|
Ossetes
The Ossetians or Ossetes (, ; os, ир, ирæттæ / дигорӕ, дигорӕнттӕ, translit= ir, irættæ / digoræ, digorænttæ, label=Ossetic) are an Iranian ethnic group who are indigenous to Ossetia, a region situated across the northern and southern sides of the Caucasus Mountains. They natively speak Ossetic, an Eastern Iranian language of the Indo-European language family, with most also being fluent in Russian as a second language. Ossetic, a remnant of the Scytho-Sarmatian dialect group which was once spoken across the Pontic–Caspian Steppe, is one of the few Iranian languages remaining inside Europe. Currently, the Ossetian homeland of Ossetia is politically divided between North Ossetia–Alania in Russia, and the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Their closest historical and linguistic relatives, the Jász people, live in the Jászság region within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
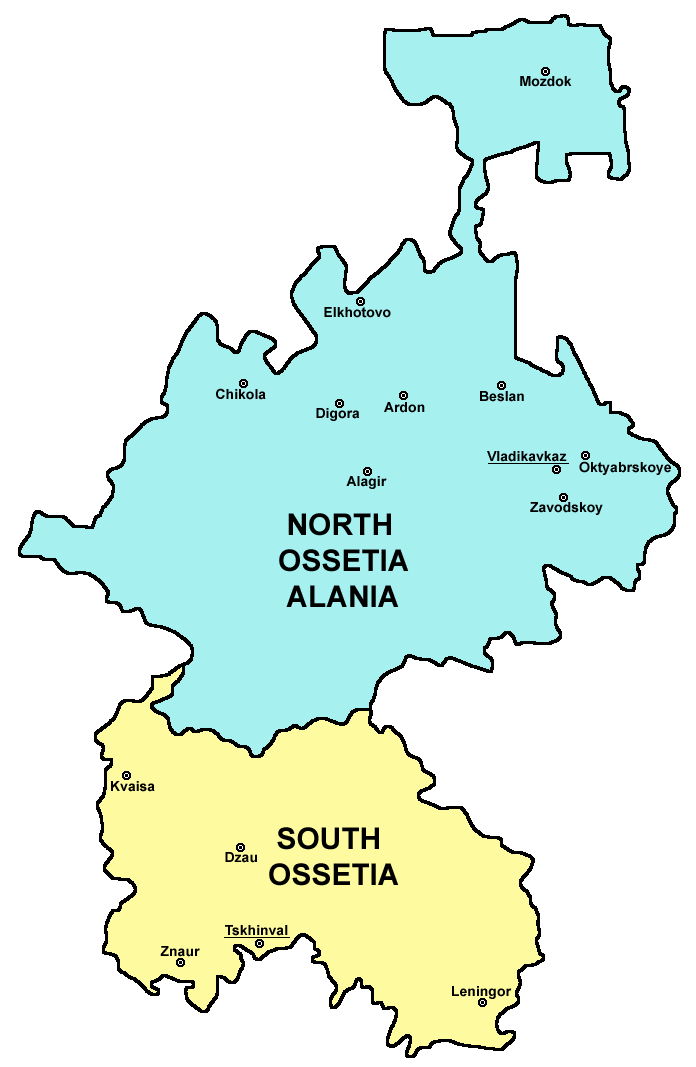
South Ossetia
South Ossetia, ka, სამხრეთი ოსეთი, ( , ), officially the Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania, is a partially recognised landlocked state in the South Caucasus. It has an officially stated population of just over 56,500 people (2022), who live in an area of , on the south side of the Greater Caucasus mountain range, with 33,000 living in the capital city, Tskhinvali. Only Russia, Venezuela, Nicaragua, Nauru, and Syria recognise South Ossetia as a sovereign state. Although Georgia does not control South Ossetia, the Georgian government and the United Nations consider the territory part of Georgia. Georgia does not recognise the existence of South Ossetia as a political entity, and the territory comprising South Ossetia does not correspond to any Georgian administrative area (although Georgian authorities have set up the Provisional Administration of South Ossetia as a transitional measure leading to the settlement of South Ossetia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetian Language
Ossetian (, , ), commonly referred to as Ossetic and rarely as Ossete (), is an Eastern Iranian language that is spoken predominantly in Ossetia, a region situated on both sides of the Greater Caucasus. It is the native language of the Ossetian people, and is one of the few Iranian languages spoken in Europe; it is a relative and possibly a descendant of the extinct Scythian, Sarmatian, and Alanic languages. The northern half of the Ossetia region is part of Russia and is known as North Ossetia–Alania, while the southern half is part of the ''de facto'' country of South Ossetia (recognized by the United Nations as Russian-occupied territory that is ''de jure'' part of Georgia). Ossetian-speakers number about 614,350, with 451,000 recorded in Russia per the 2010 Russian census. History and classification Ossetian is the spoken and literary language of the Ossetians, an Iranian ethnic group living in the central part of the Caucasus and constituting the basic population of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Ossetia–Alania
The Republic of North Ossetia–Alania; os, Республикӕ Цӕгат Ирыстон — Алани, ''Respublikæ Cægat Iryston — Alani'', ) is a republic of Russia situated in the North Caucasus of Eastern Europe. Its population according to the 2010 Census was 712,980. The republic's capital city is the city of Vladikavkaz, located on the foothills of the Caucasus Mountains. Forming 65.1% of the republic's population as of 2010, the Ossetians are an Iranian ethnic group native to the republic and neighboring South Ossetia. Ossetian is an east Iranian language descended from medieval Alanic and ancient Sarmatian. Unlike many groups in the North Caucasus, Ossetians are predominantly Christians. However, almost 30% of the population adheres to Ossetian ethnic religion, generally called Uatsdin (Уацдин, "True Faith"), and a sizable Muslim minority exists. Ethnic Russians and Ingush, who form a majority in neighboring Ingushetia, form substantial minoritie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasz People
The Jász (''Latin'': Jazones) are an Eastern Iranic ethnic group who have lived in Hungary since the 13th century. They live mostly in a region known as ''Jászság'', which comprises the north-western part of Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. They are sometimes known in English by the exonym Jassic and are also known by the endonyms ''Iasi'' and ''Jassy''. They originated as a nomadic Alanic people from the Pontic steppe. Geography The cultural and political center of Jászság is the town of Jászberény. Jászság is sometimes, erroneously, known as "Jazygia", after a somewhat related Sarmatian people, the Iazyges, who lived in a similar area in ancient times. However, there is no direct connection between the Jász and Iazyges. History The Jasz people descend from nomadic Alanic tribes who settled in the medieval Kingdom of Hungary during the 13th century following the Mongol invasions. Their language, which belonged to the east Iranian group that includes modern Osset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assianism
Assianism (, ''Watsdin'') is a modern Pagan religion derived from the traditional mythology of the Ossetians, modern descendants of the Scythians of the Alan tribes, believed to be a continuation of the ancient Scythian religion. The religion is known as "Assianism" among its Russian-speaking adherents ("Assianism" means the religion of the "As" or "Oss"—an ancient name of the Alans, from which the Greeks possibly drew the name of "Asia", which is preserved in the Russian and Georgian-derived name "Ossetians"), and as Watsdin (Уацдин), Ætsæg Din (Æцæг Дин; both meaning "True Faith"), Æss Din (Æсс Дин, Ossetian-language rendering of "Assianism"), or simply Iron Din (Ирон Дин, "Ossetian Faith") by Ossetians in their own language. It started to be revived in a conscious and organised way in the 1980s, as an ethnic religion among the Ossetians. The religion has been incorporated by some organisations, chiefly in North Ossetia–Alania within Russia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Peoples
The Iranian peoples or Iranic peoples are a diverse grouping of Indo-European peoples who are identified by their usage of the Iranian languages and other cultural similarities. The Proto-Iranians are believed to have emerged as a separate branch of the Indo-Iranians in Central Asia around the mid-2nd millennium BC. At their peak of expansion in the mid-1st millennium BC, the territory of the Iranian peoples stretched across the entire Eurasian Steppe, from the Great Hungarian Plain in the west to the Ordos Plateau in the east and the Iranian Plateau in the south.: "From the first millennium b.c., we have abundant historical, archaeological and linguistic sources for the location of the territory inhabited by the Iranian peoples. In this period the territory of the northern Iranians, they being equestrian nomads, extended over the whole zone of the steppes and the wooded steppes and even the semi-deserts from the Great Hungarian Plain to the Ordos in northern China." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossetia
Ossetia ( , ; os, Ирыстон or , or ; russian: Осетия, Osetiya; ka, ოსეთი, translit. ''Oseti'') is an ethnolinguistic region located on both sides of the Greater Caucasus Mountains, largely inhabited by the Ossetians. The Ossetian language is part of the Eastern Iranian branch of the family of Indo-European languages. Most countries recognize the Ossetian-speaking area south of the main Caucasus ridge as lying within the borders of Georgia, but it has come under the control of the ''de facto'' government of the Russian-backed Republic of South Ossetia – the State of Alania. The northern portion of the region consists of the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania within the Russian Federation. Recent history * 1774 — North Ossetia becomes part of the Russian Empire. * 1922 — Creation of the South Ossetian autonomous oblast. North Ossetia remains a part of Russian SFSR, South Ossetia remains a part of Georgian SSR. * 20 September 1990 — South Osse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism. Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or "Canon law of the Eastern Orthodox Church, canonical") Eastern Orthodox Church is Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church, organised into autocephalous churches independent from each other. In the 21st century, the Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Autocephalous Eastern Orthodox churches, number of mainstream autocephalous churches is seventeen; there also exist Organization of the Eastern Orthodox Church#Unrecognised churches, autocephalous churches unrecognized by those mainstream ones. Autocephalous churches choose their own Primate (bishop), primate. Autocephalous churches can have Ecclesiastical jurisdiction, jurisdiction (authority) over other churches, some of which have the status of "Auto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scythian Languages
The Scythian languages ( or or ) are a group of Eastern Iranian languages of the classical antiquity, classical and late antiquity, late antique period (the Middle Iranian languages, Middle Iranian period), spoken in a vast region of Eurasia by the populations belonging to the Scythian cultures and their descendants. The dominant ethnic groups among the Scythian-speakers were nomadic pastoralists of Central Asia and the Pontic–Caspian steppe. Fragments of their speech known from inscriptions and words quoted in ancient authors as well as analysis of their names indicate that it was an Indo-European language, more specifically from the Iranian languages, Iranian group of Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian languages. Most of the Scythian languages eventually became extinct, except for modern Ossetian language, Ossetian (which descends from the Alanian dialect of Scytho-Sarmatian), Wakhi language, Wakhi (which descends from the Kingdom of Khotan, Khotanese and Tumxuk, Tumshuqe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jászság
Jászság ("Jaszygia", la, Jazigia) is a historical, ethnographical and geographical region in Hungary. Its territory is situated in the north-western part of the Jász-Nagykun-Szolnok county. The main town in the region is Jászberény. Jászság is inhabited by the Jassic people, an Iranian ethnic group whose linguistic base is preserved by the Ossetians. The population of the region is around 85,000. Name Jászság means "Province of the Jász" (i.e. Province of the Jassic people). History In ancient times, this area was settled by Celts, Dacians, Sarmatians, and Germanic peoples. It was part of the Dacian Kingdom of Burebista in the first century BC. In the 1st century AD, a Sarmatian tribe known as the Iazyges settled in this region. In the early Middle Ages, the territory of present-day Jászság was mainly populated by Slavic people and was part of the Hun Empire, the Kingdom of the Gepids and the Kingdom of the Avars. At the end of the 9th century, the area was settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia (country)
Georgia (, ; ) is a transcontinental country at the intersection of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is part of the Caucasus region, bounded by the Black Sea to the west, by Russia to the north and northeast, by Turkey to the southwest, by Armenia to the south, and by Azerbaijan to the southeast. The country covers an area of , and has a population of 3.7 million people. Tbilisi is its capital as well as its largest city, home to roughly a third of the Georgian population. During the classical era, several independent kingdoms became established in what is now Georgia, such as Colchis and Iberia. In the early 4th century, ethnic Georgians officially adopted Christianity, which contributed to the spiritual and political unification of the early Georgian states. In the Middle Ages, the unified Kingdom of Georgia emerged and reached its Golden Age during the reign of King David IV and Queen Tamar in the 12th and early 13th centuries. Thereafter, the kingdom decl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally recognized. Examples Between 1805 and 1914, the ruling dynasty of Egypt were subject to the rulers of the Ottoman Empire, but acted as de facto independent rulers who maintained a polite fiction of Ottoman suzerainty. However, starting from around 1882, the rulers had only de jure rule over Egypt, as it had by then become a British puppet state. Thus, by Ottoman law, Egypt was de jure a province of the Ottoman Empire, but de facto was part of the British Empire. In U.S. law, particularly after ''Brown v. Board of Education'' (1954), the difference between de facto segregation (segregation that existed because of the voluntary associations and neighborhoods) and de jure segregation (segregation that existed because of local laws that m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |