|
Osteolaeminae
Osteolaeminae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae containing the dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae. Taxonomy Osteolaeminae was named by Christopher Brochu in 2003 as a subfamily of Crocodylidae separate from Crocodylinae, and is cladistically defined as ''Osteolaemus tetraspis'' (the Dwarf crocodile) and all crocodylians more closely related to it than to ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). This is a stem-based definition, and is the sister taxon to Crocodylinae. Osteolaeminae contains the two extant genera ''Osteolaemus'' and '' Mecistops'', along with several extinct genera, although the number of extant species within Osteolaeminae is currently in question. Phylogeny The cladogram below is based on two studies that combined morphological, molecular (DNA sequencing), and stratigraphic (fossil age) data. Alternatively, other morphological studies have recovered ''Mecistop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylidae
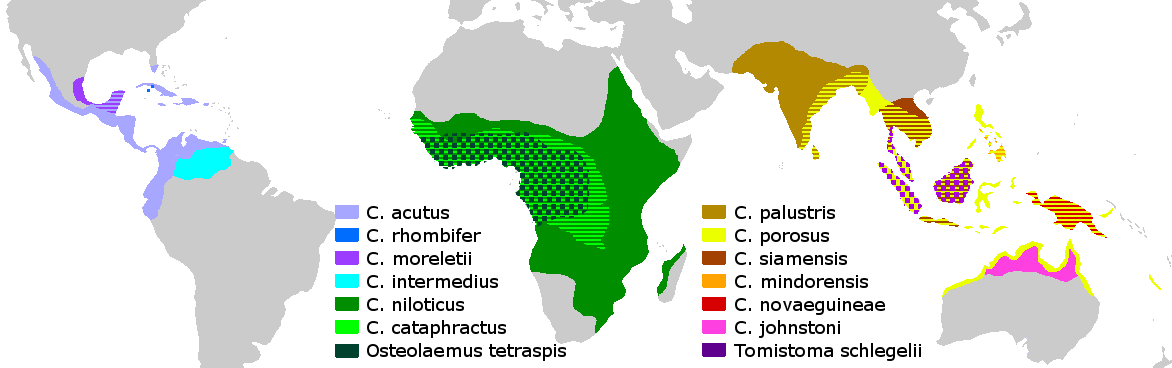
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant members of the order Crocodilia, which includes the alligators and caimans (family Alligatoridae), the gharial and false gharial (family Gavialidae) among other extinct taxa. Although they appear similar, crocodiles, alligators and the gharial belong to separate biological families. The gharial, with its narrow snout, is easier to distinguish, while morphological differences are more difficult to spot in crocodiles and alligators. The most obvious external differences are visible in the head, with crocodiles having narrower and longer heads, with a more V-shaped than a U-shaped snout compared to alligators and caimans. Another obvious trait is that the upper and lower jaws of the crocodiles are the same width, and the teeth in the lowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rimasuchus
''Rimasuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from the Miocene of Egypt and possibly Libya. Only one species - ''Rimasuchus lloydi'' - is currently known. It was previously thought to be a species of '' Crocodylus'', but is now thought to be more closely related to the modern African dwarf crocodiles (''Osteolaemus''). History and naming The first fossil of ''Rimasuchus'' an incomplete skull with associated mandible, was collected by lieutenant colonel Arthur H. Lloyd in the early 20th century in Wadi Moghara, Egypt. The holotype specimen, CGM 15597, was given to the Egyptian Geological Museum and described by Fourtau in 1920 under the name ''Crocodylus lloydi''. Other material includes an uncatalogued skull housed at the Natural History Museum, London (likewise from Wadi Moghara) and fossils found at Gebel Zelten in Libya. Eventually other skulls further south in Africa ended up being assigned to ''"Crocodylus" lloydi'' , with the oldest and southern-most material stemming f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euthecodon
''Euthecodon'' is an extinct genus of long-snouted crocodile. It was common throughout much of Africa during the Neogene, with fossils being especially common in Kenya, Ethiopia, and Libya. Although superficially resembling that of gharials, the long snout was a trait developed independently from that of other crocodilians and suggests a diet of primarily fish. ''Euthecodon'' coexisted with a wide range of other crocodiles in the areas it inhabited before eventually going extinct during the Pleistocene. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Euthecodon'' were described by French paleontologist Léonce Joleaud based on material collected by the Bourg de Bozas expedition between 1900 and 1903 in Ethiopia.Joleaud, L. (1920). Sur la présence d'un Gavialide du genre ''Tomistoma'' dans le Pliocène d'eau douce de l'Ethiopie. ''Comptes Rendus de l'Académie des Sciences'' 70:816-818. These remains, thought to belong to a species of false gharial, were first described in 1920 under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylinae
Crocodylinae is a subfamily of true crocodiles within the family Crocodylidae, and is the sister taxon to Osteolaeminae ( dwarf crocodiles and slender-snouted crocodiles). Taxonomy Crocodylinae was cladistically defined by Christopher Brochu in 1999 as ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile) and all crocodylians more closely related to it than to ''Osteolaemus tetraspis'' (the Dwarf crocodile). This is a stem-based definition, and is the sister taxon to Osteolaeminae. Crocodylinae contains the extant genus '' Crocodylus''. It is disputed as to whether is also includes '' Mecistops'' (slender-snouted crocodiles), or the extinct genus Voay. Phylogeny Some morphological studies have recovered '' Mecistops'' as a basal member of Crocodylinae, more closely related to '' Crocodylus'' than to ''Osteolaemus'' and the other members of Osteolaeminae, as shown in the cladogram below. The below cladogram is based on a 2021 study using paleogenomics that extracted DNA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinyang (genus)
''Kinyang'' is an extinct genus of osteolaemine crocodile from the Early to Middle Miocene of Kenya. Two species are currently known, ''K. mabokoensis'' from the Lake Victoria basin and ''K. tchernovi'' from the Lake Victoria and Lake Turkana basin. ''Kinyang'' had an exceptionally broad and robust skull, much wider than that of any living crocodile species. This might have allowed it to attack and kill prey its own size or even bigger. ''Kinyang'' is notably larger than its contemporary relative '' Brochuchus''. While the precise reasons for the extinction of ''Kinyang'' are not known, it coincides with a larger faunal turnover that saw osteolaemines replaced by the still dominant crocodylines. One reason for this shift may have been the drying climate of Africa at the time, which caused rainforests to be replaced by more open environments and disrupted the nesting behavior of osteolaemines due to their dependence on foliage. History and naming The fossils of ''Kinyang'' w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecistops
''Mecistops'' is a genus of crocodiles, the slender-snouted crocodiles, native to sub-Saharan Africa. Taxonomy and etymology Traditionally placed in ''Crocodylus'', recent studies in DNA and morphology have shown that it is in fact basal to ''Crocodylus'', thus was moved its own genus. This genus itself was long considered to contain only one species, '' M. cataphractus'', but recent genetic analysis has revealed the existence of two species: the West African slender-snouted crocodile (''M. cataphractus'') and the Central African slender-snouted crocodile (''M. leptorhynchus''). Both species diverged during the Miocene (about 6.5–7.5 million years ago) and are separated by the Cameroon Volcanic Line. Phylogeny The cladogram below is based on two studies that combined morphological and molecular (DNA sequencing) data. (Note that most morphological analyses find a closer relationship between ''Euthecodon'' and ''Brochuchus''.) Alternatively, other morphological studie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocodylus
''Crocodylus'' is a genus of true crocodiles in the family Crocodylidae. Taxonomy The generic name, ''Crocodylus'', was proposed by Josephus Nicolaus Laurenti in 1768. ''Crocodylus'' contains 13–14 extant (living) species and 5 extinct species. There are additional extinct species attributed to the genus ''Crocodylus'' that studies have shown no longer belong, although they have not yet been reassigned to new genera. Extant species The 13–14 living species are: Fossils ''Crocodylus'' also includes five extinct species: * † ''Crocodylus anthropophagus'' is an extinct crocodile from Plio-Pleistocene of Tanzania. * † '' Crocodylus checchiai'' is an extinct crocodile from Late Miocene of Kenya. * † '' Crocodylus falconensis'' is an extinct crocodile from Early Pliocene of Venezuela. * † '' Crocodylus palaeindicus'' is an extinct crocodile the Miocene to the Pleistocene of southern Asia. * † '' Crocodylus thorbjarnarsoni'' is an extinct crocodile from Plio-Pleistoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwarf Crocodile
The dwarf crocodile (''Osteolaemus tetraspis''), also known as the African dwarf crocodile, broad-snouted crocodile (a name more often used for the Asian mugger crocodile) or bony crocodile, is an African crocodile that is also the smallest extant (living) species of crocodile. Taxonomy and etymology The second species has had a somewhat convoluted taxonomical history. It was first described as ''Osteoblepharon osborni'' by Schmidt in 1919, based on a few specimens from the Upper Congo River Basin in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, Inger in a 1948 paper found the specimens wanting of characteristics that would justify a generic separation from ''Osteolaemus'' and referred the specimens to ''Osteolaemus osborni''. In 1961, it was reduced to subspecies rank. A study of morphology published in 2007, and studies of DNA in 2009, 2013 and 2015 indicate that three distinctly different populations of ''Osteolaemus'' may merit full species recognition. Thes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brochuchus
''Brochuchus'' is an extinct genus of crocodile known from the Early Miocene Hiwegi Formation of Rusinga Island in Lake Victoria, Kenya; it was originally named as a species of '' Crocodylus''. It contains two species, ''B. parvidens'' and ''B. pigotti''. ''Brochuchus'' belongs to the family Crocodylidae, which includes all living crocodiles. The closest living relative of ''Brochuchus'' is ''Osteolaemus'', the dwarf crocodile. Compared to ''Osteolaemus'', which has a small body and blunt snout, ''Brochuchus'' has a more generalized crocodylid anatomy. ''Brochuchus'' is characterized by a flat and relatively narrow skull, and although it is larger than ''Osteolaemus'' it is smaller than most other crocodylids. It has two prominent bumps on the surface of its snout. The genus was named in honor of Christopher A. Brochu, for his scientific work on Crocodylia and its relatives. The unusual combination and spelling are intended as an auditory and visual pun such that the ‘ch’ so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voay
''Voay'' is an extinct genus of crocodile from Madagascar that lived during the Late Pleistocene to Holocene, containing only one species, ''V. robustus''. Numerous subfossils have been found, including complete skulls, noted for their distinctive pair of horns on the posterior, as well as vertebrae and osteoderms from such places as Ambolisatra and Antsirabe. The genus is thought to have become extinct relatively recently. It has been suggested to have disappeared in the extinction event that wiped out much of the endemic megafauna on Madagascar, such as the elephant bird and Malagasy hippo, following the arrival of humans to Madagascar around 2000 years ago. Its name comes from the Malagasy word for crocodile. Description One unusual feature of ''V. robustus'' that distinguishes it from other crocodilians is the presence of prominent "horns" extending from the posterior portion of the skull. They are actually the posterolaterally extended corners of the squamosal bone. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osborn’s Dwarf Crocodile
''Osteolaemus osborni'', commonly known as Osborn's dwarf crocodile, is a species of crocodile endemic to the Congo Basin in Africa. This species has had a somewhat convoluted taxonomical history. It was first described as ''Osteoblepharon osborni'' by Schmidt in 1919, based on a few specimens from the Upper Congo River Basin in what is now the Democratic Republic of Congo. However, Inger in a 1948 paper found the specimens wanting of characteristics that would justify a generic separation from ''Osteolaemus'' and referred the specimens to ''Osteolaemus osborni''. In 1961, it was reduced to subspecies rank, but was revalidated to full species status in 2021. The subspecific name, ''osborni'', is in honor of American paleontologist Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene epoch (roughly 11,700 years before present). It includes the study of fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladogram
A cladogram (from Greek ''clados'' "branch" and ''gramma'' "character") is a diagram used in cladistics to show relations among organisms. A cladogram is not, however, an evolutionary tree because it does not show how ancestors are related to descendants, nor does it show how much they have changed, so many differing evolutionary trees can be consistent with the same cladogram. A cladogram uses lines that branch off in different directions ending at a clade, a group of organisms with a last common ancestor. There are many shapes of cladograms but they all have lines that branch off from other lines. The lines can be traced back to where they branch off. These branching off points represent a hypothetical ancestor (not an actual entity) which can be inferred to exhibit the traits shared among the terminal taxa above it. This hypothetical ancestor might then provide clues about the order of evolution of various features, adaptation, and other evolutionary narratives about an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



%2C_NPSPhoto_(9255693421).jpg)
