|
Orkhan Abasov
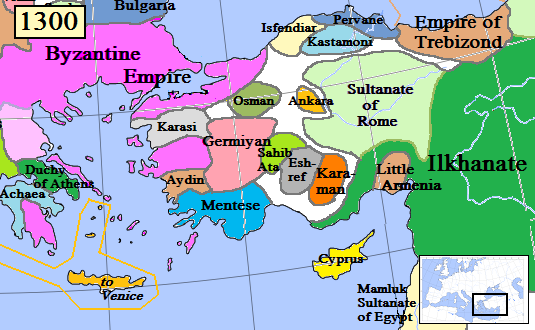
Orhan Ghazi ( ota, اورخان غازی; tr, Orhan Gazi, also spelled Orkhan, 1281 – March 1362) was the second bey of the Ottoman Beylik from 1323/4 to 1362. He was born in Söğüt, as the son of Osman I. In the early stages of his reign, Orhan focused his energies on conquering most of northwestern Anatolia. The majority of these areas were under Byzantine rule and he won his first battle at Pelekanon against the Byzantine Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos. Orhan also occupied the lands of the Karasids of Balıkesir and the Ahis of Ankara. A series of civil wars surrounding the ascension of the nine-year-old Byzantine emperor John V Palaiologos greatly benefited Orhan. In the Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, the regent John VI Kantakouzenos married his daughter Theodora to Orhan and employed Ottoman warriors against the rival forces of the empress dowager, allowing them to loot Thrace. In the Byzantine civil war of 1352–1357, Kantakouzenos used Ottoman force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazi (warrior)
A ''ghazi'' ( ar, غازي, , plural ''ġuzāt'') is an individual who participated in ''ghazw'' (, ''wikt:ghazwa, ''), meaning military expeditions or raiding. The latter term was applied in early Islamic literature to expeditions led by the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and later taken up by Turkic military leaders to describe their wars of conquest. In the context of the wars between Russia and the Muslim peoples of the Caucasus, starting as early as the late 18th century's Sheikh Mansur's resistance to Russian expansion, the word usually appears in the form ''gazavat'' (). In English-language literature, the ''ghazw'' often appears as ''Razzia (military), razzia'', a borrowing through French from Maghrebi Arabic. In modern Turkish language, Turkish, ''gazi'' is used to refer to Veteran, veterans, and also as a title for Turkic Muslim champions such as Ertuğrul and Osman I. Ghazw as raid—razzia In pre-Islamic Bedouin culture, ghazw[a] was a form of limited warfare verging ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ''Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the Muhammad in Islam, main and final Islamic prophet.Peters, F. E. 2009. "Allāh." In , edited by J. L. Esposito. Oxford: Oxford University Press. . (See alsoquick reference) "[T]he Muslims' understanding of Allāh is based...on the Qurʿān's public witness. Allāh is Unique, the Creator, Sovereign, and Judge of mankind. It is Allāh who directs the universe through his direct action on nature and who has guided human history through his prophets, Abraham, with whom he made his covenant, Moses/Moosa, Jesus/Eesa, and Muḥammad, through all of whom he founded his chosen communities, the 'Peoples of the Book.'" It is the Major religious groups, world's second-largest religion behind Christianity, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John VI Kantakouzenos
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Ángelos Palaiológos Kantakouzēnós''; la, Johannes Cantacuzenus; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under Andronikos III Palaiologos and regent for John V Palaiologos before reigning as Byzantine emperor in his own right from 1347 to 1354. Deposed by his former ward, he was forced to retire to a monastery under the name and spent the remainder of his life as a monk and historian. At age 90 or 91 at his death, he was the longest-lived of the Roman emperors. Early life Born in Constantinople, John Kantakouzenos was the son of Michael Kantakouzenos, governor of the Morea; Donald Nicol speculates that he may have been born after his father's death and raised as an only child. Through his mother Theodora Palaiologina Angelina, he was related to the then-reigning house of Palaiologos. He was also related to the imperial dynasty through his wife Ir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Byzantine Civil War Of 1341–1347
The Byzantine civil war of 1341–1347, sometimes referred to as the Second Palaiologan Civil War, was a conflict that broke out in the Byzantine Empire after the death of Andronikos III Palaiologos over the guardianship of his nine-year-old son and heir, John V Palaiologos. It pitted on the one hand Andronikos III's chief minister, John VI Kantakouzenos, and on the other a regency headed by the Empress-Dowager Anna of Savoy, the Patriarch of Constantinople John XIV Kalekas, and the Alexios Apokaukos. The war polarized Byzantine society along class lines, with the aristocracy backing Kantakouzenos and the lower and middle classes supporting the regency. To a lesser extent, the conflict acquired religious overtones; Byzantium was embroiled in the Hesychast controversy, and adherence to the mystical doctrine of Hesychasm was often equated with support for Kantakouzenos. As the chief aide and closest friend of Emperor Andronikos III, Kantakouzenos became regent for the underage J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John V Palaiologos
John V Palaiologos or Palaeologus ( el, Ἰωάννης Παλαιολόγος, ''Iōánnēs Palaiológos''; 18 June 1332 – 16 February 1391) was Byzantine emperor from 1341 to 1391, with interruptions. Biography John V was the son of Emperor Andronikos III and his wife Anna, the daughter of Count Amadeus V of Savoy by his wife Maria of Brabant. His long reign was marked by the gradual dissolution of imperial power amid numerous civil wars and the continuing ascendancy of the Ottoman Turks. Early rule and first civil war John V came to the throne at age eight. His reign began with an immediate civil war between his designated regent, his father's friend John VI Kantakouzenos, and a self-proclaimed council of regency composed of his mother Anna, the patriarch John XIV Kalekas, and the '' megas doux'' Alexios Apokaukos. During this civil war in 1343 Anna pawned the Byzantine crown jewels for 30,000 Venetian ducats. From 1346 to 1349, the Black Death devastated Constan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankara
Ankara ( , ; ), historically known as Ancyra and Angora, is the capital of Turkey. Located in the central part of Anatolia, the city has a population of 5.1 million in its urban center and over 5.7 million in Ankara Province, making it Turkey's second-largest city after Istanbul. Serving as the capital of the ancient Celtic state of Galatia (280–64 BC), and later of the Roman province with the same name (25 BC–7th century), the city is very old, with various Hattian, Hittite, Lydian, Phrygian, Galatian, Greek, Persian, Roman, Byzantine, and Ottoman archeological sites. The Ottomans made the city the capital first of the Anatolia Eyalet (1393 – late 15th century) and then the Angora Vilayet (1867–1922). The historical center of Ankara is a rocky hill rising over the left bank of the Ankara River, a tributary of the Sakarya River. The hill remains crowned by the ruins of Ankara Castle. Although few of its outworks have survived, there are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ahis
The Ahi Brotherhood ( tr, Ahî, plur. ''Ahîler''), referred to as Ahi Republic by modern historians, was a fraternity, guild and a beylik based in modern-day Ankara in the 13th and 14th century Anatolia. Background Turkic people began settling in Anatolia in the second half of the 11th century. But they mainly preferred rural areas. Seljuk government on the other hand encouraged those who preferred a settled life in cities. After the Mongols began occupying Khorosan in the early 13th century, people from Khorosan took refuge in Anatolia and Seljuk government settled some of the newcomers in the cities. So a class of Muslim craftsmen and merchants appeared in the history of Anatolia. Emergence of Ahis Ahi Evren, a Muslim preacher came to Anatolia before the Mongol invasions in Khorosan. He worked as a leather dealer in Kayseri and began organizing Muslim craftsmen in the cities. This organization was named after him. He moved to Konya and after Mongol invasions to Denizl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balıkesir
Balıkesir () is a city in Turkey and is the capital city of Balıkesir Province. Balıkesir is located in the Marmara region of Turkey and has a population of 338,936. Between 1341–1922, it was the capital of Karasi. History Close to modern Balıkesir was the Roman town of '' Hadrianutherae'', founded, as its name commemorates, by the emperor Hadrian. Hadrian came to the region in A.D. 124, as a result of a successful bear hunting he had established a city called his name here. It is estimated that the city consisted of the castle, the homestead, the stud and a few homes. It is thought that the small town was where the current stadium is present. Members of the Roman and Pre-Byzantine dynasty had used this castle as a vacation area and for hunting. During the Byzantine period, the small town which had become increasingly neglected was known as ''Palaeokastron'' ( el, Παλαιόκαστρο) meaning Old Castle. Also, when the Turkomans came from Middle Asia to Mysia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karasids
The Karasids or Karasid dynasty ( Ottoman قرا صي; Modern Turkish ''Karesioğulları'', ''Karesioğulları Beyliği''), also known as the Principality of Karasi and Beylik of Karasi (''Karasi Beyliği'' or ''Karesi Beyliği'' ), was an Anatolian beylik in the area of classical Mysia (modern Balıkesir and Çanakkale provinces) from ca. 1297–1360. It was centered in Balıkesir and Bergama, and was one of the frontier principalities established by Oghuz Turks after the decline of the Seljuk Sultanate of Rum. They became a naval power in the Aegean and the Dardanelles. History The Byzantines tried to incite beyliks like Karasids against the Ottomans. However, routes of conquest and other objectives of beyliks such as Karasids did not initially conflict with the Ottomans. The political situation clearly favored the Ottomans. Karasids were the first beylik to be taken over by the neighboring Ottoman dynasty, who were later to found the Ottoman Empire. The acquisition of Kar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andronikos III Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos_III_Palaiologos.jpg , caption = 14th-century miniature. Stuttgart, Württembergische Landesbibliothek. , succession = Byzantine emperor , reign = 24 May 1328 – 15 June 1341 , coronation = 2 February 1325 , cor-type1 = Coronation , predecessor = Andronikos II Palaiologos , successor = John V Palaiologos , spouse = Irene of BrunswickAnna of Savoy , issue = Irene, Empress of Trebizond Maria (renamed Irene)John V Palaiologos Michael Palaiologos , issue-link=#Family , issue-pipe = more... , house = Palaiologos , father = Michael IX Palaiologos , mother = Rita of Armenia , birth_date = 25 March 1297 , birth_place = Constantinople, Byzantine Empire(now Istanbul, Turkey) , death_date = 15 June 1341 (aged 44) , death_place = Constantinople, Byzantine Empire , burial_place= Andronikos III Palaiologos ( grc-x-medieval, Ἀνδρόνικος Δούκ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Byzantine Emperors
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as legitimate rulers and exercised sovereign authority are included, to the exclusion of junior co-emperors (''symbasileis'') who never attained the status of sole or senior ruler, as well as of the various usurpers or rebels who claimed the imperial title. The following list starts with Constantine the Great, the first Christian emperor, who rebuilt the city of Byzantium as an imperial capital, Constantinople, and who was regarded by the later emperors as the model ruler. It was under Constantine that the major characteristics of what is considered the Byzantine state emerged: a Roman polity centered at Constantinople and culturally dominated by the Greek East, with Christianity as the state religion. The Byzantine Empire was the direct lega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Pelekanon
The Battle of Pelekanon, also known by its Latinised form Battle of Pelecanum, occurred on June 10–11, 1329 between an expeditionary force by the Byzantines led by Andronicus III and an Ottoman army led by Orhan I. The Byzantine army was defeated, with no further attempt made at relieving the cities in Anatolia under Ottoman siege. Background By the accession of Andronicus in 1328, the Imperial territories in Anatolia had dramatically shrunk from almost all of the west of modern Turkey forty years earlier to a few scattered outposts along the Aegean Sea and a small core province around Nicomedia within about 150 km of the capital city Constantinople. Recently the Turks had captured the important city of Prusa (Bursa) in Bithynia. Andronicus decided to relieve the important besieged cities of Nicomedia and Nicaea, and hoped to restore the frontier to a stable position.Treadgold, p.761. Clash and outcome Together with the Grand Domestic John Cantacuzene, Andronicus led a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)