|
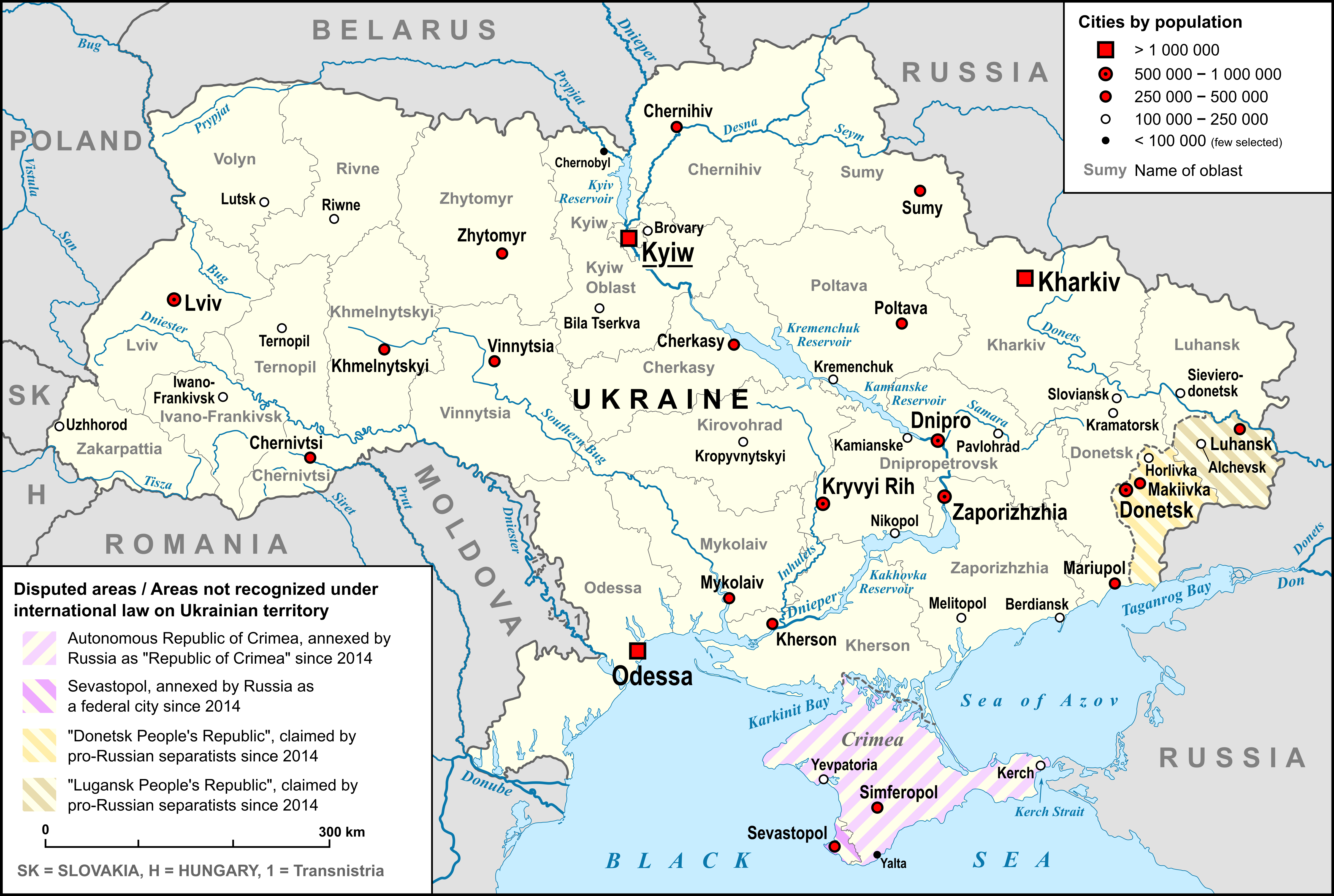
Ostroh (Poustka)
Ostroh ( uk, Остро́г; pl, Ostróg) is a historic city located in Rivne Oblast (province) of western Ukraine, on the Horyn River. Ostroh was the administrative center of the Ostroh Raion (district) until 2020. Administratively, Ostroh is incorporated as a city of oblast significance and does not belong to the raion. Population: The Ostroh Academy was established here in 1576, the first higher educational institution in modern Ukraine. Furthermore, in the 16th century, the first East Slavic books, notably the Ostrog Bible, were printed there. History The Hypatian Codex first mentions Ostroh in 1100, as a fortress of the Volhynian princes. Since the 14th century, it was the seat of the powerful Ostrogski princely family, who developed their town into a great centre of learning and commerce. Upon the family's demise in the 17th century, Ostroh passed to the Zasławski and then Lubomirski families. In the second half of the 14th century, Ostroh, together with the wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In Ukraine
This is a complete list of cities in Ukraine. On 1 January 2022, there were 461 cities ( uk, місто, ''misto'') in Ukraine. City status is granted by the Verkhovna Rada, the Ukrainian parliament. The city status is only partially related to the size of a populated place in Ukraine. Smaller settlements are urban-type settlements (comparable to towns in English-speaking countries) and villages ( uk, село, ''selo''). Historically, there were systems of city rights, granted by the territorial lords, which defined the status of a place as a ''misto'' or ''selo''. Cities were self-governing and had several privileges. The list of cities is ordered by 2021 estimates of population and compared to the 2001 Ukrainian Census, except for Chernobyl for which population is an unofficial estimate. The cities with special status are shown in ''italic''. Cities in Ukraine Jump to table of cities See also * Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of Regional Significance (Ukraine)
City of regional significance ( uk, місто обласного значення, ''misto oblasnoho znachennia'') in Ukraine was a type of second-level administrative division or municipality, the other type being raions (districts). In the first-level division of oblasts, they were referred to as ''cities of oblast significance''; in the first-level autonomous republic of Crimea, they were ''cities of republican significance''. The designation was created with the introduction of oblasts in 1932. It was abolished in a 2020 reform that merged raions together and integrated the city municipalities into them. Such city municipality was complex and usually combined the city proper and adjacent populated places. The city of regional (oblast) significance was governed by a city council known as ''mis'krada'', which was chaired by a mayor. There were instances where a municipality might have included only the city alone (city proper), while in others instances a municipality might ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the German city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Bohemia, Hungary, Poland and Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries, the Baltic states, and the interior (for example Braunschweig). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partitions Of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 123 years. The partitions were conducted by the Habsburg monarchy, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Russian Empire, which divided up the Commonwealth lands among themselves progressively in the process of territorial seizures and annexations. The First Partition was decided on August 5, 1772 after the Bar Confederation lost the war with Russia. The Second Partition occurred in the aftermath of the Polish–Russian War of 1792 and the Targowica Confederation of 1792 when Russian and Prussian troops entered the Commonwealth and the partition treaty was signed during the Grodno Sejm on January 23, 1793 (without Austria). The Third Partition took place on October 24, 1795, in reaction to the unsuccessful Polish Kościuszko Uprising the previ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, including the Kingdom of Poland proper. The Polish Crown was at the helm of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth from 1569 to 1795. Major political events The Kingdom of Poland has been traditionally dated back to c. 966, when Mieszko I and his pagan Slavic realm joined Christian Europe (Baptism of Poland), establishing the state of Poland, a process started by his Polan Piast dynasty ancestors. His oldest son and successor, Prince Bolesław I Chrobry, Duke of Poland, became the first crowned King of Poland in 1025. Union of Krewo The Union of Krewo was a set of prenuptial agreements made in the Kreva Castle on August 13, 1385. Once Jogaila confirmed the prenuptial agreements on August 14, 1385, Poland and Lithuania formed a personal uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union Of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the personal union of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania with a real union and an elective monarchy, since Sigismund II Augustus, the last of the Jagiellons, remained childless after three marriages. In addition, the autonomy of Royal Prussia was largely abandoned. The Duchy of Livonia, tied to Lithuania in real union since the Union of Grodno (1566), became a Polish–Lithuanian condominium. The Commonwealth was ruled by a single elected monarch who carried out the duties of King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, and governed with a common Senate and parliament (the ''Sejm''). The Union is seen by some as an evolutionary stage in the Polish–Lithuanian alliance and personal union, necessitated also by L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire of Austria. The state was founded by Lithuanians, who were at the time a polytheistic nation born from several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. The Grand Duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Lithuania, Belarus and parts of Ukraine, Latvia, Poland, Russia and Moldova. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multi-ethnic and multiconfessional state, with great diversity in languages, religion, and cultural heritage. The consolidation of the Lithuanian lands began in the late 13th century. Mindaugas, the first ruler of the Grand Duchy, was crowned as Catholic King of Lithuania in 1253. The pagan state was targeted in a religious crusade by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubomirski
The House of Lubomirski is a Polish princely family. The Lubomirski family's coat of arms is the Drużyna coat of arms, which is similar to the Szreniawa coat of arms but without a cross. Origin and the coat of arms The Lubomirski family have been actors in the history of Poland since the 10th century. There are two theories regarding the family's origin. One, by Adam Boniecki, a Polish heraldist, assumes that there were two branches of the family. One settled at the Szreniawa River in Proszowice County while the other established itself in Szczyrzyc County. The time of this division of the family is not known, but most likely it was before the adoption of Christianity by Poland. The Szreniawici family used a similar coat of arms, which means that the two families had the same ancestry. At the time of Mieszko I, the members of the Lubomirski family demonstrated bravery in battle against pagans. For this they were awarded the rank of knight and a coat of arms, which de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zasławski
The House of Zasławski (plural ''Zasławscy'') was the name of a Polish– Ruthenian noble family and a cadet branch of the Ostrogski family. The Zasławski family had its power base in Volhynia, Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (today in Ukraine), and traced its origins to a branch of the Rurikids that took its name from the Iziaslav. Due to their relation to the Rurikids, the Zasławski family held the title of '' Knyaz'' (prince). History The Zasławski family was one of the three major families in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth to trace its origins to either Kaributas (they used Korybut coat of arms) or, according to modern historical interpretations, the Ruthenian Rurikids; the other two families were the Ostrogski family and the Wiśniowiecki family. The Zasławski family was sometimes seen as a junior line of the Ostrogoski family. After the death in 1620 of the last male heir of the Ostrogoski family, Janusz Ostrogski, many of the Ostrogoski possessions were i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrogski Family
The House of Ostrogski ( pl, Ostrogscy, lt, Ostrogiškiai, ua, Острозькі - ''Ostroz'ki'') was one of the more prominent families in the Kingdom of Poland, the Grand Duchy of Lithuania and in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The family was of Ruthenian origin, founded by the 14th century noble Danylo Ostrogski, who took his name from the historic city of Ostroh in contemporary Ukraine. After the death in 1620 of Janusz Ostrogski, the last male heir, most of the family's possessions passed to the Zasławski family. History The Ostrogski family was most likely of Rurikid stock and descended from Sviatopolk II of Kiev. Some scholars however claim that their descent is from the Galicia-Volhynia line of the Rurikid dynasty. Vasilko Romanovich (c.1256-1282), Prince of Slonim, may have been the grandfather of Prince Daniel Ostrogski. The probable progenitor of this family was Prince Danylo Dmytrovych (''or Danylo Wasilijewicz''), who received Ostroh from Liubartas, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volhynia
Volhynia (also spelled Volynia) ( ; uk, Воли́нь, Volyn' pl, Wołyń, russian: Волы́нь, Volýnʹ, ), is a historic region in Central and Eastern Europe, between south-eastern Poland, south-western Belarus, and western Ukraine. The borders of the region are not clearly defined, but the territory that still carries the name is Volyn Oblast, in western Ukraine. Volhynia has changed hands numerous times throughout history and been divided among competing powers. For centuries it was part of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth. After the Russian annexation, all of Volhynia was part of the Pale of Settlement designated by Imperial Russia on its south-western-most border. Important cities include Lutsk, Rivne, Volodymyr, Ostroh, Ustyluh, Iziaslav, Peresopnytsia, and Novohrad-Volynskyi (Zviahel). After the annexation of Volhynia by the Russian Empire as part of the Partitions of Poland, it also included the cities of Zhytomyr, Ovruch, Korosten. The city of Zviahel was r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypatian Codex
The Hypatian Codex (also known as Hypatian Letopis or Ipatiev Letopis; be, Іпацьеўскі летапіс; russian: Ипатьевская летопись; uk, Іпатіївський літопис) is a ''svod'' (compendium) of three ''letopis'' chronicles: the ''Primary Chronicle'', ''Kievan Chronicle'' and '' Galician-Volhynian Chronicle''. It is the most important source of historical data for southern Rus'. The codex was rediscovered in what is today Ukraine in 1617 by Zacharias Kopystensky, where it was copied by monks in 1621.Velychenko, p. 144. It was re-discovered yet again in the 18th century at the Hypatian Monastery of Kostroma by the Russian historian Nikolay Karamzin. The codex is the second oldest surviving manuscript of the "Initial svod" (Primary Chronicle), after the Laurentian Codex. The Hypatian manuscript dates back to ca. 1425, but it incorporates much precious information from the lost 12th-century Kievan and 13th-century Galician chronicles. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)
