|
Organonickel Compounds
Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process. Classes of compounds : Alkyl and aryl complexes A popular reagent is Tetramethylethylenediamine(dimethyl)nickel(II), Ni(CH3)2(tetramethylethylenediamine). Many alkyl and aryl complexes are known with the formula NiR(X)L2. Examples include [(dppf)Ni(cinnamyl)Cl)], ''trans''-(PCy2Ph)2Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (dppf)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (TMEDA)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, and (TMEDA)NiMe2. Nickel co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organonickel
Organonickel chemistry is a branch of organometallic chemistry that deals with organic compounds featuring nickel-carbon bonds. They are used as a catalyst, as a building block in organic chemistry and in chemical vapor deposition. Organonickel compounds are also short-lived intermediates in organic reactions. The first organonickel compound was nickel tetracarbonyl Ni(CO)4, reported in 1890 and quickly applied in the Mond process for nickel purification. Organonickel complexes are prominent in numerous industrial processes including carbonylations, hydrocyanation, and the Shell higher olefin process. Classes of compounds : Alkyl and aryl complexes A popular reagent is Ni(CH3)2(tetramethylethylenediamine). Many alkyl and aryl complexes are known with the formula NiR(X)L2. Examples include dppf)Ni(cinnamyl)Cl) ''trans''-(PCy2Ph)2Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (dppf)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, (TMEDA)Ni(''o''-tolyl)Cl, and (TMEDA)NiMe2. Nickel compounds of the type NiR2 also exist with just 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hélène Olivier-Bourbigou
Hélène Olivier-Bourbigou (born 9 March 1962 in Toulouse), is a French chemist. She is a research fellow in the field of homogeneous molecular catalysis at IFP Énergies Nouvelle, and her work aims to develop homogeneous catalytic processes that are more respectful of the environment. She received the Irène Joliot-Curie Prize in 2014 in the category "Female Scientist of the Year." Life and work Olivier-Bourbigou completed her engineering degree in 1985 at the National School of Chemistry in Rennes and went on to finish her doctorate in 1988 at Université Paris VI under the supervision of Yves Chauvin (winner of the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2005). She carried out her post-doctoral research at the University of Sussex in the United Kingdom where she worked with Michael Lappert, Fellow of the Royal Society. She earned her habilitation in 2003 at Université Paris VI (formerly known as Pierre and Marie Curie University). She joined IFP Énergies nouvelles in 1989 and, si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Magnesium Bromide
Allylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent used for introducing the allyl group. It is commonly available as a solution in diethyl ether. It may be synthesized by treatment of magnesium with allyl bromide Allyl bromide (3-bromopropene) is an organic halide. It is an alkylating agent used in synthesis of polymers, pharmaceuticals, synthetic perfumes and other organic compounds. Physically, allyl bromide is a colorless liquid with an irritating and p ... while maintaining the reaction temperature below 0 °C to suppress formation of hexadiene. Allyl chloride can also be used in place of the bromide to give allylmagnesium chloride. These reagents are used to prepare metal allyl complexes. References Further reading * {{cite book , author = Chabot, P. , editor1=Rakita, P. E. , editor2=Silverman, G. , chapter = 7. Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy , title = Handbook of Grignard Reagents , year = 1996 , pages = 93–102 , location = New York, N.Y. , publisher = Marcel Dekke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bis(allyl)nickel
Bis(allyl)nickel is an organonickel compound with the formula Ni(η3-C3H5)2. The molecule consists of two allyl ligands bound to nickel(II). It has inversion symmetry. It is a volatile yellow liquid. Preparation and reactions It can be prepared by the reaction of allyl magnesium bromide with anhydrous nickel chloride. It was first prepared similarly by Gunther Wilke et al. The same group reported that the complex react with carbon monoxide to give nickel tetracarbonyl and 1,5-hexadiene. It catalyzes the trimerization of butadiene 1,3-Butadiene () is the organic compound with the formula (CH2=CH)2. It is a colorless gas that is easily condensed to a liquid. It is important industrially as a precursor to synthetic rubber. The molecule can be viewed as the union of two viny .... With tertiary phosphines, the complex gives the tetrakis derivative. Such reactions to proceed via the intermediacy of the 18-electron adduct. : : : References {{Reflist Organometallic chemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidation Number
In chemistry, the oxidation state, or oxidation number, is the hypothetical charge of an atom if all of its bonds to different atoms were fully ionic. It describes the degree of oxidation (loss of electrons) of an atom in a chemical compound. Conceptually, the oxidation state may be positive, negative or zero. While fully ionic bonds are not found in nature, many bonds exhibit strong ionicity, making oxidation state a useful predictor of charge. The oxidation state of an atom does not represent the "real" formal charge on that atom, or any other actual atomic property. This is particularly true of high oxidation states, where the ionization energy required to produce a multiply positive ion is far greater than the energies available in chemical reactions. Additionally, the oxidation states of atoms in a given compound may vary depending on the choice of electronegativity scale used in their calculation. Thus, the oxidation state of an atom in a compound is purely a formalism. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleophile
In chemistry, a nucleophile is a chemical species that forms bonds by donating an electron pair. All molecules and ions with a free pair of electrons or at least one pi bond can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are Lewis bases. ''Nucleophilic'' describes the affinity of a nucleophile to bond with positively charged atomic nuclei. Nucleophilicity, sometimes referred to as nucleophile strength, refers to a substance's nucleophilic character and is often used to compare the affinity of atoms. Neutral nucleophilic reactions with solvents such as alcohols and water are named solvolysis. Nucleophiles may take part in nucleophilic substitution, whereby a nucleophile becomes attracted to a full or partial positive charge, and nucleophilic addition. Nucleophilicity is closely related to basicity. History The terms ''nucleophile'' and ''electrophile'' were introduced by Christopher Kelk Ingold in 1933, replacing the terms ''anionoid'' and ''cationoid' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
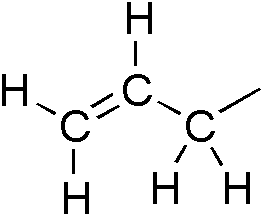
Allyl
In organic chemistry, an allyl group is a substituent with the structural formula , where R is the rest of the molecule. It consists of a methylene bridge () attached to a vinyl group (). The name is derived from the scientific name for garlic, . In 1844, Theodor Wertheim isolated an allyl derivative from garlic oil and named it "". The term allyl applies to many compounds related to , some of which are of practical or of everyday importance, for example, allyl chloride. Allylation is any chemical reaction that adds an allyl group to a substrate. Nomenclature A site adjacent to the unsaturated carbon atom is called the allylic position or allylic site. A group attached at this site is sometimes described as allylic. Thus, "has an allylic hydroxyl group". Allylic C−H bonds are about 15% weaker than the C−H bonds in ordinary sp3 carbon centers and are thus more reactive. Benzylic and allylic are related in terms of structure, bond strength, and reactivity. Other re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allyl Complex
Transition-metal allyl complexes are coordination complexes with allyl and its derivatives as ligands. Allyl is the radical with the connectivity CH2CHCH2, although as a ligand it is usually viewed as an allyl anion CH2=CH−CH2−, which is usually described as two equivalent resonance structures. Examples The allyl ligand is commonly found in organometallic chemistry. Most commonly, allyl ligands bind to metals via all three carbon atoms, the η3-binding mode. The η3-allyl group is classified as an LX-type ligand in the Green LXZ ligand classification scheme, serving as a 3e– donor using neutral electron counting and 4e– donor using ionic electron counting. More common are complexes with allyl and other ligands. Examples include (η3-allyl)Mn(CO)4 and CpPd(allyl). Homoleptic complexes * bis(allyl)nickel * bis(allyl)palladium * bis(allyl)platinum *tris(allyl)chromium * tris(allyl)rhodium * tris(allyl)iridium Synthetic methods Allyl complexes are often generated by ox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ni(allyl)2
NI or Ni may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Ni, or Nishada, the seventh note of the Indian musical scale in raga * ''New Internationalist'', a magazine * Knights Who Say "Ni!", characters from the film ''Monty Python and the Holy Grail'' Businesses * National Instruments, a U.S. producer of automated test equipment and virtual instrumentation software * National Insurance, a system of taxes and related social security benefits in the United Kingdom * Native Instruments, a music software production company * News International, a British newspaper publisher * Portugália airline (IATA code NI) Language * Ni (letter), or Nu, a letter in the Greek alphabet: uppercase Ν, lowercase ν * Ni (kana), romanisation of the Japanese kana に and ニ * Ni (cuneiform), a sign in cuneiform writing Names * Ni (surname) (倪), a Chinese surname * Ní, a surname prefix from the shortened form of the Irish word for a daughter * Ni, female prefix to some Balinese names Places * Ni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalyst
Catalysis () is the process of increasing the rate of a chemical reaction by adding a substance known as a catalyst (). Catalysts are not consumed in the reaction and remain unchanged after it. If the reaction is rapid and the catalyst recycles quickly, very small amounts of catalyst often suffice; mixing, surface area, and temperature are important factors in reaction rate. Catalysts generally react with one or more reactants to form intermediates that subsequently give the final reaction product, in the process of regenerating the catalyst. Catalysis may be classified as either homogeneous, whose components are dispersed in the same phase (usually gaseous or liquid) as the reactant, or heterogeneous, whose components are not in the same phase. Enzymes and other biocatalysts are often considered as a third category. Catalysis is ubiquitous in chemical industry of all kinds. Estimates are that 90% of all commercially produced chemical products involve catalysts at some s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclooctadiene
A cyclooctadiene (sometimes abbreviated COD) is any of several cyclic diene with the formula (CH2)4(C2H2)2. Focusing only on cis derivatives, four isomers are possible: 1,2-, which is an allene, 1,3-, 1,4-, and 1,5-. Commonly encountered isomers are the conjugated isomer 1,3-cyclooctadiene and 1,5-cyclooctadiene, which is used as a ligand for transition metal In chemistry, a transition metal (or transition element) is a chemical element in the d-block of the periodic table (groups 3 to 12), though the elements of group 12 (and less often group 3) are sometimes excluded. They are the elements that can ...s. These dienes are colorless volatile liquids.Thomas Schiffer, Georg Oenbrink “Cyclododecatriene, Cyclooctadiene, and 4-Vinylcyclohexene” in Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2005, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. References External links1,5-Cyclooctadiene Cycloalkenes Dienes Eight-membered rings {{hydrocarbon-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

2.png)