually double or triple strung, and often has a characteristic flat end clasp. The Cobza is played with a plectrum (traditionally, a goose feather) in elaborate and florid melodic passagework, and has a pick-guard similar to that of an oud. Its strings are widely spaced at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouzouki
The bouzouki (, also ; el, μπουζούκι ; alt. pl. ''bouzoukia'', from Greek ), also spelled buzuki or buzuci, is a musical instrument popular in Greece. It is a member of the long-necked lute family, with a round body with a flat top and a long neck with a fretted fingerboard. It has steel strings and is played with a plectrum producing a sharp metallic sound, reminiscent of a mandolin but pitched lower. There are two main types of bouzouki: the ''trichordo'' (''three-course'') has three pairs of strings (known as courses) and the ''tetrachordo'' (''four-course'') has four pairs of strings. The instrument was brought to Greece in the early 1900s by Greek refugees from Anatolia, and quickly became the central instrument to the rebetiko genre and its music branches. It is now an important element of modern Laïko pop Greek music. Etymology The name ''bouzouki'' comes from the Turkish word , meaning "broken" or "modified", and comes from a particular re-entrant tuning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Setar
A setar ( fa, سهتار, ) is a stringed instrument, a type of lute used in Persian traditional music, played solo or accompanying voice. It is a member of the tanbur family of long-necked lutes with a range of more than two and a half octaves. Originally a three stringed instrument, a fourth string was added by the mid 19th century. It is played with the index finger of the right hand. It has been speculated that the setar originated in Persia by the 9th century C.E. A more conservative estimate says "it originated in the 15th century, or even earlier." Although related to the tanbur, in recent centuries, the setar has evolved so that, musically, it more closely resembles the tar, both in tuning and playing style. Etymology According to Curt Sachs, Persians chose to name their lutes around the word ''tar'', meaning string, combined with a word for the number of strings. Du + tar is the 2-stringed dutār, se + tar is the 3-stringed setār, čartar (4 strings), pančt� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |