|
Operation Buster–Jangle
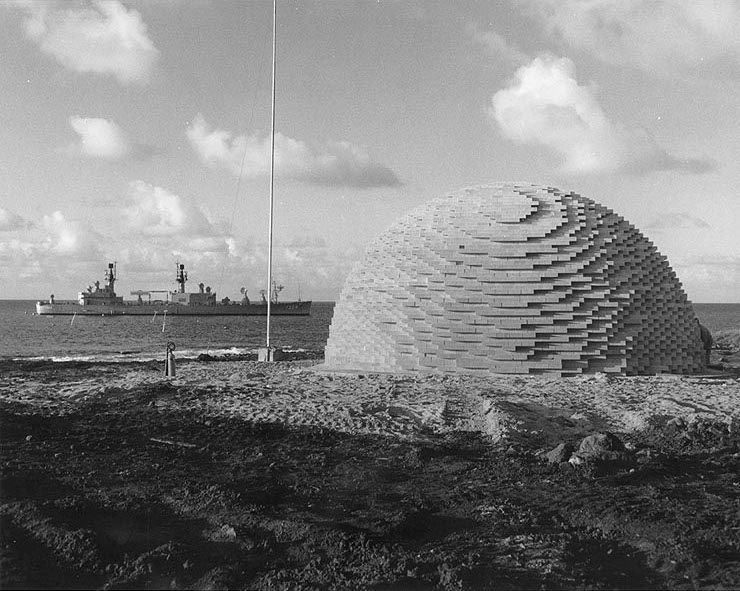
Operation Buster–Jangle was a series of seven (six atmospheric, one cratering) nuclear weapons tests conducted by the United States in late 1951 at the Nevada Test Site. ''Buster–Jangle'' was the first joint test program between the DOD (Operation ''Buster'') and Los Alamos National Laboratories (Operation ''Jangle''). As part of Operation ''Buster'', 6,500 troops were involved in the Operation Desert Rock I, II, and III exercises in conjunction with the tests.Operation Buster–Jangle Fact Sheet , Defense Threat Reduction Agency The last two tests, Operation ''Jangle'', evaluated the cratering effects of low-yield nuclear devices. This series preceded '' Operation Tumbler– ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Greenhouse
Operation Greenhouse was the fifth American nuclear test series, the second conducted in 1951 and the first to test principles that would lead to developing thermonuclear weapons (''hydrogen bombs''). Conducted at the new Pacific Proving Ground, on islands of the Enewetak Atoll, all of the devices were mounted in large steel towers, to simulate air bursts. This series of nuclear weapons tests was preceded by Operation Ranger and succeeded by Operation Buster-Jangle. Operation Greenhouse showcased new and aggressive designs for nuclear weapons. The main idea was to reduce the size, weight, and most importantly, reduce the amount of fissile material necessary for nuclear weapons, while increasing the destructive power. With the Soviet Union's first nuclear test a year and half earlier, the United States had begun stockpiling the new designs before they were actually proven. Thus the success of Operation Greenhouse was vital before the development of thermonuclear weapons coul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tz Database
The tz database is a collaborative compilation of information about the world's time zones, primarily intended for use with computer programs and operating systems. Paul Eggert is its current editor and maintainer, with the organizational backing of ICANN. The tz database is also known as tzdata, the zoneinfo database or Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, IANA time zone database, and occasionally as the Olson database, referring to the founding contributor, Arthur David Olson. Its uniform naming convention for time zones, such as ''America/New_York'' and ''Europe/Paris'', was designed by Paul Eggert. The database attempts to record historical time zones and all civil changes since 1970, the Unix time epoch. It also includes transitions such as daylight saving time, and also records leap seconds. The database, as well as some reference source code, is in the public domain. New editions of the database and code are published as changes warrant, usually several times per year. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weakly radioactive because all isotopes of uranium are unstable; the half-lives of its naturally occurring isotopes range between 159,200 years and 4.5 billion years. The most common isotopes in natural uranium are uranium-238 (which has 146 neutrons and accounts for over 99% of uranium on Earth) and uranium-235 (which has 143 neutrons). Uranium has the highest atomic weight of the primordially occurring elements. Its density is about 70% higher than that of lead, and slightly lower than that of gold or tungsten. It occurs naturally in low concentrations of a few parts per million in soil, rock and water, and is commercially extracted from uranium-bearing minerals such as uraninite. In nature, uranium is found as uranium-238 (99.2739 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 4 Nuclear Bomb
The Mark 4 nuclear bomb was an American implosion-type nuclear bomb based on the earlier Mark 3 Fat Man design, used in the Trinity test and the bombing of Nagasaki. With the Mark 3 needing each individual component to be hand-assembled by only highly trained technicians under closely controlled conditions, the purpose of the Mark 4 was to produce an atomic weapon as a practical piece of ordnance. The Mark 4 Mod 0 entered the stockpile starting March 19, 1949 and was in use until 1953. With over 500 units procured, the Mark 4 was the first mass-produced nuclear weapon. Design The Mark 4 utilized a near-identical nuclear explosive package to the 1561 assembly of the Mark 3 Fat Man, but the newly-formed Z Division of Los Alamos focused on re-engineering the electronics and conventional explosives packages to be more modular for easier assembly in the field. The priority objectives of the Mark 4 bomb program were to have the ability to monitor the weapon battery and electrical sy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutonium
Plutonium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, and forms a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation states. It reacts with carbon, halogens, nitrogen, silicon, and hydrogen. When exposed to moist air, it forms oxides and hydrides that can expand the sample up to 70% in volume, which in turn flake off as a powder that is pyrophoric. It is radioactive and can accumulate in bones, which makes the handling of plutonium dangerous. Plutonium was first synthetically produced and isolated in late 1940 and early 1941, by a deuteron bombardment of uranium-238 in the cyclotron at the University of California, Berkeley. First, neptunium-238 ( half-life 2.1 days) was synthesized, which subsequently beta-decayed to form the new element with atomic number 94 and atomic weight 238 (half-life 88 years). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fizzle (nuclear Test)
A fizzle occurs when the detonation of a device for creating a nuclear explosion (such as a nuclear weapon) grossly fails to meet its expected yield. The cause(s) for the failure can be linked to improper design, poor construction, or lack of expertise.Staff Writer.NBC Weapons: North Korean Fizzle Bomb" ''Strategy Page.'' Retrieved on 2008-05-04. Earl Lane.Nuclear Experts Assess the Threat of a "Backyard Bomb”" ''American Association for the Advancement of Science.'' Retrieved on 2008-05-04. All countries that have had a nuclear weapons testing program have experienced some fizzles. Meirion Jones.A short history of fizzles" ''BBC News.'' Retrieved on 2008-05-04. A fizzle can spread radioactive material throughout the surrounding area, involve a partial fission reaction of the fissile material, or both.Theodore E. Liolios.The Effects of Nuclear Terrorism: Fizzles" (PDF) ''European Program on Science and International Security.'' Retrieved on 2008-05-04. For practical purposes, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mark 6 Nuclear Bomb
The Mark 6 nuclear bomb was an American nuclear bomb based on the earlier Mark 4 nuclear bomb and its predecessor, the Mark 3 Fat Man nuclear bomb design. The Mark 6 was in production from 1951 to 1955 and saw service until 1962. Seven variants and versions were produced, with a total production run of all models of 1100 bombs. The basic Mark 6 design was in diameter and long, the same basic dimensions as the Mark 4. Various models of the Mark 6 were roughly 25% lighter than either the Mark 4 or Fat Man, and weighed . Early models of the Mark 6 used the same 32-point implosion system design concept as the earlier Mark 4 and Mark 3; the Mark 6 Mod 2 and later used a different, 60-point implosion system. Various models and pit options gave nuclear yields of 18, 26, 80, 154, and 160 kilotons for Mark 6 models. Survivors There are several Mark 6 casings on display: * Defense Nuclear Weapons School on Kirtland Air Force Base in Albuquerque, New Mexico * Cold War Gallery of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nevada National Security Site
The Nevada National Security Site (N2S2 or NNSS), known as the Nevada Test Site (NTS) until 2010, is a United States Department of Energy (DOE) reservation located in southeastern Nye County, Nevada, about 65 miles (105 km) northwest of the city of Las Vegas. Formerly known as the Nevada Proving Grounds, the site was established in 1951 for the testing of nuclear devices. It covers approximately 1,360 square miles (3,500 km2) of desert and mountainous terrain. Nuclear weapons testing at the site began with a 1-kiloton-of-TNT (4.2 TJ) bomb dropped on Frenchman Flat on January 27, 1951. Over the subsequent four decades, over 1,000 nuclear explosions were detonated at the site. Many of the iconic images of the nuclear era come from the site. During the 1950s, the mushroom clouds from the 100 atmospheric tests could be seen from almost away. The city of Las Vegas experienced noticeable seismic effects, and the mushroom clouds, which could be seen from the downtown ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Fallout
Nuclear fallout is the residual radioactive material propelled into the upper atmosphere following a nuclear blast, so called because it "falls out" of the sky after the explosion and the shock wave has passed. It commonly refers to the radioactive dust and ash created when a nuclear weapon explodes. The amount and spread of fallout is a product of the size of the weapon and the altitude at which it is detonated. Fallout may get entrained with the products of a pyrocumulus cloud and fall as black rain (rain darkened by soot and other particulates, which fell within 30–40 minutes of the atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki). This radioactive dust, usually consisting of fission products mixed with bystanding atoms that are neutron-activated by exposure, is a form of radioactive contamination. Types of fallout Fallout comes in two varieties. The first is a small amount of carcinogenic material with a long half-life. The second, depending on the height of detonation, i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TNT Equivalent
TNT equivalent is a convention for expressing energy, typically used to describe the energy released in an explosion. The is a unit of energy defined by that convention to be , which is the approximate energy released in the detonation of a metric ton (1,000 kilograms) of TNT. In other words, for each gram of TNT exploded, (or 4184 joules) of energy is released. This convention intends to compare the destructiveness of an event with that of conventional explosive materials, of which TNT is a typical example, although other conventional explosives such as dynamite contain more energy. Kiloton and megaton The "kiloton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 terajoules (). The "megaton (of TNT)" is a unit of energy equal to 4.184 petajoules (). The kiloton and megaton of TNT have traditionally been used to describe the energy output, and hence the destructive power, of a nuclear weapon. The TNT equivalent appears in various nuclear weapon control treaties, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nuclear Weapon Yield
The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy released when that particular nuclear weapon is detonated, usually expressed as a TNT equivalent (the standardized equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene which, if detonated, would produce the same energy discharge), either in kilotonnes (kt—thousands of tonnes of TNT), in megatonnes (Mt—millions of tonnes of TNT), or sometimes in terajoules (TJ). An explosive yield of one terajoule is equal to . Because the accuracy of any measurement of the energy released by TNT has always been problematic, the conventional definition is that one kilotonne of TNT is held simply to be equivalent to 1012 calories. The yield-to-weight ratio is the amount of weapon yield compared to the mass of the weapon. The practical maximum yield-to-weight ratio for fusion weapons ( thermonuclear weapons) has been estimated to six megatonnes of TNT per tonne of bomb mass (25 TJ/kg). Yields of 5.2 megatonnes/tonne and higher have been re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Nuclear Weapons
This is a list of nuclear weapons listed according to country of origin, and then by type within the states. United States US nuclear weapons of all types – bombs, warheads, shells, and others – are numbered in the same sequence starting with the Mark 1 and () ending with the W-91 (which was canceled prior to introduction into service). All designs which were formally intended to be weapons at some point received a number designation. Pure test units which were experiments (and not intended to be weapons) are not numbered in this sequence. Early weapons were very large and could only be used as free fall bombs. These were known by "Mark" designators, like the Mark 4 which was a development of the Fat Man weapon. As weapons became more sophisticated they also became much smaller and lighter, allowing them to be used in many roles. At this time the weapons began to receive designations based on their role; bombs were given the prefix "B", while the same warhead used in other r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |