|
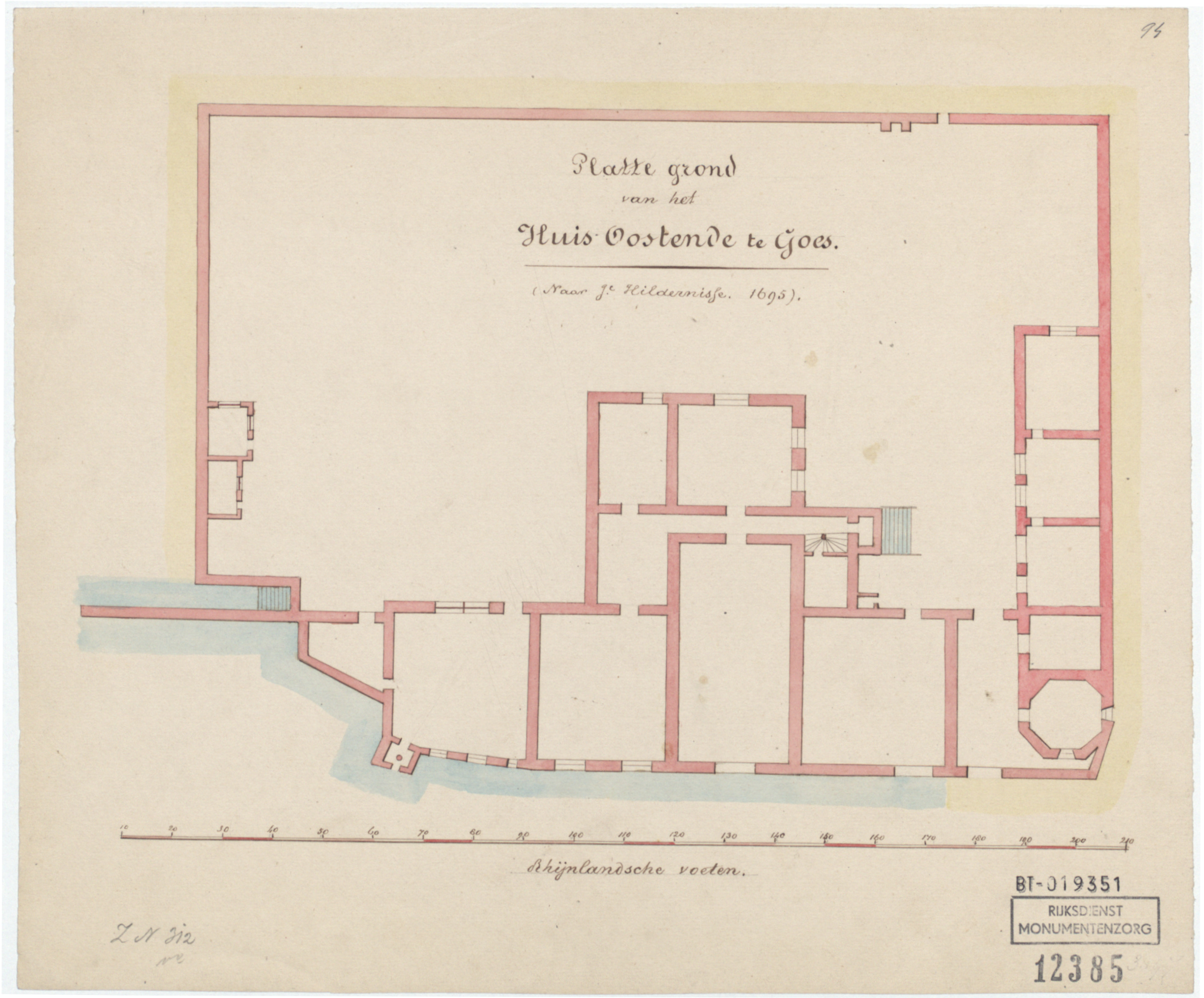
Oostende Castle
Oostende Castle is a castle in Goes, the Netherlands. The current castle was part of a motte-and-bailey castle. Its grounds formed the outer bailey. The motte was directly south of it, now under the Maria Magdalena Church. The castle consists of a 14th-century tower house built on top of a ring wall that was surrounded by a moat. The foundations of this ring wall have been found west and east of the house. The segment to the west had two towers on the inside, and has been made visible for the public. The tower house has been restored, and is now part of a craft brewery, hotel and restaurant. Castle Characteristics Phase 1: Motte and bailey Castle In its first phase, Oostende Castle has always been assumed to have been a motte-and-bailey castle, consisting of two more or less round hills, each with its own moat. Both were thought situated west of the natural ridge that runs through the center of Goes, below the central market. The whole terrain is roughly delimited by the Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goes
Goes () is a city and municipality in the southwestern Netherlands on Zuid-Beveland, in the province of Zeeland. The city of Goes has approximately 27,000 residents. History Goes was founded in the 10th century on the edge of a creek: de Korte Gos (the Short Gos). The village grew fast, and in the early 12th century it had a market square and a church devoted to Mary Magdalene. By 1300 it had a brick castle, now known as Oostende Castle. In 1405 Goes received city rights from William, Duke of Bavaria, by his right as count of Holland, and in 1417 it was allowed to build town walls. The prosperity of the city was based upon the cloth industry and the production of salt. In the 16th century Goes declined. Its connection to the sea silted up and in 1554 a large fire destroyed part of the city. In the Autumn of 1572, during the course of the Eighty Years' War, Goes, in the Spanish Netherlands, was besieged by Dutch forces with the support of English troops. The siege was relieve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zuid-Beveland
Zuid-Beveland (; "South Beveland") is part of the province of Zeeland in the Netherlands north of the Western Scheldt and south of the Eastern Scheldt. Topography It is a former island, now peninsula, crossed by the Canal through Zuid-Beveland on the west and the Scheldt–Rhine Canal on the east. It consists of four municipalities: * Borsele *Goes *Kapelle * Reimerswaal Goes is Zuid-Beveland's principal urban center. Zuid-Beveland is a former island which was joined (together with Walcheren) to the mainland by a railway embankment in 1903 and to Noord-Beveland by the Delta Works. A shipping canal connecting the Belgian port of Antwerp with the Rhine River traverses Zuid-Beveland. History Third and fourth centuries This was the period during which most of Zeeland appears to have been submerged. The area was and for several centuries would remain almost unpeopled. Middle Ages During the eleventh century the area began to be drained, as little by little polders and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tillegem Castle
Tillegem Castle is a castle in Belgium. Since 1980, the castle and its park have been property of the Province of West Flanders West Flanders ( nl, West-Vlaanderen ; vls, West Vloandern; french: (Province de) Flandre-Occidentale ; german: Westflandern ) is the westernmost Provinces of Belgium, province of the Flemish Region, in Belgium. It is the only coastal Belgian prov .... See also * List of castles in Belgium References Castles in Belgium {{Belgium-castle-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or concerts. Its most common form is triangular in shape and made of wood. Some have multiple rows of strings and pedal attachments. Ancient depictions of harps were recorded in Current-day Iraq (Mesopotamia), Iran (Persia), and Egypt, and later in India and China. By medieval times harps had spread across Europe. Harps were found across the Americas where it was a popular folk tradition in some areas. Distinct designs also emerged from the African continent. Harps have symbolic political traditions and are often used in logos, including in Ireland. History Harps have been known since antiquity in Asia, Africa, and Europe, dating back at least as early as 3000 BCE. The instrument had great popularity in Europe during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandelier
A chandelier (; also known as girandole, candelabra lamp, or least commonly suspended lights) is a branched ornamental light fixture designed to be mounted on ceilings or walls. Chandeliers are often ornate, and normally use incandescent light bulbs, though some modern designs also use fluorescent lamps and recently LEDs. Classic chandeliers have arrays of hanging crystal prisms to illuminate a room with refracted light, while contemporary chandeliers assume a more minimalist design that does not contain prisms and illuminate a room with direct light from the lamps, sometimes also equipped with translucent glass covering each lamp. Modern chandeliers have a more modernized design that uses LEDs, and combines the elements of both classic and contemporary designs; some are also equipped with refractive crystal prisms or small mirrors. Chandeliers are distinct from pendant lights, as they usually consist of multiple lamps and hang in branched frames, whereas pendant lights h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tapestry
Tapestry is a form of textile art, traditionally woven by hand on a loom. Tapestry is weft-faced weaving, in which all the warp threads are hidden in the completed work, unlike most woven textiles, where both the warp and the weft threads may be visible. In tapestry weaving, weft yarns are typically discontinuous; the artisan interlaces each coloured weft back and forth in its own small pattern area. It is a plain weft-faced weave having weft threads of different colours worked over portions of the warp to form the design. Tapestry is relatively fragile, and difficult to make, so most historical pieces are intended to hang vertically on a wall (or sometimes in tents), or sometimes horizontally over a piece of furniture such as a table or bed. Some periods made smaller pieces, often long and narrow and used as borders for other textiles. European tapestries are normally made to be seen only from one side, and often have a plain lining added on the back. However, other tradit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bailiff
A bailiff (from Middle English baillif, Old French ''baillis'', ''bail'' "custody") is a manager, overseer or custodian – a legal officer to whom some degree of authority or jurisdiction is given. Bailiffs are of various kinds and their offices and duties vary greatly. Another official sometimes referred to as a ''bailiff'' was the ''Vogt''. In the Holy Roman Empire a similar function was performed by the ''Amtmann''. British Isles Historic bailiffs ''Bailiff'' was the term used by the Normans for what the Saxons had called a '' reeve'': the officer responsible for executing the decisions of a court. The duty of the bailiff would thus include serving summonses and orders, and executing all warrants issued out of the corresponding court. The district within which the bailiff operated was called his '' bailiwick'', even to the present day. Bailiffs were outsiders and free men, that is, they were not usually from the bailiwick for which they were responsible. Throughout Nor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hook And Cod Wars
The Hook and Cod wars ( nl, Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten) comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of count of Holland, but some have argued that the underlying reason was because of the power struggle of the bourgeois in the cities against the ruling nobility. The Cod faction generally consisted of the more progressive cities of Holland. The Hook faction consisted for a large part of the conservative noblemen. The origin of the name "Cod" is uncertain, but is most likely a case of reappropriation. Perhaps it derives from the arms of Bavaria, that look like the scales of a fish. The ''Hook'' refers to the hooked stick that is used to catch cod. Another possible explanation is that as a cod grows it tends to eat more, growing even bigger and eating even more, thus encapsulating how the noblemen perhaps saw the expanding middle classes of the time. Aftermath of William IV's reign (13 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guy II, Count Of Blois
Guy II of Châtillon, Count of Blois (died 22 December 1397), the youngest son of Louis I of Châtillon and Joan of Avesnes, was Count of Blois and Soissons, and lord of Avesnes, Schoonhoven, and Gouda 1381–1397, and lord of Beaumont and Chimay. In 1360, he was one of the hostages sent to the Kingdom of England by the terms of the Treaty of Brétigny. He was eventually ransomed by the sale of Soissons and was released on 15 August 1367. He was knighted in 1370 while crusading with the Teutonic Knights in Lithuania. In 1374 he married Marie, daughter of William I, Marquis of Namur, and they had one son: * Louis III of Châtillon (d. 1391) Thereafter he joined in the wars of king Charles VI, and commanded the rearguard at the Battle of Roosebeke. The death of his only son in 1391 prompted him to sell the inheritance of the County of Blois to Louis of Valois, Duke of Orléans. He was for some time the patron of Jean Froissart: he appointed him his chaplain in 1384 and obtained f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Beaumont
John of Beaumont (1288 – 11 March 1356) was a younger brother of count William III of Holland. He was the lord of Beaumont and count of Soissons by virtue of his marriage. Life He was born in 1288 as John of Hainault, 4th son of John II, Count of Holland and Philippa of Luxembourg. He was the brother of William I of Hainault (III of Holland) and Alice of Hainault, among others. When his uncle John I, Count of Holland died in 1299, he left behind no descendants. As a result, his father inherited the county of Holland and Zeeland as John II, Count of Holland through his mother Adelaide of Holland. From then on Hainault and Holland were in a personal union. John of Hainault bought the ''heerlijkheid'' (comparably to the English Barony) of Beaumont, located in the southern Netherlands, for his son. Count John II of Holland died in 1304 and was succeeded by his eldest son William III of Holland. On 21 June 1308, John received from his brother all the possessions of Gerard van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melis Stoke
Melis Stoke ( 1235 – c. 1305) was a Dutch writer who lived in the 13th century. Biography Melis Stoke was probably born in the Dutch province of Zeeland around 1235. He died somewhere around 1305. He started writing in 1290 in Middle Dutch a chronicle in rhyme on the countship of Holland. His most famous work was the ''Rijmkroniek'', the ''chronicle in rhyme'', among the first books written in the Dutch language. In it is the account of the murder of count Floris V. Stoke found his information from written sources, eyewitness accounts and his own observations. Melis Stoke was a clerk in Floris V's service. He probably learned to read and write in a monastery. Sources do not mention whether Stoke was a monk himself. There is evidence he had been in the service of the city of Dordrecht Dordrecht (), historically known in English as Dordt (still colloquially used in Dutch, ) or Dort, is a city and municipality in the Western Netherlands, located in the province of South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John II, Count Of Holland
John II (1247 – 22 August 1304) was Count of Hainaut, Holland, and Zeeland. Life John II, born 1247, was the eldest son of John I of Hainaut and Adelaide of Holland.Detlev Schwennicke, ''Europäische Stammtafeln: Stammtafeln zur Geschichte der Europäischen Staaten'', Neue Folge, Band II (Marburg, Germany: Verlag von J. A. Stargardt, 1984), Tafel 22 He became Count of Hainaut on the death of his grandmother, Countess Margaret I of Hainaut. John continued the war between the House of Dampierre and the Avesnes family against Count Guy of Flanders for Imperial Flanders. John II became Count of Holland in 1299 upon the death of his cousin John I.Johan C H Blom, ''History of the Low Countries'' (New York: Berghahn Books, 2006), p. 58 The personal union he established between Hainaut and Holland–Zeeland lasted for another half-century. John I's father, Floris V, had been fighting against Flanders for Zeeland.Johan C H Blom, ''History of the Low Countries'' (New York: Berghahn Boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |