|
Orleans Territory
The Territory of Orleans or Orleans Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from October 1, 1804, until April 30, 1812, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Louisiana. History In 1804, all of the Louisiana Purchase south of the 33rd parallel became the Orleans Territory, and the remainder became the District of Louisiana. (The District of Louisiana was later renamed the Louisiana Territory; and still later, when the Orleans Territory became the State of Louisiana, the Louisiana Territory was renamed the Missouri Territory.) The Organic Act of 1804, passed on March 26 for October 1 implementation, also created the United States District Court for the District of Orleans—the only time Congress has ever provided a territory with a United States district court equal in its authority and jurisdiction to those of the states. Congress also established the Superior Court for the Territory of Orleans whose three judges wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organized Incorporated Territories Of The United States
The territory of the United States and its overseas possessions has territorial evolution of the United States, evolved over time, from the colonial United States, colonial era to the present day. It includes formally organized territories, proposed and failed states, unrecognized breakaway states, international and interstate purchases, cessions, and land grants, and historical military departments and administrative districts. The last section lists informal regions from American vernacular geography known by popular nicknames and linked by geographical, cultural, or economic similarities, some of which are still in use today. For a more complete list of regions and subdivisions of the United States used in modern times, see List of regions of the United States. Colonial era (before 1776) Thirteen Colonies * Connecticut Colony * Delaware Colony * Province of Georgia * Province of Maryland * Province of Massachusetts Bay * Province of New Hampshire * Province of New Je ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Judicial Center
The Federal Judicial Center is the education and research agency of the United States federal courts. It was established by in 1967, at the recommendation of the Judicial Conference of the United States. According to , the main areas of responsibility for the Center include: #conducting and promoting "research and study of the operation of the courts of the United States," and to act to encourage and coordinate the same by others; #developing "recommendations for improvement of the administration and management of .S.courts," and presenting these to the Judicial Conference of the U.S.; and # through all means available, see to conducting programs for the "continuing education and training for personnel" of the U.S. judiciary, for all employees in the justice system, from judges through probation officers and mediators. In addition to these major provisions, §620 (b)(4)(5)(6) sets forth the additional provisions that the FJC will (i) provide staff and assistance to the Judici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nueva Orleans) is a Consolidated city-county, consolidated city-parish located along the Mississippi River in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census, it is the List of municipalities in Louisiana, most populous city in Louisiana and the twelfth-most populous city in the southeastern United States. Serving as a List of ports in the United States, major port, New Orleans is considered an economic and commercial hub for the broader Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast region of the United States. New Orleans is world-renowned for its Music of New Orleans, distinctive music, Louisiana Creole cuisine, Creole cuisine, New Orleans English, uniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the U.S. Department of Commerce and its director is appointed by the President of the United States. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the U.S. House of Representatives to the states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses make informed decisions. The information provided by the census informs decisions on where to build and maintain schools, hospitals, transportation infrastructure, and police and fire departments. In addition to the decennial census, the Census Bureau continually conducts over 130 surveys and programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Parishes In Louisiana
The U.S. state of Louisiana is divided into 64 parishes ( French: ''paroisses'', Spanish: ''parroquias'') in the same manner that Alaska is divided into boroughs, and the remaining 48 other states are divided into counties. Louisiana's usage of the term "parish" for a geographic region or local government dates back to the Spanish colonial and French colonial periods. Thirty-eight parishes are governed by a council called a Police Jury. The remaining 26 have various other forms of government, including: council-president, council-manager, parish commission, and consolidated parish/city. History Louisiana was formed from French and Spanish colonies, which were both officially Roman Catholic. Local colonial government was based upon parishes, as the local ecclesiastical division. Following the Louisiana Purchase in 1803, the territorial legislative council divided the Territory of Orleans (the predecessor of Louisiana state) into 12 counties. The borders of these counties we ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1810 United States Census
The United States census of 1810 was the third census conducted in the United States. It was conducted on August 6, 1810. It showed that 7,239,881 people were living in the United States, of whom 1,191,362 were slaves. The 1810 census included one new state: Ohio. The original census returns for the District of Columbia, Georgia, Mississippi, New Jersey, and Ohio were lost or destroyed over the years. Most of Tennessee's original forms were also lost, other than Grainger and Rutherford counties. This was the first census in which New York was ranked as the most populous state, if excluding West Virginia from Virginia. Otherwise this would be the last census with Virginia ranked as the most populous state. Census questions The 1810 census form contained the following information (identical to the 1800 census): # City or township # Name of the head of family # Number of free white males under age 10 # Number of free white males age 10 to under 16 # Number of free white males age ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabine River (Texas–Louisiana)
The Sabine River () is a long riverU.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed June 20, 2011 in the Southern U.S. states of Texas and Louisiana, From the 32nd parallel north and downstream, it serves as part of the boundary between the two states and empties into Sabine Lake, an estuary of the Gulf of Mexico. Over the first half of the 19th century, the river formed part of the Spanish–American, Mexican–American, and Texan–American international boundaries. The upper reaches of the river flow through the prairie country of northeast Texas. Along much of its lower reaches, it flows through pine forests along the Texas–Louisiana border, and eventually the bayou country near the Gulf Coast. The river drains an area of , of which are in Texas and in Louisiana. It flows through an area of abundant rainfall and discharges the largest volume of any river in Texas. The name Sabine ( es: ''Río de Sabinas'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sabine Free State
The Neutral Ground (also known as the Neutral Strip, the Neutral Territory, and the No Man's Land of Louisiana; sometimes anachronistically referred to as the Sabine Free State) was a disputed area between Spanish Texas and the United States' newly acquired Louisiana Purchase. Local officers of Spain and the United States agreed to leave the Neutral Ground temporarily outside the jurisdiction of either country. The area, now in western Louisiana, had neutral status from 1806 to 1821. Background Spain had been concerned for many years with what it viewed as the encroachment of the French from Louisiana into Texas. About 1734, the French moved their post at Natchitoches, Louisiana, Natchitoches from the east to the west side of the Red River of the South, Red River. The Spanish governor of Texas, Manuel de Sandoval, was reprimanded for not protesting this violation of what Spain believed was its sovereign territory. In 1740, Governor Prudencio de Orobio y Basterra was ordered to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined the boundary between the U.S. and New Spain. It settled a standing border dispute between the two countries and was considered a triumph of American diplomacy. It came in the midst of increasing tensions related to Spain's territorial boundaries in North America against the United States and the United Kingdom in the aftermath of the American Revolution; it also came during the Latin American wars of independence. Florida had become a burden to Spain, which could not afford to send settlers or garrisons, so the Spanish government decided to cede the territory to the United States in exchange for settling the boundary dispute along the Sabine River in Spanish Texas. The treaty established the boundary of U.S. territory and claims through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Texas
Spanish Texas was one of the interior provinces of the colonial Viceroyalty of New Spain from 1690 until 1821. The term "interior provinces" first appeared in 1712, as an expression meaning "far away" provinces. It was only in 1776 that a legal jurisdiction called "Interior Provinces" was created. Spain claimed ownership of the territory in 1519, which comprised part of the present-day U.S. state of Texas, including the land north of the Medina and Nueces Rivers, but did not attempt to colonize the area until after locating evidence of the failed French colony of Fort Saint Louis in 1689. In 1690 Alonso de León escorted several Catholic missionaries to east Texas, where they established the first mission in Texas. When native tribes resisted the Spanish invasion of their homeland, the missionaries returned to Mexico, abandoning Texas for the next two decades. The Spanish returned to southeastern Texas in 1716, establishing several missions and a presidio to maintain a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
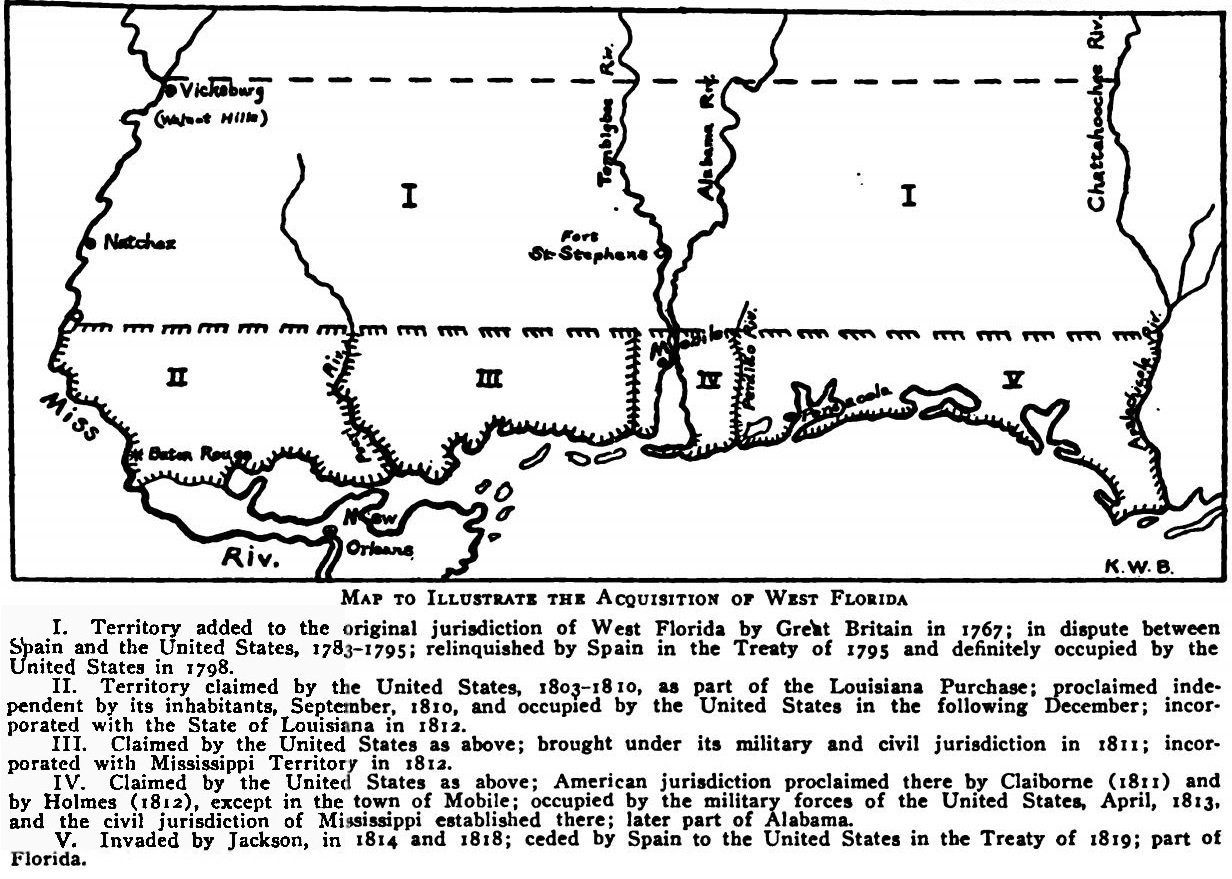
West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former Spanish Florida (East Florida formed the eastern part, with the Apalachicola River as the border), along with lands taken from French Louisiana; Pensacola became West Florida's capital. The colony included about two thirds of what is now the Florida Panhandle, as well as parts of the modern U.S. states of Louisiana, Mississippi, and Alabama. Great Britain established West and East Florida in 1763 out of land acquired from France and Spain after the Seven Years' War. As the newly acquired territory was too large to govern from one administrative center, the British divided it into two new colonies separated by the Apalachicola River. British West Florida included the part of formerly Spanish Florida which lay west of the Apalachicola, as wel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |