|
Hook And Cod Wars
The Hook and Cod wars ( nl, Hoekse en Kabeljauwse twisten) comprise a series of wars and battles in the County of Holland between 1350 and 1490. Most of these wars were fought over the title of count of Holland, but some have argued that the underlying reason was because of the power struggle of the bourgeois in the cities against the ruling nobility. The Cod faction generally consisted of the more progressive cities of Holland. The Hook faction consisted for a large part of the conservative noblemen. The origin of the name "Cod" is uncertain, but is most likely a case of reappropriation. Perhaps it derives from the arms of Bavaria, that look like the scales of a fish. The ''Hook'' refers to the hooked stick that is used to catch cod. Another possible explanation is that as a cod grows it tends to eat more, growing even bigger and eating even more, thus encapsulating how the noblemen perhaps saw the expanding middle classes of the time. Aftermath of William IV's reign (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cod Wars
The Cod Wars ( is, Þorskastríðin; also known as , ; german: Kabeljaukriege) were a series of 20th-century confrontations between the United Kingdom (with aid from West Germany) and Iceland about fishing rights in the North Atlantic. Each of the disputes ended with an Icelandic victory. Some Icelandic historians view the history of Iceland's struggle for control of its maritime resources in ten episodes, or ten cod wars. Fishing boats from Britain have been sailing to waters near Iceland in search of their catch since the 14th century. Agreements struck during the 15th century started a centuries-long series of intermittent disputes between the two countries. Demand for seafood and consequent competition for fish stocks grew rapidly in the 19th century. The modern disputes or wars began in 1952 after Iceland expanded its territorial waters from 3 to based on a decision by the International Court of Justice. The United Kingdom responded by banning Icelandic ships landi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IV, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis IV (german: Ludwig; 1 April 1282 – 11 October 1347), called the Bavarian, of the house of Wittelsbach, was King of the Romans from 1314, King of Italy from 1327, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1328. Louis' election as king of Germany in 1314 was controversial, as his Habsburg cousin Frederick the Fair was simultaneously elected king by a separate set of electors. Louis defeated Frederick in the Battle of Mühldorf in 1322, and the two eventually reconciled. Louis was opposed and excommunicated by the French Pope John XXII; Louis in turn attempted to depose the pope and install an anti-pope. Louis IV was Duke of Upper Bavaria from 1294 to 1301 together with his elder brother Rudolf I, was Margrave of Brandenburg until 1323, and Count Palatine of the Rhine until 1329, and became Duke of Lower Bavaria in 1340. He was the last Bavarian to be a king of Germany until 1742. He became Count of Hainaut, Holland, Zeeland, and Friesland in 1345 when his wife Margaret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Le Quesnoy
Le Quesnoy (; pcd, L' Kénoé) is a Communes of France, commune and small town in the east of the Nord (French department), Nord Departments of France, department of northern France. It was part of the historical province of French Hainaut. It had a keynote industry in shoemaking before the late 1940s, followed by a chemical factory and dairy, giving way to its weekly market, tourism, local commuting to elsewhere such as Valenciennes and local shops. Le Quesnoy's inhabitants are known as ''Quercitains''. Economy The town of Le Quesnoy has somehow missed much of the Industrial Revolution. Unlike the neighboring towns of Valenciennes or Maubeuge, iron/steel works did not take hold. The lack of wealth underground and of a major transportation route partly explains this. The authorities, however, took note of this weakness and proposed the Ecaillon canal from Sambre to Scheldt; considered but abandoned because of low water yield in the forest of Mormal. Shoemaking was a major l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoonhoven
Schoonhoven () is a city and former municipality in the western Netherlands, in the province of South Holland. Since 2015 it has been a part of the municipality of Krimpenerwaard, before it had been an independent municipality. The former municipality had a population of in , and covered an area of of which water. From 2010 to 2014, it was the smallest municipality in the Netherlands in land area, following the merger of Rozenburg into Rotterdam. The first winner of the Dutch version of Pop Idol, Jamai Loman, is from this town. Also Jan-Arie van der Heijden, football player for Feyenoord, lives in Schoonhoven. History Circa 1220 a castle was built on the north side of a small stream called "Zevender", near its mouth at the Lek River. The city of Schoonhoven was then formed near the castle. The oldest reference to the city is in a document from 1247, where it is referred to as ''Sconhoven''. In 1280, it was granted city rights. Around 1350, city walls and gates were constructe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oudewater
Oudewater () is a municipality and a town in the Netherlands. History The origin of the town of Oudewater is obscure and no information has been found concerning the first settlement of citizens. It is also difficult to recover the name of Oudewater. One explanation is that the name is a corruption of ''old water-meadow''. Oudewater was an important border city between Holland and Utrecht. Oudewater (lit. "Old water") was of great strategic importance. The town was granted city rights in 1265 by Hendrik van Vianden, the bishop of Utrecht. Oudewater took its place in the First Free States council in Dordrecht on 19 July 1572, Oudewater was one of the twelve cities taking part in the first free convention of the States General in Dordrecht. This was a meeting that laid down the origin of the State of the Netherlands, as we know it now, under the leadership of the House of Orange. This happened at the beginning of the Eighty Years' War (1568–1648) when the Netherlands were sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jutphaas
Jutphaas is a former village and municipality in the province of Utrecht in the Netherlands. The municipality merged with Vreeswijk in 1971, and is now the northern half of the town of Nieuwegein Nieuwegein () is a municipality and city in the Dutch province of Utrecht. It is bordered on the north by the city of Utrecht, the provincial capital. It is separated from Vianen to the south by the river Lek and borders on IJsselstein in the sout .... The former village was located on the Merwedekanaal, and some of the buildings can still be found there, surrounded by the suburbs of Nieuwegein. External links * Former populated places in the Netherlands Populated places in Utrecht (province) Former municipalities of Utrecht (province) Nieuwegein {{Utrecht-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William I, Duke Of Bavaria
William I, Duke of Bavaria- Straubing (Frankfurt am Main, 1330–1389, Le Quesnoy), was the second son of Emperor Louis IV and Margaret II of Hainaut. He was also known as William V, Count of Holland, as William III, Count of Hainaut and as William IV, Count of Zeeland. Biography In 1345 William's father was conferring Hainaut, Holland, Zeeland and Friesland upon his wife Margaret, and shortly later also upon their son William. After his father's death in 1347, William ruled Bavaria, Holland and Hainaut together with his five brothers until 1349. With the first division of the Wittelsbach possessions in 1349 he received Hainaut, Holland and Lower Bavaria together with his brothers Stephen II and Albert I. After the next division of Bavaria in 1353, he ruled together with his younger brother Albert I in Bavaria-Straubing, Holland and Hainaut. William had engaged in a long struggle with his mother Margaret, obtaining Holland and Zeeland , nl, Ik worstel en kom b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
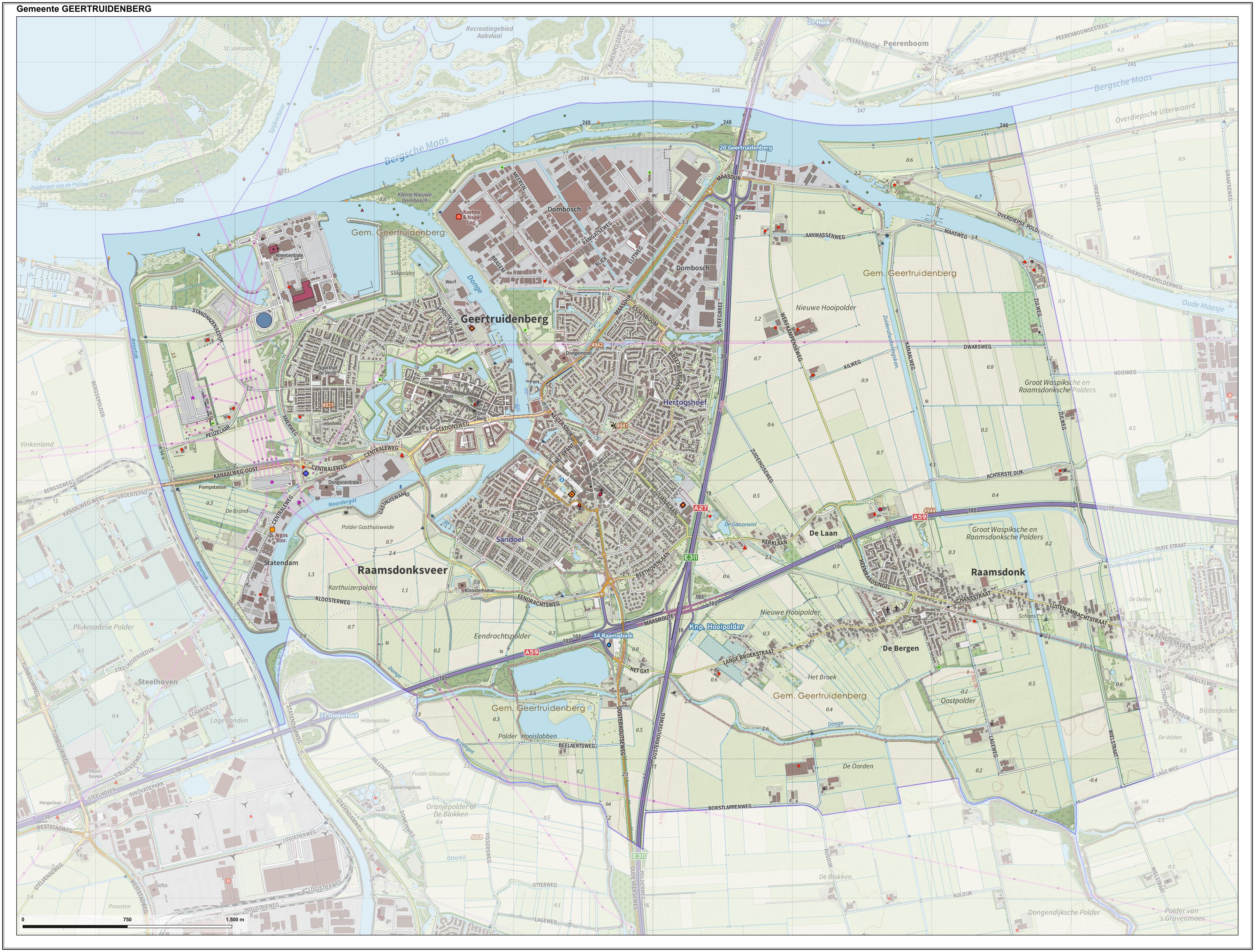
Geertruidenberg
Geertruidenberg () is a city and municipality in the province North Brabant in the south of the Netherlands. The city, named after Saint Gertrude of Nivelles, received city rights in 1213 from the count of Holland. The fortified city prospered until the 15th century. Today, the municipality of Geertruidenberg also includes the population centres Raamsdonk and Raamsdonksveer. The municipality has a total area of and had a population of in . The city government consists of the mayor Willemijn van Hees and three aldermen. History Geertruidenberg is named after Saint Gertrude of Nivelles. In 1213, Sint Geertruidenberg (English: "Saint Gertrude's Mountain") received city rights from Count William I of Holland. The fortified city became a trade center, where counts and other nobility gathered for negotiations. The Hook and Cod wars in 1420 and the Saint Elizabeth's flood in 1421 ended the prosperity of the city. During the Eighty Years War the city was captured by an English, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet (assembly)
In politics, a diet (, ) is a formal deliberative assembly. The term is used historically for deliberative assemblies such as the German Imperial Diet (the general assembly of the Imperial Estates of the Holy Roman Empire), as well as a designation for modern-day legislative bodies of certain countries and states such as the National Diet of Japan, or the German Bundestag, the Federal Diet. Etymology The term (also in the nutritional sense) might be derived from Medieval Latin ''dieta'', meaning both "parliamentary assembly" and "daily food allowance", from earlier Latin , possibly from the Greek (= arbitration), or transcribing Classical Greek , meaning "way of living", and hence also "diet", "regular (daily) work". Through a false etymology, reflected in the spelling change replacing ''ae'' with ''e'', the word "diet" came to be associated with Latin , "date". It came to be used in postclassical Europe in the sense of "an assembly" because of its use for the work o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Of Namur (1323–91)
Robert of Namur may refer to: * Robert of Namur (died 981), count of the Lommegau * Robert of Namur (1323–1391), a noble from the Low Countries close to King Edward III of England {{hndis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William V, Duke Of Jülich
William V, Duke of Jülich ( – 25/26 February 1361) was a German nobleman. Some authors call him William I, because he was the first '' Duke of Jülich''; the earlier Williams had been ''Count of Jülich''. Other authors call the subject of this article "William VI"; they count the son and co-ruler of William IV as William V. William V was the eldest son of Gerhard V of Jülich and Elisabeth of Brabant-Aarschot, daughter of Godfrey of Brabant.Walther Möller, ''Stammtafeln westdeutscher Adelsgeschlechter im Mittelalter'' (Darmstadt, 1922, reprint Verlag Degener & Co., 1995), Vol. 1, page 14. William V was a key political figure of his time, being a brother-in-law to both Edward III of England and Emperor Ludwig IV. He spent enormous sums of money to have his brother Walram of Jülich appointed as Archbishop of Cologne over Adolph II of the Marck. In 1337 he was crucially involved in the German-English alliance which caused the start of the Hundred Years' War. William was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joanna Of Hainaut
Joanna of Hainault (1315–1374) was a Duchess of Jülich by marriage to William V, Duke of Jülich. She was the third daughter of William I, Count of Hainaut, and Joan of Valois. She was a younger sister of Philippa of Hainault, Queen of England, and Margaret II, Countess of Hainault. Life Joanna married William V, Duke of Jülich, their children were as follows: *Gerhard VI of Jülich, Count of Berg and Ravensberg, grandfather of Adolph I, Duke of Cleves *William II, Duke of Jülich *Richardis of Jülich, married Count Engelbert III of the Mark *Philippa of Jülich, married Godfrey II of Heinsberg *Reinold *Joanna of Jülich, married William I, Count of Isenburg-Wied *Isabella of Jülich, married John Plantagenet, 3rd Earl of Kent Ancestry {{ahnentafel , collapsed=yes , align=center , boxstyle_1=background-color: #fcc; , boxstyle_2=background-color: #fb9; , boxstyle_3=background-color: #ffc; , boxstyle_4=background-color: #bfc; , boxstyle_5=background-color: #9fe; , 1= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |