|
Oneida Castle, New York
Oneida Castle ( one, tkanaˀalóhaleˀ) is a village in Oneida County, New York, United States. The population was 625 at the 2010 census. The Village of Oneida Castle is in the northwestern corner of the Town of Vernon. Oneida Castle is east of the City of Oneida (located in Madison County) and west of the City of Sherrill in New York State. History The village was formerly the site of a major fortified village, Kanonwalohale (written as "tkanaˀalóhaleˀ" modern Oneida Orthography), of the Oneida tribe, one of the original Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederacy. They established it in the beginning of the 18th century, moving from an area where they suffered raids by parties from the French colony of Quebec, which was trying to control their fur trade. The village was surrounded by tall wooden palisades, with a moat bordering this. Dwellings and storage structures were protected inside. Mohawk Joseph Brant led a war party which destroyed the village in July 1780. Later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village (United States)
In the United States, the meaning of village varies by geographic area and legal jurisdiction. In many areas, "village" is a term, sometimes informal, for a type of administrative division at the local government level. Since the Tenth Amendment to the United States Constitution prohibits the federal government from legislating on local government, the states are free to have political subdivisions called "villages" or not to and to define the word in many ways. Typically, a village is a type of municipality, although it can also be a special district or an unincorporated area. It may or may not be recognized for governmental purposes. In informal usage, a U.S. village may be simply a relatively small clustered human settlement without formal legal existence. In colonial New England, a village typically formed around the meetinghouses that were located in the center of each town.Joseph S. Wood (2002), The New England Village', Johns Hopkins University Press Many of these colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois Confederacy
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Nations peoples in northeast North America/Turtle Island (Native American folklore), Turtle Island. They were known during the Colonial history of the United States, colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English people, English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk people, Mohawk, Oneida people, Oneida, Onondaga people, Onondaga, Cayuga people, Cayuga, and Seneca people, Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by The Great Peacem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villages In New York (state)
This is a list of villages in New York, which includes all 534 villages in the U.S. state of New York. At the time of the 2010 United States Census, the state of New York had 555 villages. Since then, 21 villages were dissolved (four in Cattaraugus County, three in Oneida County, two each in Chautauqua County, St. Lawrence County and Wayne County, one each in Essex County, Jefferson County, Seneca County, Washington County and Oswego County as well as Keeseville in Clinton and Essex counties), while one new village was created in Suffolk County (Mastic Beach).New York State Department of State, ''New York Department of State Announces Grant Awards to Assist th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poverty Line
The poverty threshold, poverty limit, poverty line or breadline is the minimum level of income deemed adequate in a particular country. The poverty line is usually calculated by estimating the total cost of one year's worth of necessities for the average adult.Poverty Lines – Martin Ravallion, in The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, 2nd Edition, London: Palgrave Macmillan The cost of housing, such as the rent for an apartment, usually makes up the largest proportion of this estimate, so economists track the real estate market and other housing cost indicators as a major influence on the poverty line. Individual factors are often used to account for various circumstances, such as whether one is a parent, elderly, a child, married, etc. The poverty threshold may be adjusted annually. In practice, like the definition of poverty, the official or common understanding of the poverty line is significantly higher in developed countries than in developing countries. In October ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Race And Ethnicity In The United States Census
Race and ethnicity in the United States census, defined by the federal Office of Management and Budget (OMB) and the United States Census Bureau, are the self-identified categories of race or races and ethnicity chosen by residents, with which they most closely identify, and indicate whether they are of Hispanic or Latino origin (the only categories for ethnicity). The racial categories represent a social-political construct for the race or races that respondents consider themselves to be and, "generally reflect a social definition of race recognized in this country." OMB defines the concept of race as outlined for the U.S. census as not "scientific or anthropological" and takes into account "social and cultural characteristics as well as ancestry", using "appropriate scientific methodologies" that are not "primarily biological or genetic in reference." The race categories include both racial and national-origin groups. Race and ethnicity are considered separate and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
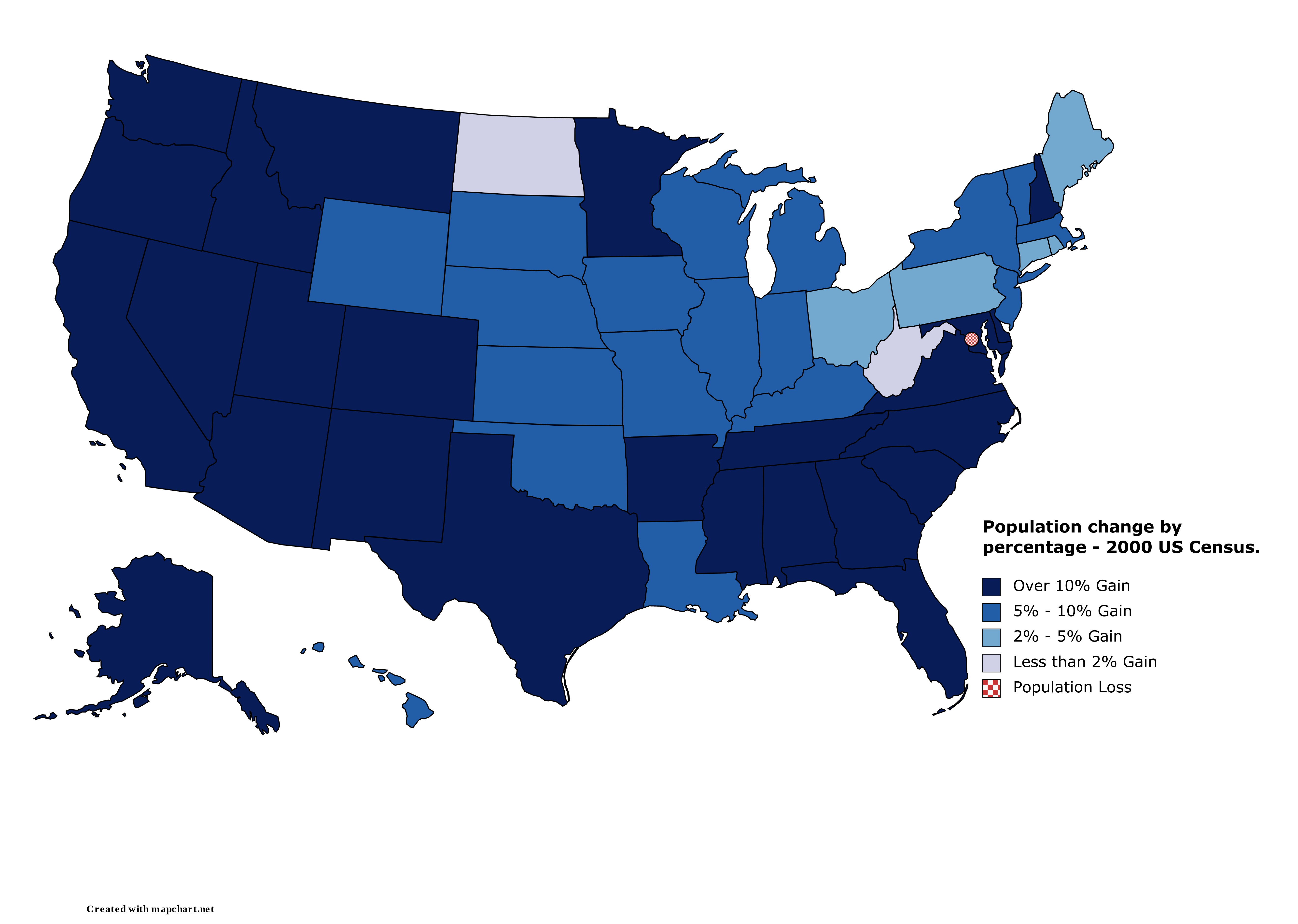
2000 United States Census
The United States census of 2000, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States on April 1, 2000, to be 281,421,906, an increase of 13.2 percent over the 248,709,873 people enumerated during the 1990 census. This was the twenty-second federal census and was at the time the largest civilly administered peacetime effort in the United States. Approximately 16 percent of households received a "long form" of the 2000 census, which contained over 100 questions. Full documentation on the 2000 census, including census forms and a procedural history, is available from the Integrated Public Use Microdata Series. This was the first census in which a state – California – recorded a population of over 30 million, as well as the first in which two states – California and Texas – recorded populations of more than 20 million. Data availability Microdata from the 2000 census is freely available through the Integrated Public Use Microdata S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with t .... The Census Bureau is part of the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce and its Director of the United States Census Bureau, director is appointed by the President of the United States. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the United States census, U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the U.S. House of Representatives to the U.S. state, states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Beard's Town
Little Beard's Town, also known as Chenussio (in Seneca) and "Genesee Castle", was a powerful Seneca town in the Genesee River Valley near modern Leicester in Livingston County, New York, where Cuylerville stands today. It surrounded the area that is now Rt. 39, between Geneseo and Cuylerville, New York. At the time of its destruction by Sullivan, the town was located on the west side of the Genesee River. Ten years prior, it had been on the east side of the river, as the Seneca villages were generally moved approximately every 10 years. The town was named after its founder, Little Beard, a prominent Seneca ''sachem'' in the late 18th century. It was famous for its beautiful surroundings and the productivity of its vegetable gardens, fruit orchards, and fields of corn. It had about 130 houses-- "finely built log cabins with ample furnishings; some even had glass window panes," as well as a large council building, built around a central square. It was located near three other S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seneca Castle
Kanadaseaga (aka Kanadesaga or Kanatasaka or Kanadasaga or Canasadego or Ganûndase?'ge? or Seneca Castle or Canadasaga), was a major village, perhaps a capital, of the Seneca nation of the Iroquois Confederacy in west-central New York State, United States. It was located between the northern ends of Seneca and Canandaigua lakes, one and a half miles northwest of the present-day city of Geneva in the township of Seneca. The village was situated on both sides of Kanadaseaga Creek. The Seneca established this village at least as early as 1687. It was likely established by the former residents of Ganondagan, after its destruction by the French. Around 1754, the Senecas moved north from the nearby New Ganechstage village (and prior to that, the White Springs village) to a settlement that would become known as Kanadesaga. A blockhouse was built here in 1756 by Sir William Johnson, the remains of which were in existence in 1779. During the Revolutionary War, the British added defensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Brant
Thayendanegea or Joseph Brant (March 1743 – November 24, 1807) was a Mohawk military and political leader, based in present-day New York, who was closely associated with Great Britain during and after the American Revolution. Perhaps the Native American of his generation best known to the Americans and British, he met many of the most significant Anglo-American people of the age, including both George Washington and King George III. While not born into a hereditary leadership role within the Iroquois League, Brant rose to prominence due to his education, abilities, and connections to British officials. His sister, Molly Brant, was the wife of Sir William Johnson, the influential British Superintendent of Indian Affairs in the province of New York. During the American Revolutionary War, Brant led Mohawk and colonial Loyalists known as "Brant's Volunteers" against the rebels in a bitter partisan war on the New York frontier. He was accused by the Americans of committing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to Western Europe and parts of Asia. Its trade developed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Government of Canada, Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the List of Canadian provinces and territories by area, largest province by area and the second-largest by Population of Canada by province and territory, population. Much of the population lives in urban areas along the St. Lawrence River, between the most populous city, Montreal, and the provincial capital, Quebec City. Quebec is the home of the Québécois people, Québécois nation. Located in Central Canada, the province shares land borders with Ontario to the west, Newfoundland and Labrador to the northeast, New Brunswick to the southeast, and a coastal border with Nunavut; in the south it borders Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, and New York (state), New York in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |