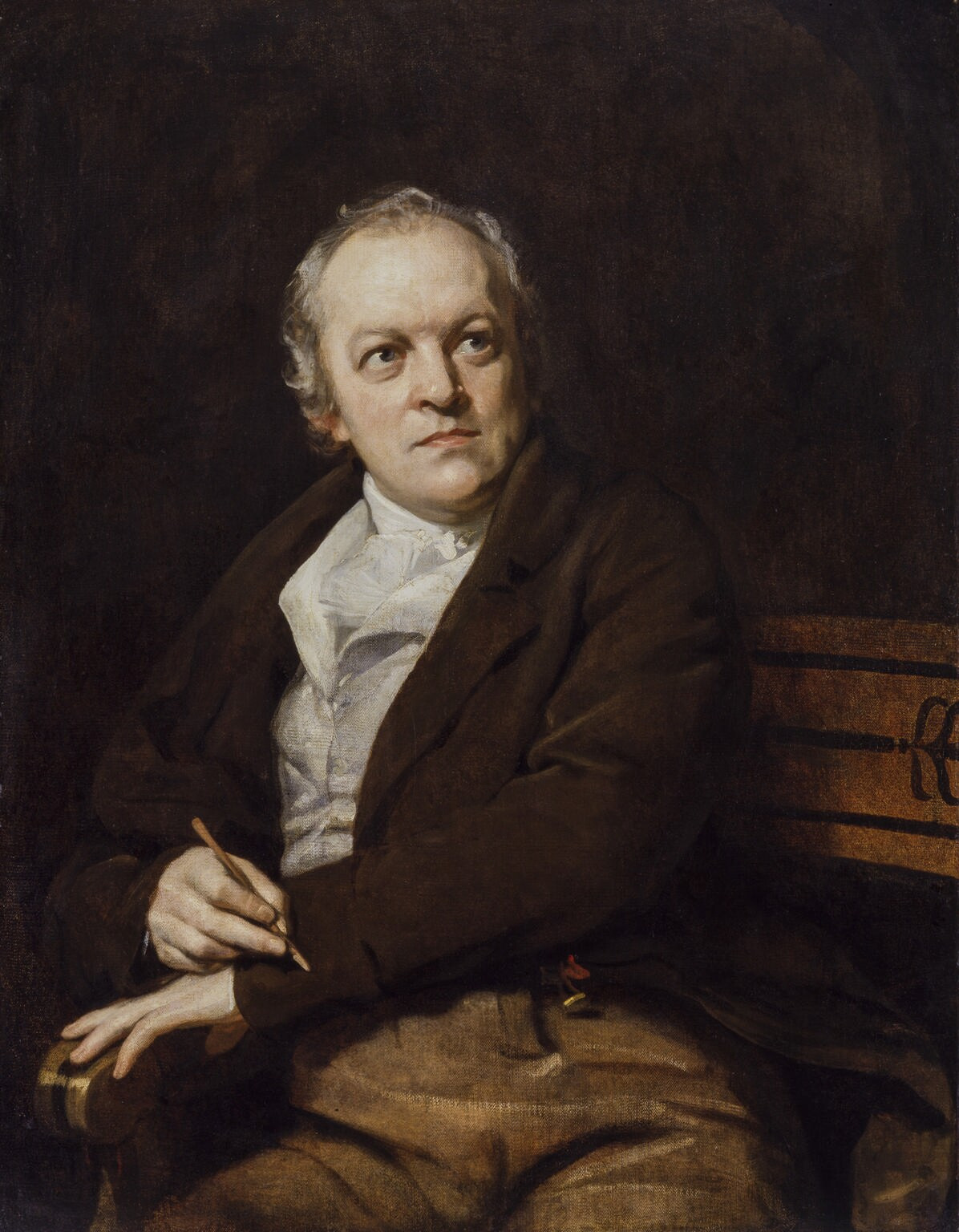|
Organic Form
In romantic literature, a work has organic form if the structure has originated from the materials and subjects used by the author. Using the organic metaphor, the structure is seen to grow as a plant. It stands in contrast to a mechanical form, a work which has been produced in accordance with artificial rules. The lack of rules in Shakespeare's works led some critics to claim that they lacked form; Samuel Taylor Coleridge leapt to his defence with the concept of organic form. Overview Coleridge, an English poet, philosopher, literary critic, and founder of the Romantic movement, suggested that the concept of organic form meant that a poem or literary piece was shaped, rather than structured, from within. The use of the form allowed a piece to uniquely develop itself as it unfolded, and ultimately revealed an emphasis on the whole outcome of the piece, including the connections of each development to each other. In contrast to the more mechanical processes and rules which many c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romantic Literature
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate period from 1800 to 1850. Romanticism was characterized by its emphasis on emotion and individualism, clandestine literature, paganism, idealization of nature, suspicion of science and industrialization, and glorification of the past with a strong preference for the medieval rather than the classical. It was partly a reaction to the Industrial Revolution, the social and political norms of the Age of Enlightenment, and the scientific rationalization of nature. It was embodied most strongly in the visual arts, music, and literature, but had a major impact on historiography, education, chess, social sciences, and the natural sciences. It had a significant and complex effect on politics, with romantic thinkers influencing conservatism, lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Taylor Coleridge
Samuel Taylor Coleridge (; 21 October 177225 July 1834) was an English poet, literary critic, philosopher, and theologian who, with his friend William Wordsworth, was a founder of the Romantic Movement in England and a member of the Lake Poets. He also shared volumes and collaborated with Charles Lamb, Robert Southey, and Charles Lloyd. He wrote the poems ''The Rime of the Ancient Mariner'' and ''Kubla Khan'', as well as the major prose work ''Biographia Literaria''. His critical work, especially on William Shakespeare, was highly influential, and he helped introduce German idealist philosophy to English-speaking cultures. Coleridge coined many familiar words and phrases, including "suspension of disbelief". He had a major influence on Ralph Waldo Emerson and American transcendentalism. Throughout his adult life, Coleridge had crippling bouts of anxiety and depression; it has been speculated that he had bipolar disorder, which had not been defined during his lifetime.Jamis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romantic Literature In English
Romanticism was an artistic, literary, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe toward the end of the 18th century. Scholars regard the publishing of William Wordsworth's and Samuel Coleridge's ''Lyrical Ballads'' in 1798 as probably the beginning of the movement, and the crowning of Queen Victoria in 1837 as its end. Romanticism arrived in other parts of the English-speaking world later; in the United States, it arrived around 1820. The Romantic period was one of major social change in England, due to the depopulation of the countryside and the rapid development of overcrowded industrial cities that took place roughly between 1798 and 1832. The movement of so many people in England was the result of two forces: the Agricultural Revolution, which involved enclosures that drove workers and their families off the land, and the Industrial Revolution which provided them employment, "in the factories and mills, operated by machines driven by steam-power". Indeed, Romantici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physiognomy
Physiognomy (from the Greek , , meaning "nature", and , meaning "judge" or "interpreter") is the practice of assessing a person's character or personality from their outer appearance—especially the face. The term can also refer to the general appearance of a person, object, or terrain without reference to its implied characteristics—as in the physiognomy of an individual plant (see plant life-form) or of a plant community (see vegetation). Physiognomy as a practice meets the contemporary definition of pseudoscience and it is so regarded among academic circles because of its unsupported claims; popular belief in the practice of physiognomy is nonetheless still widespread. The practice was well-accepted by ancient Greek philosophers, but fell into disrepute in the Middle Ages while practised by vagabonds and mountebanks. It revived and was popularised by Johann Kaspar Lavater, before falling from favor in the late 19th century. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerard Manley Hopkins
Gerard Manley Hopkins (28 July 1844 – 8 June 1889) was an English poet and Jesuit priest, whose posthumous fame placed him among leading Victorian poets. His prosody – notably his concept of sprung rhythm – established him as an innovator, as did his praise of God through vivid use of imagery and nature. Only after his death did Robert Bridges publish a few of Hopkins's mature poems in anthologies, hoping to prepare for wider acceptance of his style. By 1930 Hopkins's work was seen as one of the most original literary advances of his century. It intrigued such leading 20th-century poets as T. S. Eliot, Dylan Thomas, W. H. Auden, Stephen Spender and Cecil Day-Lewis. Early life and family Gerard Manley Hopkins was born in Stratford, EssexW. H. Gardner (1963), ''Gerard Manley Hopkins: Poems and Prose'' Penguin p. xvi. (now in Greater London), as the eldest of probably nine children to Manley and Catherine Hopkins, née Smith. He was christened at the Anglican church of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victorian Era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwardian period, and its later half overlaps with the first part of the '' Belle Époque'' era of Continental Europe. There was a strong religious drive for higher moral standards led by the nonconformist churches, such as the Methodists and the evangelical wing of the established Church of England. Ideologically, the Victorian era witnessed resistance to the rationalism that defined the Georgian period, and an increasing turn towards romanticism and even mysticism in religion, social values, and arts. This era saw a staggering amount of technological innovations that proved key to Britain's power and prosperity. Doctors started moving away from tradition and mysticism towards a science-based approach; medicine advanced thanks to the adoption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inscape
Inscape and instress are complementary and enigmatic concepts about individuality and uniqueness derived by the poet Gerard Manley Hopkins from the ideas of the medieval philosopher Duns Scotus.Chevigny, Bell Gale. Instress and Devotion in the Poetry of Gerard Manley Hopkins ''Victorian Studies'' Vol. 9, No. 2 (Dec., 1965), pp. 141–153. Inscape has been rendered variously as: external design, aesthetic conception, intrinsic beauty, the intrinsic form of a thing, a form perceived in nature, the individual self, the expression of the inner core of individuality, the peculiar inner nature of things and persons, expressed in form and gesture, and an essence or identity embodied in a thing. These twin concepts are what his most famous poems are about. __NOTOC__ [Hopkins] felt that everything in the universe was characterized by what he called ''inscape'', the distinctive design that constitutes individual identity. This identity is not static but dynamic. Each being in the universe ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denise Levertov
Priscilla Denise Levertov (24 October 1923 – 20 December 1997) was a British-born naturalised American poet. She was a recipient of the Lannan Literary Award for Poetry. Early life and influences Levertov was born and grew up in Ilford, Essex.Couzyn, Jeni (1985) ''Contemporary Women Poets''. Bloodaxe, p74 Her mother, Beatrice Adelaide (née Spooner-Jones) Levertoff, came from a small mining village in North Wales. Her father, Paul Levertoff, had been a teacher at Leipzig University and as a Russian Hasidic Jew was held under house arrest during the First World War as an 'enemy alien' by virtue of his ethnicity. He emigrated to the UK and became an Anglican priest after converting to Christianity. In the mistaken belief that he would want to preach in a Jewish neighbourhood, he was housed in Ilford, within reach of a parish in Shoreditch, in East London. His daughter wrote, "My father's Hasidic ancestry, his being steeped in Jewish and Christian scholarship and mysticism, his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enjambment
In poetry, enjambment ( or ; from the French ''enjamber'') is incomplete syntax at the end of a line; the meaning 'runs over' or 'steps over' from one poetic line to the next, without punctuation. Lines without enjambment are end-stopped. The origin of the word is credited to the French word ''enjamber'', which means 'to straddle or encroach'. In reading, the delay of meaning creates a tension that is released when the word or phrase that completes the syntax is encountered (called the rejet); the tension arises from the "mixed message" produced both by the pause of the line-end, and the suggestion to continue provided by the incomplete meaning.Preminger 359 In spite of the apparent contradiction between rhyme, which heightens closure, and enjambment, which delays it, the technique is compatible with rhymed verse. Even in couplets, the closed or heroic couplet was a late development; older is the open couplet, where rhyme and enjambed lines co-exist. Enjambment has a long histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Romantic Epistemology
Romantic epistemology emerged from the Romantic challenge to both the static, materialist views of the Enlightenment (Hobbes) and the contrary idealist stream (Hume) when it came to studying life. Romanticism needed to develop a new theory of knowledge that went beyond the method of inertial science, derived from the study of inert nature (''natura naturata''), to encompass vital nature (''natura naturans''). Samuel Taylor Coleridge was at the core of the development of the new approach, both in terms of art and the 'science of knowledge' itself (epistemology). Coleridge's ideas regarding the philosophy of science involved Romantic science in general, but Romantic medicine in particular, as it was essentially a philosophy of the science(s) of life. :What is Life? Were such a question proposed, we should be tempted to answer, what is ''not'' Life that really ''is''? Background European thought had come through the scientific revolution concerning heaven (astronomy) and earth (phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

%2C_Portrait_miniature%2C1809.jpg)