|
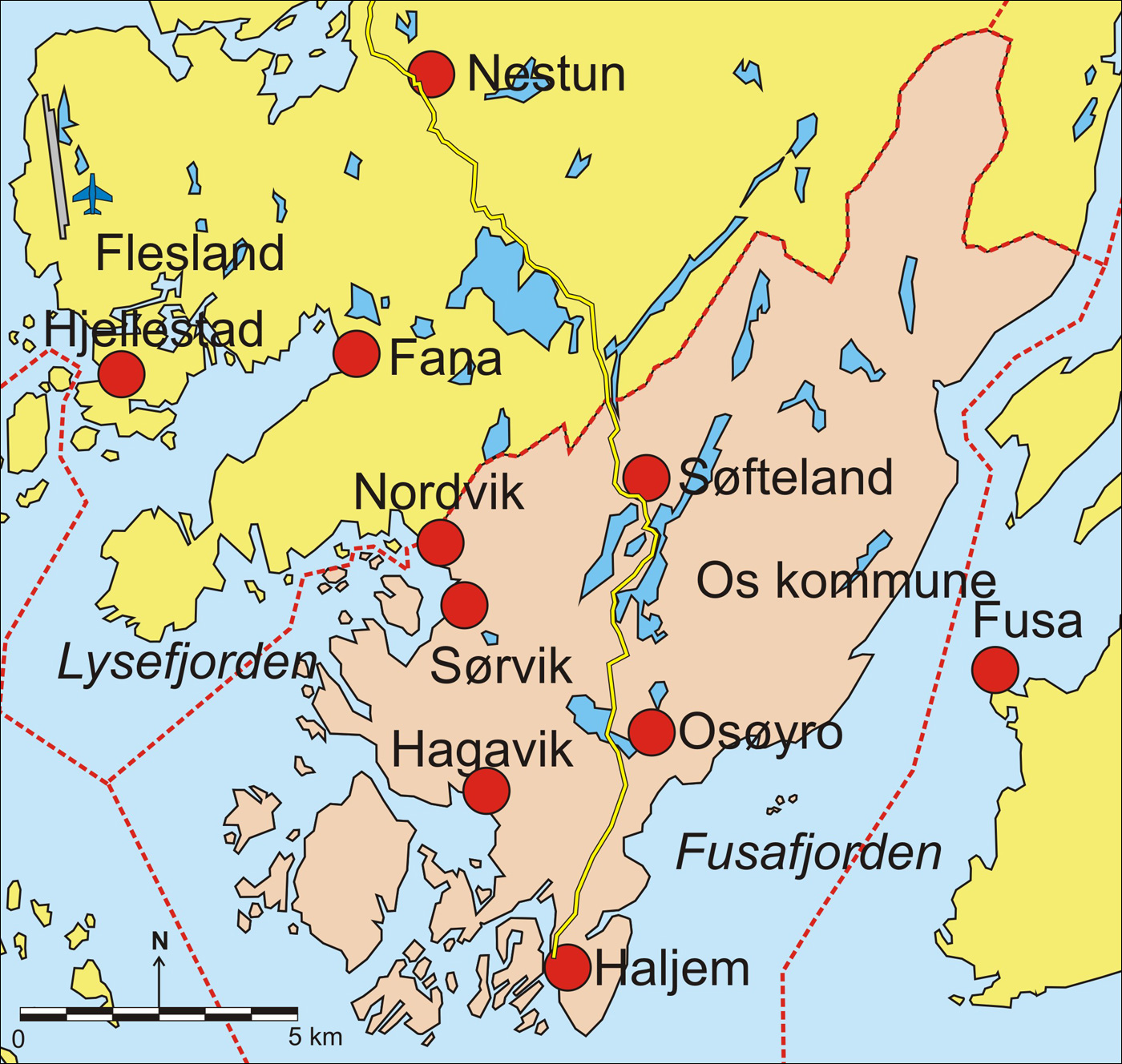
Os, Hordaland
Os is a former municipality in the old Hordaland county, Norway. It was located in the Midhordland region, just south of Norway's second-largest city, Bergen. Due to its proximity to Bergen, Os experienced strong population growth. The administrative centre (and commercial centre) of Os was the village of Osøyro. It is the largest settlement in the municipality, with over 60% of the municipal residents living here. Other large villages in Os included Hagavik, Halhjem, Søfteland, Søre Øyane, and Søvik. On 1 January 2020, the municipality became part of Bjørnafjorden Municipality in Vestland county. Prior to its dissolution in 2020, the municipality is the 360th largest by area out of the 422 municipalities in Norway. Os is the 57th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 20,152. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 29.2% over the last decade. History The parish of Os was established as a formannskapsdistr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osøyro
Osøyro is the administrative centre of Bjørnafjorden municipality in Vestland county, Norway. The village lies on the southwestern part of the Bergen Peninsula, along the western shore of the Fusafjorden, about south of the city centre of Bergen. The European route E39 highway runs through the village on its way to Bergen. There is a car ferry from the east side of Osøyro to the village of Fusa, across the Fusafjorden. Os Church is located in the village. Osøyro has several smaller suburban villages surrounding it: Søfteland to the north, Søvik to the northwest, Hagavik to the west, Søre Øyane to the southwest, and Halhjem Halhjem is a village in Bjørnafjorden municipality in Vestland county, Norway. The village is a suburb of the municipal centre of Osøyro, located immediately to the north. The village is the site of an important ferry quay along the European r ... to the south. The village has a population (2022) of 14,232 and a population density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulven Concentration Camp
no, Ulven fangeleir , known for = , location = Osøyro, Norway , coordinates = , built by =Norwegian Army , operated by = Sicherheitspolizei , commandant = Otmar Holenia , original use = Military exercise camp , companies involved = , construction =1876 , in operation = June 1940-1944 , gas chambers = , prisoner type = , inmates = , killed = , liberated by = , notable inmates = , notable books = , website = Ulven detention camp (German: ''Polizeihäftlingslager Ulven,'' no, Ulven fangeleir ("''Ulven"'' means "the wolf")) was a concentration camp in Norway that was located in what was Os Municipality in Hordaland county (now part of Bjørnafjorden Municipality in Vestland county). It was located just outside the village of Osøyro, south of the city of Bergen. Originally a military training camp built by the Norwegian Arm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics Norway
Statistics Norway ( no, Statistisk sentralbyrå, abbreviated to ''SSB'') is the Norwegian statistics bureau. It was established in 1876. Relying on a staff of about 1,000, Statistics Norway publish about 1,000 new statistical releases every year on its web site. All releases are published both in Norwegian and English. In addition a number of edited publications are published, and all are available on the web site for free. As the central Norwegian office for official government statistics, Statistics Norway provides the public and government with extensive research and analysis activities. It is administratively placed under the Ministry of Finance but operates independently from all government agencies. Statistics Norway has a board appointed by the government. It relies extensively on data from registers, but are also collecting data from surveys and questionnaires, including from cities and municipalities. History Statistics Norway was originally established in 1876. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schei Committee
The Schei Committee ( no, Schei-komitéen) was a committee named by the Government of Norway to look into the organization of municipalities in Norway post-World War II World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power .... It convened in 1946, and its formal name was (The 1946 Committee on Municipal Division). Its more commonly used name derives from the committee leader, Nikolai Schei, who was County Governor of Sogn og Fjordane at the time. The committee concluded its work in 1962. By that time, it had published an eighteen-volume work called ''Kommuneinndelingskomitéens endelige tilråding om kommunedelingen''. The findings of the committee were highly influential; it spurred a series of mergers of municipalities, especially during the 1960s, reducing the number of municipali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samnanger
Samnanger () is a municipality in the Midhordland region of Vestland county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the village of Tysse. Other main villages in the municipality include Haga and Bjørkheim in Nordbygda. The municipality is located about east of the city of Bergen, Norway's second largest city. It surrounds the inner part of the Samnangerfjorden and the surrounding valleys. There are mountains that surround the municipality. The development of hydroelectric power plants started here in 1909. The municipality is the 274th largest by area out of the 356 municipalities in Norway. Samnanger is the 251st most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 2,501. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 3.5% over the previous 10-year period. In 2016, the chief of police for Vestlandet formally suggested a reconfiguration of police districts and stations. He proposed that the police station in Samnang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norwegian And Swedish Travellers
The Norwegian and Swedish Romanisæl Travellers ( no, romanifolket, tatere, sigøynere; sv, resande, zigenare, tattare; rmu, romanisæl, romanoar, rom(m)ani, tavringer/ar, tattare) are a group or branch of the Romani people who have been resident in Norway and Sweden for some 500 years. The estimated number of Romanisael Travellers in Sweden is 65,000, while in Norway, the number is probably about 10,000. Origins By history and culture, they are related to British Romani Groups, such as English Romanichals, Welsh Kale and Scottish Gypsy and Traveller groups. Modern-day Romanisael (Tater) Travellers are the descendants of the first Romanies who arrived in Scandinavia during the 16th century. Most were deportees from Britain to Norway, but small numbers came via Denmark. Norwegian and Swedish Romani identify as Romanisæl, this word has origins in the Angloromani word Romanichal, Romanichal is the word English Romani and Scottish Border Romani and Southern Welsh Romani use t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romani People
The Romani (also spelled Romany or Rromani , ), colloquially known as the Roma, are an Indo-Aryan ethnic group, traditionally nomadic itinerants. They live in Europe and Anatolia, and have diaspora populations located worldwide, with significant concentrations in the Americas. In the English language, the Romani people are widely known by the exonym Gypsies (or Gipsies), which is considered pejorative by many Romani people due to its connotations of illegality and irregularity as well as its historical use as a racial slur. For versions (some of which are cognates) of the word in many other languages (e.g., , , it, zingaro, , and ) this perception is either very small or non-existent. At the first World Romani Congress in 1971, its attendees unanimously voted to reject the use of all exonyms for the Romani people, including ''Gypsy'', due to their aforementioned negative and stereotypical connotations. Linguistic and genetic evidence suggests that the Roma origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusa
Fusa () is a List of former municipalities of Norway, former municipality in the old Hordaland county, Norway. It existed from 1856 until its dissolution in 2020. It was located east of the city of Bergen in the Midhordland region. The administrative centre of the municipality was the village of Eikelandsosen. Other villages in the municipality include Fusa (village), Fusa, Holdhus, Holmefjord, Vinnes, Strandvik, and Sundvord. The Frank Mohn company's Fusa marine division is headquartered here, with almost 500 employees. On 1 January 2020, the municipality became part of the new Bjørnafjorden Municipality in Vestland county. Prior to its dissolution in 2020, the municipality was the 247th largest by area out of the 422 municipalities in Norway. Fusa was the 234th most populous municipality in Norway with a population of 3,895. The municipality's population density is and its population has increased by 3.9% over the last decade. General information The district of Fusa was s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fusafjorden
Fusafjorden () is a fjord in Vestland county, Norway. It lies in between Bjørnafjorden Municipality and Tysnes Municipality. The long fjord branches off northwards from the Bjørnafjorden at the village of Osøyro. The Fusafjorden is a wide fjord that branches into three arms at Bogøya. The three arms are Samnangerfjorden, Ådlandsfjorden, and Eikelandsfjorden. See also * List of Norwegian fjords This list of Norwegian fjords shows many of the fjords in Norway. In total, there are about 1,190 fjords in Norway and the Svalbard islands. The sortable list includes the lengths and locations of those fjords. Fjords See also * List of gl ... References Fjords of Vestland Bjørnafjorden Tysnes {{Vestland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formannskapsdistrikt
() is the name for Norwegian local self-government districts that were legally enacted on 1 January 1838. This system of municipalities was created in a bill approved by the Parliament of Norway and signed into law by King Carl Johan on 14 January 1837. The ''formannskaps'' law, which fulfilled an express requirement of the Constitution of Norway, required that every parish ( no, prestegjeld) form a ''formannsskapsdistrikt'' (municipality) on 1 January 1838. In this way, the parishes of the state Church of Norway became worldly, administrative districts as well. (Although some parishes were divided into two or three municipalities.) In total, 396 ''formannsskapsdistrikts'' were created under this law, and different types of ''formannskapsdistrikts'' were created, also: History The introduction of self government in rural districts was a major political change. The Norwegian farm culture (''bondekultur'') that emerged came to serve as a symbol of nationalistic resistance to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestegjeld
A ''prestegjeld'' was a geographic and administrative area within the Church of Norway (''Den Norske Kirke'') roughly equivalent to a parish. This traditional designation was in use for centuries to divide the kingdom into ecclesiastical areas that were led by a parish priest. ''Prestegjelds'' began in the 1400s and were officially discontinued in 2012. History Prior to the discontinuation of the ''prestegjeld'', Norway was geographically divided into 11 dioceses (''bispedømme''). Each diocese was further divided into deaneries (''prosti''). Each of those deaneries were divided into several parishes (''prestegjeld''). Each parish was made up of one or more sub-parishes or congregations (''sogn'' or ''sokn''). Within a ''prestegjeld'', there were usually one or more clerical positions (chaplains) serving under the administration of a head minister (''sogneprest'' or ''sokneprest''). In 1838, the formannskapsdistrikt () is the name for Norwegian local self-government districts t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |